(Press-News.org) Sodium chloride, better known as table salt, isn't exactly the type of mineral that captures the imagination of scientists. However, a smattering of tiny salt crystals discovered in a sample from an asteroid has researchers at the University of Arizona Lunar and Planetary Laboratory excited, because these crystals can only have formed in the presence of liquid water.
Even more intriguing, according to the research team, is the fact that the sample comes from an S-type asteroid, a category known to mostly lack hydrated, or water-bearing, minerals. The discovery strongly suggests that a large population of asteroids hurtling through the solar system may not be as dry as previously thought. The finding, published in Nature Astronomy, gives renewed push to the hypothesis that most, if not all, water on Earth may have arrived by way of asteroids during the planet's tumultuous infancy.
Zega and lead study author Shaofan Che, a postdoctoral fellow at the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, performed a detailed analysis of samples collected from asteroid Itokawa in 2005 by the Japanese Hayabusa mission and brought to Earth in 2010.
The study is the first to prove that the salt crystals originated on the asteroid's parent body, ruling out any possibility they might have formed as a consequence of contamination after the sample reached Earth, a question that had plagued previous studies that found sodium chloride in meteorites of a similar origin.
"The grains look exactly like what you would see if you took table salt at home and placed it under an electron microscope," said Tom Zega, the study's senior author and a professor of planetary sciences at the UArizona Lunar and Planetary Laboratory. "They're these nice, square crystals. It was funny, too, because we had many spirited group meeting conversations about them, because it was just so unreal."
Zega said the samples represent a type of extraterrestrial rock known as an ordinary chondrite. Derived from so-called S-type asteroids such as Itokawa, this type makes up about 87% of meteorites collected on Earth. Very few of them have been found to contain water-bearing minerals.
"It has long been thought that ordinary chondrites are an unlikely source of water on Earth," said Zega who is the director of the Lunar and Planetary Laboratory's Kuiper Materials Imaging & Characterization Facility. "Our discovery of sodium chloride tells us this asteroid population could harbor much more water than we thought."
Today, scientists largely agree that Earth, along with other rocky planets such as Venus and Mars, formed in the inner region of the roiling, swirling cloud of gas and dust around the young sun, known as the solar nebula, where temperatures were very high – too high for water vapor to condense from the gas, according to Che.
"In other words, the water here on Earth had to be delivered from the outer reaches of the solar nebula, where temperatures were much colder and allowed water to exist, most likely in the form of ice," Che said. "The most likely scenario is that comets or another type of asteroid known as C-type asteroids, which resided farther out in the solar nebula, migrated inward and delivered their watery cargo by impacting the young Earth."
The discovery that water could have been present in ordinary chondrites, and therefore been sourced from much closer to the sun than their "wetter" kin, has implications for any scenario attempting to explain the delivery of water to the early Earth.
The sample used in the study is a tiny dust particle spanning about 150 micrometers, or roughly twice the diameter of a human hair, from which the team cut a small section about 5 microns wide – just large enough to cover a single yeast cell – for the analysis.
Using a variety of techniques, Che was able to rule out that the sodium chloride was the result of contamination from sources such as human sweat, the sample preparation process or exposure to laboratory moisture.
Because the sample had been stored for five years, the team took before and after photos and compared them. The photos showed that the distribution of sodium chloride grains inside the sample had not changed, ruling out the possibility that any of the grains were deposited into the sample during that time. In addition, Che performed a control experiment by treating a set of terrestrial rock samples the same as the Itokawa sample and examining them with an electron microscope.
"The terrestrial samples did not contain any sodium chloride, so that convinced us the salt in our sample is native to the asteroid Itokawa," he said. "We ruled out every possible source of contamination."
Zega said tons of extraterrestrial matter is raining down on Earth every day, but most of it burns up in the atmosphere and never makes it to the surface.
"You need a large enough rock to survive entry and deliver that water," he said.
Previous work led by the late Michael Drake, a former director of the Lunar and Planetary Lab, in the 1990s proposed a mechanism by which water molecules in the early solar system could become trapped in asteroid minerals and even survive an impact on Earth.
"Those studies suggest several oceans worth of water could be delivered just by this mechanism," Zega said. "If it now turns out that the most common asteroids may be much 'wetter' than we thought, that will make the water delivery hypothesis by asteroids even more plausible."
Itokawa is a peanut-shaped near-Earth asteroid about 2,000 feet long and 750 feet in diameter and is believed to have broken off from a much larger parent body. According to Che and Zega, it is conceivable that frozen water and frozen hydrogen chloride could have accumulated there, and that naturally occurring decay of radioactive elements and frequent bombardment by meteorites during the solar system's early days could have provided enough heat to sustain hydrothermal processes involving liquid water. Ultimately, the parent body would have succumbed to the pummeling and broken up into smaller fragments, leading to the formation of Itokawa.
"Once these ingredients come together to form asteroids, there is a potential for liquid water to form," Zega said. "And once you have liquids form, you can think of them as occupying cavities in the asteroid, and potentially do water chemistry."
The evidence pointing at the salt crystals in the Itokawa sample as being there since the beginning of the solar system does not end here, however. The researchers found a vein of plagioclase, a sodium-rich silicate mineral, running through the sample, enriched with sodium chloride.
"When we see such alteration veins in terrestrial samples, we know they formed by aqueous alteration, which means it must involve water," Che said. "The fact that we see that texture associated with sodium and chlorine is another strong piece of evidence that this happened on the asteroid as water was coursing through this sodium-bearing silicate."
END
Pass the salt: This space rock holds clues as to how Earth got its water
The discovery of tiny salt grains in an asteroid sample brought to Earth by the Japanese Hayabusa spacecraft provides strong evidence that liquid water may be more common in the solar system's largest asteroid population than previously thought.
2023-06-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Understanding tumor microenvironment with photoacoustic spectral analysis
2023-06-13
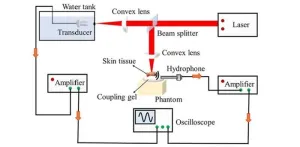
Tumors are not just isolated clumps of abnormal cells but are associated with more complex system known as the “tumor microenvironment” (TME). Over the past few years, research has revealed that the TME consists of a complex combination of blood vessels, connective tissue, and a matrix of extracellular proteins and molecules. Most importantly, the composition of the TME is different from that of nearby healthy tissues. In particular, the lipid and collagen contents of tumors differ from those of normal tissues, making them important potential biomarkers for diagnosing various types of ...
Special issue of JICM on global public health and the Declaration of Astana
2023-06-13
A special focus issue of the peer-reviewed Journal of Integrative and Complementary Medicine (JICM) on Global Public Health is a response to the Declaration of Astana, developed by the World Health Organization and UNICEF. With contributions from traditional, complementary, and integrative medicine (TCIM) scholars and thought leaders around the world, the issue showcases research and scholarship examining the opportunities and challenges that TCIM approaches offer global health to governments and health service providers seeking to fulfill ...
ASU establishes ʻĀkoʻakoʻa, a new collaborative effort to seed renewed connection between human and coral communities in Hawaiʻi
2023-06-13
With a group of core partners, Arizona State University is creating a new $25 million collaboration to preserve and restore vitality to Hawaiʻi’s coral reefs and the health of its coastlines.
The community-based effort looks to fuse state-of-the-art science programs with the leadership and cultural knowledge of Hawaiʻi’s community partners to enable coastal and reef sustainability for generations to come. Named ʻĀkoʻakoʻa (pronounced ah kō-a kō-a), the effort shares a dual meaning ʻto assemble’ and ‘coral.’
“For ...
Men and women with migraine both carry an increased risk of ischemic stroke
2023-06-13
Women and men who experience migraine headaches also carry an elevated risk of having an ischemic stroke, but women alone may carry an additional risk of heart attack and hemorrhagic stroke, according to a new study led by Cecilia Hvitfeldt Fuglsang of Aarhus University, Denmark publishing June 13th in the open access journal PLOS Medicine.
People diagnosed with migraine are believed to have a higher risk of experiencing a heart attack or stroke before the age of 60. Previous studies have suggested ...
How seeing corpses reduces the lifespan of flies
2023-06-13
Researchers led by Christi Gendron at the University of Michigan, US, have found the link between death perception and reduced aging in flies. Their new study, published June 13th in the open access journal PLOS Biology shows that a specific group of brain cells in the fly, called R2 and R4 neurons, are activated when flies encounter other dead flies, and that this increased activity leads to more rapid aging.
Aging is a complex process that can be affected by both genetics and the environment. While we know that perceptual experiences can affect ...
Study develops primer scheme for human monkeypox virus that can be plugged into currently existing amplicon-based sequencing and bioinformatics infrastructure
2023-06-13
Study develops primer scheme for human monkeypox virus that can be plugged into currently existing amplicon-based sequencing and bioinformatics infrastructure; this approach has enabled public health laboratories to quickly adapt their genomic workflows in response to a newly emerging pathogen.
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002151
Article Title: Development of an amplicon-based sequencing approach in response ...
Key regulator of COVID viral receptor may be new drug target
2023-06-13
Entry of the SARS-CoV-2 virus into human tissues depends on the activity of a host gene that regulates production of a key viral receptor, according to a study publishing June 13th in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Madison Strine and Craig Wilen of Yale University, US, and colleagues. The finding provides important new information on how the virus responsible for COVID-19 causes infection and may lead to new antiviral treatments.
In previous work, the authors identified the gene DYRK1A as critical for SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. The gene encodes a kinase, a type of enzyme, and had been previously implicated in regulating cell proliferation ...
Illinois Tech earns prestigious recognition as Dassault Systèmes Global 3DX Education Center of Excellence
2023-06-13
CHICAGO—June 13, 2023—Illinois Institute of Technology (Illinois Tech) has been named as a Dassault Systèmes Global 3DEXPERIENCE (3DX) Education Centers of Excellence, a prominent distinction achieved by only three universities in the United States.
On May 11, Illinois Tech recognized this esteemed recognition with the unveiling of a plaque in the newly-launched 3DEXPERIENCE demonstration space. This prestigious honor places Illinois Tech at the forefront of educational institutions leveraging the most advanced digital technology tools and amplifies Illinois Tech's role in equipping ...
Powering the future: UH professor to use NSF Career Award for game-changing research
2023-06-13
In today's dynamic environment where electricity demand is skyrocketing, power converters are the unsung heroes quietly transforming the way we harness and utilize electrical energy and seamlessly fueling our daily lives – from the ubiquitous wall chargers powering up everything from laptops to cell phones to integral parts of electrical systems that keep offshore wind turbines spinning. By 2030, over 80% of electricity is expected to flow through power converters, creating a pressing need to extend their operational lifetime.
“Without power conversion, you cannot really get energy from or efficiently from solar panels and wind turbines, you cannot charge electric ...
Are emoji helping your physician communicate better? What new research tells us about emoji use among hospitalists
2023-06-13
You may have heard it said before that a picture is worth a thousand words, but what about an emoji?
Since emoji were first created in the 1990s, their use has evolved and increased significantly in text messaging, social media, email and more. And now, even clinicians are using them when communicating with each other at work.
“It's very interesting, the idea that a single emoji has some some kind of meaning, but could mean something different to different people,” said Colin Halverson, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at Indiana University School of Medicine.
Halverson, along with Mike ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Pass the salt: This space rock holds clues as to how Earth got its waterThe discovery of tiny salt grains in an asteroid sample brought to Earth by the Japanese Hayabusa spacecraft provides strong evidence that liquid water may be more common in the solar system's largest asteroid population than previously thought.