A novel technique to observe colloidal particle degradation in real time
Researchers develop an innovative approach using atomic force microscopy to shed light on the degradation of colloidal particles
2023-06-14
(Press-News.org)
In the early 2000s, scientists from the UK made a worrisome discovery that the oceans are teeming with small particles of plastic (less than one millimeter in length) due to the continuous degradation of plastic waste. These microscopic particles of plastic have become a major environmental concern. Scientists classify these small particles as either microplastics or nanoplastics based on their size; the latter term is used exclusively for particles smaller than one micrometer.
These particles easily get embedded into the bodies of marine and freshwater animals, which has raised alarms regarding the pervasive problem of micro- and nanoplastics pollution. Unfortunately, despite substantial efforts, researchers are yet to decipher the detailed mechanisms through which micro- and nanoplastics originate and change over time. The issue lies mainly in the techniques that have been used so far to observe the degradation process of plastic particles. Simply put, these methods cannot observe the degradation into single particles in real time.
Against this backdrop, a research team led by Associate Professor Daisuke Suzuki from Shinshu University in Japan set out to find a solution to this challenge. In their latest study, which was published in Soft Matter on May 26, 2023, they demonstrated an innovative approach to observe the degradation process of single microgel particles in real time with nanometric precision. The study was co-authored by Professor Takayuki Uchihashi from Nagoya University in Japan.
The proposed approach has two main lines of investigation. In the first part of the study, a microgel was used as a model for understanding the behavior of nanoplastic particles. The microgel employed was composed of a polymer with cross-linking points that could be cleaved via chemical reactions using an oxidizing agent. In other words, the bonds between the long fiber-like molecules that made up the tiny microgel spheres could be broken in a semi-controlled way by adjusting the temperature and the chemical environment.
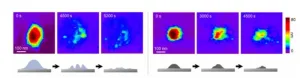
The second main line of investigation of the study was the development of a state-of-the-art technique to visualize the degradation of the microgel in real time. The researchers employed a carefully configured high-speed atomic force microscopy (HS-AFM) setup, which involved ‘touching’ the sample with an atomic-sized tip placed at the end of a cantilever and measuring its deflection. Thanks to HS-AFM, the team could observe the change in the shape of the microgel over time with extremely high precision.
After several experiments at different temperatures and microgel compositions, the researchers gained valuable insight into how nanoplastics originate and evolve over time depending on their environment. “The experiments revealed that while nanoplastics containing water easily allowed chemical reactants to diffuse inside, nanoplastics in a water-free state do not readily allow reactants to diffuse. Thus, nanoplastics in different states exhibited completely different degradation behaviors,” explains Prof. Suzuki.
The videos of the microgels degrading in real time illustrate how useful this new approach could be to further the understanding of micro- and nanoplastics. Excited about the possible implications of their remarkable work, Prof. Suzuki comments: “The presented approach has the potential to be expanded into an observation technique that can assess not only temperature variations, but also other external stimuli encountered in everyday life, such as ultraviolet light and stress, enabling nanoscale observations in diverse environmental conditions.”
Overall, the results of this study will pave the way to a better understanding of nanoplastics. In turn, this will give scientists and engineers a better chance at fighting this elusive facet of marine pollution. Moreover, since micro- and nanoplastics are essential materials used in everyday products like adhesives, paints, and cosmetics, having a firmer grasp on their degradation process will help devise guidelines to mitigate their environmental impact. Such knowledge would also be useful in advanced drug delivery systems, where gels play a pivotal role as delivery agents for drugs.
With eyes on a brighter future, Prof. Suzuki concludes: “This research will hopefully generate interest in micro- and nanoplastics among the general public, prompting them to reconsider their plastic usage, the primary source of nanoplastics.”
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-14
Researchers have created a small device that ‘sees’ and creates memories in a similar way to humans, in a promising step towards one day having applications that can make rapid, complex decisions such as in self-driving cars.
The neuromorphic invention is a single chip enabled by a sensing element, doped indium oxide, that’s thousands of times thinner than a human hair and requires no external parts to operate.
RMIT University engineers in Australia led the work, with contributions from researchers at Deakin University and the University of Melbourne.
The team’s research demonstrates a working device that captures, processes and stores visual ...
2023-06-14
SDE BOKER, Israel, June 14, 2023 – Photovoltaic technology is indispensable for our ability to mitigate climate change. Nonetheless, more than 70% of the energy made available to us by the sun is wasted in conventional photovoltaic cells. There is little hope for sustainable technological advancement without addressing this issue.
The operational temperature is a critical factor in a solar cell's ability to convert sunlight to free energy. Accordingly, much research has been directed toward understanding the temperature effects in the efficiency of photovoltaic solar cells. Surprisingly, ...
2023-06-14
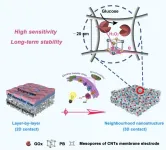
Glucose oxidase (GOx)-based biosensors have attracted much attention for their potential in rapid glucose detection and continuous monitoring, which are crucial for disease diagnosis and prevention, as well as for controllable production in sugar-making and fermentation processes.
The glucose oxidase/electrocatalysts/electrode (GOx/ECs/electrode) cascade system serves as the core part of most glucose biosensing devices (both invasive and non-invasive). However, patterned assembly of these cascade sensing units remains challenging, thus limiting the ...
2023-06-14
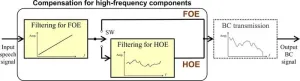
Ishikawa, Japan -- Bone-conduction (BC) headphones enhance hearing capability by generating vibrations in bone or skin close to the ear, including the regio temporalis. They simultaneously leave the ear canal open to allow the surrounding air-conducted (AC) sounds for normal hearing. However, word intelligibility – recognition ability – is often poor during bone-conducted speech perceived using BC headphones due to the attenuation of its high-frequency components, especially under noisy conditions. While inserting ear plugs in the ear canal help improve ...
2023-06-14
A new study from Australia, New Zealand and Germany published in the New England Journal of Medicine raises important questions about the success or otherwise of emergency medicine.
The study examined the drug tranexamic acid, which is commonly used to limit bleeding during surgery. However, its usefulness in emergency settings as a pre-emptive strike in life-threatening bleeding has been controversial, and recent studies have provided contradictory results about whether or not it saves lives or causes dangerous blood clotting.
The Pre-hospital ...
2023-06-14
AMES, IA — Last month, the American Psychological Association and the U.S. Surgeon General both issued health advisories. Their concerns and recommendations for teens, parents and policymakers addressed a mounting body of research that shows two trends are intertwined.
Young people are using social media more, and their mental health is suffering.
Researchers at Iowa State University found a simple intervention could help. During a two-week experiment with 230 college students, half were asked to limit their ...
2023-06-14
Dr. Mustapha Ishak-Boushaki, a theoretical astrophysicist at The University of Texas at Dallas, has spent his career seeking answers to some of the universe’s greatest mysteries, including why the expansion of the universe seems to be accelerating and whether gravity behaves differently beyond our closest cosmic neighbors.
To study these and other questions, a large collaboration of scientists, including Ishak-Boushaki and UTD physics doctoral students Cristhian Garcia Quintero, Leonel Medina Varela and Yunan Xie, are using data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic ...
2023-06-14
Scientists need to get out of the lab and into the rain, say an interdisciplinary group of researchers led by John T. Van Stan of Cleveland State University. Writing in the journal BioScience, the authors make the case that human observation of storm events (be it rain, snow, or occult deposition) is key to understanding wet weather and its myriad effects on the natural world.
Recently, Van Stan and colleagues noted a trend in the scientific community towards relying on remote ...
2023-06-14
A study led by researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research shows for the first time how a gene called RELA, known to regulate inflammation, also plays an essential role in maintaining normal blood-sugar levels.
The findings, published in Diabetologia, have implications for the prevention of steroid-induced diabetes, a temporary form of diabetes that affects up to half of hospital patients treated with high-dose steroids.
“Our discovery sheds new light on a complex network of factors governing glucose metabolism and how it can go awry in diabetes,” says Professor ...
2023-06-14
Wildfire smoke is a threat to air quality, public health, and ecosystems throughout the U.S. Notwithstanding the impact of this year’s Canadian wildfires, the West typically sees much higher exposure to wildfire smoke than other regions of the country. New research from Harvard University, the U.S. Forest Service, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration indicates that controlled burns – particularly in coastal areas of northern California and the Pacific Northwest – could dramatically reduce the overall amount of wildfire smoke exposure in vulnerable rural communities and dense ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A novel technique to observe colloidal particle degradation in real time
Researchers develop an innovative approach using atomic force microscopy to shed light on the degradation of colloidal particles