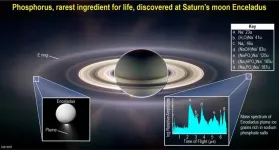
(Press-News.org) SAN ANTONIO —Wednesday, June 14, 2023 —The search for extraterrestrial life in our solar system just got more exciting. A team of scientists including Southwest Research Institute’s Dr. Christopher Glein has discovered new evidence that the subsurface ocean of Saturn’s moon Enceladus contains a key building block for life. The team directly detected phosphorus in the form of phosphates originating from the moon’s ice-covered global ocean using data from NASA’s Cassini mission. Cassini explored Saturn and its system of rings and moons for over 13 years.
“In 2020 (published in 2022), we used geochemical modeling to predict that phosphorus should be abundant in Enceladus’ ocean,” said Glein, a leading expert in extraterrestrial oceanography. He is a co-author of a paper in the journal Nature describing this research. “Now, we have found abundant phosphorus in plume ice samples spraying out of the subsurface ocean.”
The Cassini spacecraft discovered Enceladus’ subsurface liquid water and analyzed samples in a plume of ice grains and gases erupting into space from cracks in the moon’s icy surface. Analysis of a class of salt-rich ice grains by Cassini’s Cosmic Dust Analyzer showed the presence of sodium phosphates. The team’s observational results, together with laboratory analogue experiments, suggest that phosphorus is readily available in Enceladus’ ocean as phosphates.
Phosphorus in the form of phosphates is vital for all life on Earth. It is essential for the creation of DNA and RNA, energy-carrying molecules, cell membranes, bones and teeth in people and animals, and even the sea’s microbiome of plankton. Life as we know it is simply not possible without phosphates.
“We found phosphate concentrations at least 100 times higher in the moon’s plume-forming ocean waters than in Earth’s oceans,” Glein said. “Using a model to predict the presence of phosphate is one thing, but actually finding the evidence for phosphate is incredibly exciting. This is a stunning result for astrobiology and a major step forward in the search for life beyond Earth.”
One of the most profound discoveries in planetary science over the past 25 years is that worlds with oceans beneath a surface layer of ice are common in our solar system. Such worlds include the icy satellites of the giant planets, such as Europa, Titan and Enceladus, as well as more distant bodies like Pluto. Worlds like Earth with surface oceans must reside within a narrow range of distances from their host stars to maintain the temperatures that support surface liquid water. Interior ocean worlds, however, can occur over a much wider range of distances, greatly expanding the number of habitable worlds likely to exist across the galaxy.
“Geochemical experiments and modeling demonstrate that such high phosphate concentrations result from enhanced phosphate mineral solubility, in Enceladus and possibly other icy ocean worlds in the solar system beyond Jupiter,” Glein said. “With this finding, the ocean of Enceladus is now known to satisfy what is generally considered to be the strictest requirement for life. The next step is clear – we need to go back to Enceladus to see if the habitable ocean is actually inhabited.”
The lead author of the Nature paper, “Detection of Phosphates Originating from Enceladus’ Ocean,” is Frank Postberg from the Institut für Geologische Wissenschaften, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany. The research team includes scientists from 10 institutions around the world. Glein was the lead U.S. investigator. The paper is available at: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-05987-9 or https://www.geo.fu-berlin.de/en/geol/fachrichtungen/planet/projects/habitat_oasis/_layout/Postberg_2023_Nature618_Phosphates_Enceladus.pdf.
For more information, visit https://www.swri.org/planetary-science.
END
Key building block for life found at Saturn’s moon Enceladus
SwRI helped find evidence for phosphorus in the liquid water ocean beneath the moon’s icy surface
2023-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows psychedelic drugs reopen ‘critical periods’ for social learning
2023-06-14
Neuroscientists have long searched for ways to reopen “critical periods” in the brain, when mammals are more sensitive to signals from their surroundings that can influence periods of brain development. Now, researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine say a new study in mice shows that psychedelic drugs are linked by their common ability to reopen such critical periods, but differ in the length of time the critical period is open — from two days to four weeks with a single dose.
The findings, published June 16 in the journal Nature, provide a new explanation for how psychedelic drugs work, say the scientists, and suggest potential to treat a wider ...
Building a new vaccine arsenal to eradicate polio
2023-06-14
Despite some of the most successful international vaccination campaigns in history, the poliovirus continues to circulate around the world, posing a threat of neurological damage and even paralysis to anyone who is not vaccinated.
While the original polio strains, called wildtype, have largely been eliminated, new strains can develop from the oral polio vaccine (OPV), which is the one most used in the developing world. Oral vaccines use live, weakened virus that occasionally mutates to an active form, leading to outbreaks even in countries believed to have eliminated polio.
Scientists at UCSF and the UK’s National Institute of Biological Standards and Control (NIBSC) have developed ...
Food allergy is highest among Hispanic, Black and Asian individuals
2023-06-14
· Many racial and ethnic groups not well aware of food allergies
· Lack of food allergy research in racial and ethnic communities
· ‘These individuals need to be aware so they can be diagnosed and treated’
CHICAGO --- Food allergy has not been on the radar of most racial and ethnic communities. But a new Northwestern Medicine study — the first population-based food allergy study in the U.S. to explore racial and ethnic differences in all age groups — shows why it should be.
The new study found the prevalence of food allergy is highest among Hispanic, non-Hispanic Black and ...
World’s first transgenic ants reveal how colonies respond to an alarm
2023-06-14
Ants navigate their richly aromatic world using an array of odor receptors and chemical signals called pheromones. Whether foraging or defending the nest, mating or tending to their young, ants both send and receive chemical signals throughout their lives. The importance of this system is underscored by how well equipped the ant brain is to process the abundance of scents: The olfactory processing center in the ant’s brain has 10 times as many subdivisions as fruit flies do, for example, even though their brains are about the same size.
And yet how the ant olfactory system encodes scent data has remained largely unknown. To whittle ...
For experimental physicists, quantum frustration leads to fundamental discovery
2023-06-14
AMHERST, Mass. – A team of physicists, including University of Massachusetts assistant professor Tigran Sedrakyan, recently announced in the journal Nature that they have discovered a new phase of matter. Called the “chiral bose-liquid state,” the discovery opens a new path in the age-old effort to understand the nature of the physical world.
Under everyday conditions, matter can be a solid, liquid or gas. But once you venture beyond the everyday—into temperatures approaching absolute zero, things smaller than a fraction ...
Metamaterials with built-in frustration have mechanical memory
2023-06-14
Researchers from the UvA Institute of Physics and ENS de Lyon have discovered how to design materials that necessarily have a point or line where the material doesn’t deform under stress, and that even remember how they have been poked or squeezed in the past. These results could be used in robotics and mechanical computers, while similar design principles could be used in quantum computers.
The outcome is a breakthrough in the field of metamaterials: designer materials whose responses are determined by their structure rather than their chemical composition. To construct a metamaterial with mechanical memory, physicists ...
Earth was created much faster than we thought. This makes the chance of finding other habitable planets in the Universe more likely
2023-06-14
When we walk around in our everyday life, we might not think of the Earth itself very often. But this planet is the foundation of our life. The air we breathe, the water we drink and the gravity that pins us to the ground.
Up until now, researchers believed that it took more than 100 million years for the Earth to form. And it was also common belief that water was delivered by lucky collisions with water-rich asteroids like comets.
However, a new study from the University of Copenhagen suggests that it might not have happened entirely by chance.
“We show that the Earth formed by the very ...
A scorching-hot exoplanet scrutinized by UdeM astronomers
2023-06-14
An international team led by Stefan Pelletier, a Ph.D. student at Université de Montréal's Trottier Institute for Research on Exoplanets announced today having made a detailed study of the extremely hot giant exoplanet WASP-76 b.
Using the MAROON-X instrument on the Gemini-North Telescope, the team was able to identify and measure the abundance of 11 chemical elements in the atmosphere of the planet.
Those include rock-forming elements whose abundances are not even known for giant planets in the Solar System such as Jupiter or Saturn. The team's study is published in ...
A growing number of producers and industries interested in precision livestock farming
2023-06-14
Some of the world’s best minds that are focused on profitable and sustainable livestock production attended and presented at the recent Second U.S. Precision Livestock Farming Conference. Hosted by University of Tennessee AgResearch, the May 21-24 event at the UT Conference Center in Knoxville attracted 219 attendees representing 22 countries and 32 U.S. states. Participants included academics, representatives of government agencies and allied industries as well as producers. The conference had a central theme of “Field Application of PLF Technologies” and academic presentations along with two industry and producer panels included interactive dialogues among the attendees ...
It takes a village: Study shows community is key to a sustained passion for science among adolescents
2023-06-14
The results of a yearlong science program show that one of the best ways to instill a lasting interest in science among children is to engage them alongside their family members. This finding runs counter to the current framework, in which children attend science-related summer camps and after-school programs apart from their families, diminishing the long-term potential of what they learn.
“We wanted to see if we could support families as a whole, as opposed to giving a student a really amazing one-off experience and sending them ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
[Press-News.org] Key building block for life found at Saturn’s moon EnceladusSwRI helped find evidence for phosphorus in the liquid water ocean beneath the moon’s icy surface