(Press-News.org) Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan have discovered a set of related mutations that lead to intracranial aneurysms—weakened blood vessels in the brain that can burst at any time. The mutations all appear to act on the same biological signaling pathway, and the researchers report the first ever pharmaceutical treatment in a mouse model, which works by blocking this signal. The study was published in Science Translational Medicine on June 14.
About 5% of the population have unruptured intracranial aneurysms in blood vessels on the surface of the brain. Despite being ballooned arteries with weakened walls, intracranial aneurysms often go undetected -- until a rupture leads to deadly bleeding around the brain. Even when they are detected in advance, the only currently available treatment options involve surgery, which has its own set of risks, especially if the aneurysm is in a sensitive location. Finding other, non-surgical options is thus a high priority, and research into the origin of intracranial aneurysms has led the RIKEN CBS team to one such potential treatment.
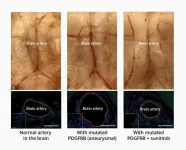
Intracranial aneurysms actually come in two types called intracranial fusiform aneurysms (IFAs) and intracranial saccular aneurysms (ISAs ), with about 90% being the ISA variety. Previous research reported mutations in IFA arteries, but the origins of the more common ISA type remain unclear. To address this issue, the RIKEN team sequenced the entire exomes—all protein-encoding pieces of DNA— in cells that made up 65 aneurysmal arteries and 24 normal arteries. Along with subsequent deep-targeted sequencing, they found that six genes were common among IFAs and ISAs and never appeared in non-aneurysmal arteries, while 10 others appeared only in either IFAs or ISAs. While several factors, such as age, hypertension, and alcohol consumption, increase the risk of intracranial aneurysms, project leader Hirofumi Nakatomi from RIKEN CBS notes, “the unexpected finding that greater than 90% of aneurysms had mutations in a common set of 16 genes indicates that somatic mutation could be the major trigger in most cases.”
Further testing showed that mutations to all six of the genes common to IFAs and ISAs triggered the same NF-κB biological signaling pathway. The next step was to learn more about the mutations and try to block the abnormal signaling. First, they showed that mutations to one of the six genes, PDGDRB, could be traced along different layers within samples of human aneurysms. Then, after linking the PDGDRB mutation with faster cell migration and inflammation in cultured cells, they discovered that these effects could be blocked with sunitinib, a drug that prevents the changes to PDGDRB that allow signaling.
Next, they created a mouse model of intracranial aneurysm by using an adenovirus to insert mutant PDGFRB into the basilar artery at the base of the brain. After a month, the size of the artery had doubled in diameter and become very weak. As in the cultured cells, the effect of the mutant gene was blocked when the mice were given sunitinib; their basilar arteries remained normal sized and strong. “Establishing the first non-surgical animal model of intracranial aneurysm is in itself an achievement,” says Nakatomi, “but more importantly, we suppressed artery expansion with a drug, indicating that intracranial aneurysms can be pharmacologically treated.”
Additional research will be required to demonstrate that this kind of drug treatment is effective for human patients. But perhaps the more difficult hurdle will be detection. As Nakatomi explains, “unruptured intracranial aneurysms are usually detected by Magnetic Resonance Angiography or Computed Tomography Angiography during health checkups. If these tests are not available, then aneurysms are undetectable until they burst.” In Japan, where this research was conducted, many people can receive these tests as part of their annual health checkup, making the development of drug treatments particularly useful.
--
Reference: Shima Y, et al. (2023) Increased PDGFRB and NF-κB signaling caused by highly prevalent somatic mutations in intracranial aneurysms. Sci Transl Med. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abq7721
END
The mutant origin of brain aneurysms and the first drug treatment
2023-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Massive hemorrhages are often deadly. Can a perfume ingredient stop the bleed and save lives?
2023-06-14
The chances of surviving massive blood loss from a traumatic injury such as a gunshot wound are around 50 percent. To survive, a patient needs two things to happen quickly: a large infusion of blood and coagulation at the wound to stop the bleeding.
The problem is one of these solutions prevents the other. Introducing a large amount of blood to those suffering a massive hemorrhage impairs the blood’s ability to clot, a condition known as coagulopathy.
Now, Tulane University researchers have uncovered the cause of coagulopathy in trauma victims receiving a blood infusion. They also found that a synthetic compound ...
Altered gut bacteria may be early sign of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-06-14
People in the earliest stage of Alzheimer’s disease — after brain changes have begun but before cognitive symptoms become apparent — harbor an assortment of bacteria in their intestines that differs from the gut bacteria of healthy people, according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
The findings, published June 14 in Science Translational Medicine, open up the possibility of analyzing the gut bacterial community to identify people at higher risk of developing dementia, and of designing microbiome-altering preventive treatments to stave off cognitive decline.
“We don’t yet know ...
Elimination of type of bacteria suggests treatment for endometriosis
2023-06-14
A research group from the Graduate School of Medicine and iGCORE at Nagoya University in Japan, has discovered that using an antibiotic to target Fusobacterium reduced the formation of lesions associated with endometriosis, a gynecological disorder characterized by endometrial tissue usually found inside the uterus being found outside it. Their findings suggest an alternative treatment for this disorder. The study was published in Science Translational Medicine.
Endometriosis affects one in ten women between the ages of 15 and 49. The disorder can cause lifelong health problems, including pelvic pain and infertility. ...
Newly planted vegetation accelerates dune erosion during extreme storms, research shows
2023-06-14
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Newly planted vegetation on coastal sand dunes can accelerate erosion from extreme waves, a study involving researchers from the Oregon State University College of Engineering suggests.
The authors note the findings run counter to the widely accepted paradigm that vegetation always acts to reduce erosion on dunes, the first line of storm defense for landscapes that are among the world’s most ecologically important and economically valuable.
The experiments involved building beach dune profiles 70 meters long and 4.5 meters high and subjecting ...
Preserving forests to protect deep soil from warming
2023-06-14
A recent study led by scientists at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of Zurich has revealed that the organic compounds proposed for carbon sequestration in deep soil are highly vulnerable to decomposition under global warming.
The finding has implications for a key strategy in carbon management that relies on soil and forests – natural carbon “sinks” – to mitigate global warming.
About 25 percent of global carbon emissions are captured by forests, grasslands, and rangelands. During photosynthesis, plants store carbon in their cell walls and in the soil. Because ...
Treatment creates steel alloys with superior strength and plasticity
2023-06-14
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — A new treatment tested on a high-quality steel alloy produces extraordinary strength and plasticity, two traits that must typically be balanced rather than combined. Ultra-fine metal grains that the treatment produced in the outermost layer of steel appear to stretch, rotate and then elongate under strain, conferring super-plasticity in a way that Purdue University researchers cannot fully explain.
The researchers treated T-91, a modified steel alloy that is used in nuclear and petrochemical ...
TCT 2023 Program Guide now available
2023-06-14
NEW YORK – June 14, 2023 – The Cardiovascular Research Foundation (CRF) has announced the TCT 2023 Program Guide is now available. TCT is the annual scientific symposium of CRF and the world’s premier educational meeting specializing in interventional cardiovascular medicine. TCT 2023 will take place October 23-26 in San Francisco, California, at the Moscone Center and will celebrate 35 years of leading the field.
Every year, TCT features major medical research breakthroughs and gathers ...
Plate tectonics not required for the emergence of life
2023-06-14
Scientists have taken a journey back in time to unlock the mysteries of Earth’s early history, using tiny mineral crystals called zircons to study plate tectonics billions of years ago. The research sheds light on the conditions that existed in early Earth, revealing a complex interplay between Earth’s crust, core, and the emergence of life.
Plate tectonics allows heat from Earth’s interior to escape to the surface, forming continents and other geological features necessary for life to emerge. Accordingly, “there has been the assumption that plate tectonics is necessary for life,” says John Tarduno, who teaches in the Department ...
Novel research shows older breast cancer survivors experience accelerated aging, worse functional outcomes
2023-06-14
For Immediate Release
Contact
Colleen McDonald
Sr. Consultant, Earned Media - MCW
414.801.3146 | cmcdonald@mcw.edu
Milwaukee, Wis., June 14, 2023 – In a new multi-center study, researchers from the Medical College of Wisconsin (MCW) joined with leading cancer centers from across the nation to examine whether cancer and its treatments accelerate aging. Using novel epigenetic measures to assess biological aging, investigators found that older breast cancer survivors – particularly those exposed to chemotherapy – showed greater epigenetic aging than their same-aged peers without cancer, which ...
The life below our feet: team discovers microbes thriving in groundwater and producing oxygen in the dark
2023-06-14
WOODS HOLE, Mass. – Nearly a third of Earth’s freshwater resources lie in groundwater – much more than in all lakes, rivers and the atmosphere combined, and exceeded only by the frozen water in polar ice caps. Accordingly, about half of humankind depends on groundwater as a source of drinking water.
Despite the global occurrence and essential importance of groundwater, however, knowledge of the organisms that inhabit it, and how they survive, remains thin.
A recent investigation led by microbial ecologist Emil Ruff of the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) has discovered ...