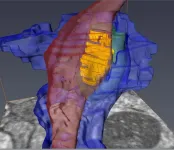
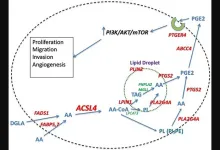
ACSL4: Biomarker, mediator and target in quadruple negative breast cancer
2023-06-14
(Press-News.org)
“ACSL4 has been demonstrated to play a pivotal role in both normal physiology as well as in a variety of disease states, including breast and other cancers.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 14, 2023 – A new review paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on June 12, 2023, entitled, “ACSL4: biomarker, mediator and target in quadruple negative breast cancer.”
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease for which effective treatment depends on correct categorization of its molecular subtype. For the last several decades this determination has relied on hormone receptor status for estrogen, progesterone and HER2. More recently, gene expression data have been generated that further stratify both receptor-positive and receptor-negative cancers.
In this new review, researcher Marie E. Monaco from NYU Grossman School of Medicine and VA NY Harbor Healthcare System discusses the fatty acid-activating enzyme, ACSL4, which has been demonstrated to play a role in the malignant phenotype of a variety of cancers, including breast. This lipid metabolic enzyme is differentially expressed as a function of subtype in breast tumors, with highest expression observed in the mesenchymal (claudin low) and basal-like subtypes.
“ACSL4 is one of five mammalian enzyme isoforms responsible for activation (thioesterification) of long-chain fatty acids as a prerequisite to their further utilization in lipid biosynthetic and fatty acid oxidative pathways [1].”
Here, Dr. Monaco reviews data that support the potential of utilizing ACSL4 status as both a biomarker of molecular subtype and a predictor of response to a variety of targeted and non-targeted treatment regimens. The ability of ACSL4 to induce a more aggressive phenotype suggests it might be a potential target for inhibition in the treatment of breast cancer. Additional studies are needed to demonstrate the utility of this protein as both a biomarker and target in the classification and treatment of breast cancer.
“Based on these findings, we suggest 3 expanded roles for ACSL4: 1. as a biomarker for classification of breast cancer subtypes; 2. as a predictor of sensitivity to hormone-based and certain other therapies; and 3. as a target for the development of new treatment modalities.”
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28453
Correspondence to: Marie E. Monaco - Email: mem6@nyu.edu
Keywords: ACSL4, breast cancer, ferroptosis, molecular subtype, quadruple negative breast cancer
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://oncotarget.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Foncotarget.28453
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-14
New research indicates the fungal pathogen Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans (Bsal) could be devastating to amphibian biodiversity if introduced to North America. Nature Communications published the findings June 5 from a group of researchers at the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture, the University of Massachusetts-Boston and Washington State University.
“We could see over 80 species of salamanders in the United States and 140 species in North America experience population declines if Bsal is introduced,” said Matt Gray, the lead author and professor of ...
2023-06-14
Scientists have created one of the most detailed 3D images of the synapse, the important juncture where neurons communicate with each other through an exchange of chemical signals. These nanometer scale models will help scientists better understand and study neurodegenerative diseases such as Huntington’s disease and schizophrenia.
The new study appears in the journal PNAS and was authored by a team led by Steve Goldman, MD, PhD, co-director of the Center for Translational Neuromedicine at the University of Rochester and the University of Copenhagen. The findings represent a significant technical achievement ...
2023-06-14
ORLANDO, June 14, 2023 — The number of older adults in the U.S. population is growing, expecting to nearly double by 2060, and becoming more diverse with racial and ethnic minority populations projected to increase by 105% by 2040.
“As a society, we’re not ready for that,” says Norma Conner, a professor in the University of Central Florida’s College of Nursing. “We need to be cognizant of the large population of older adults that is going to be ours to care for, and we need to have a better understanding that reflects them.”
To ...
2023-06-14
Responding to rapid advances in artificial intelligence and the urgent need to define its responsible use in health and medicine, Stanford Medicine and the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI) today announced the launch of RAISE-Health (Responsible AI for Safe and Equitable Health). This pioneering initiative seeks to address critical ethical and safety issues surrounding AI innovation and help others navigate this complex and evolving field.
Co-led by Stanford School ...
2023-06-14
People with weakened immune systems are at constant risk of infection. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a common environmental bacterium, can colonize different body parts, such as the lungs, leading to persistent, chronic infections that can last a lifetime – a common occurrence in people with cystic fibrosis.
But the bacteria can sometimes change their behavior and enter the bloodstream, causing chronic localized infections to become acute and potentially fatal. Despite decades of studying the transition in lab environments, how and why the switch happens in humans has remained unknown.
However, researchers ...
2023-06-14
Researchers at the University of Houston are working to make T-cell immunotherapy safer, developing a tool called CrossDome, which uses a combination of genetic and biochemical information to predict if T-cell immunotherapies might mistakenly attack healthy cells.
T-cell based immunotherapies hold tremendous potential in the fight against cancer and infectious diseases, thanks to their capacity to specifically target diseased cells, including cancer metastasis. Nevertheless, this potential has been tempered with safety concerns regarding ...
2023-06-14
The brain is one of the most metabolically active organs in the human body. Although it represents only about 2 percent of the human body’s weight, it receives 15 to 20 percent of the body’s total blood supply. Disrupted blood flow to the brain over a long period of time, a condition known as “chronic cerebral hypoperfusion” (CCH), can lead to serious cerebrovascular diseases such as white matter disease.
CCH manifests as lesions in the white matter, a brain region vulnerable to problems with blood supply. Unfortunately, CCH has no available cure. An early diagnosis by visualizing the microvascular changes in the brain that occur prior to lesion ...
2023-06-14
A new study by investigators from Mass General Brigham has found that a brief, simulated task of navigating a phone menu can detect the earliest changes in daily functioning in people at risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Investigators found that an older adult’s performance on the test, which can be completed in a matter of minutes, was associated with the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease pathology, including amyloid and tau depositions in the brain. The findings, which were published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, could help inform prevention trials testing treatments for Alzheimer’s disease before ...
2023-06-14
Rich individuals living in communities with greater levels of economic inequality tend to be more generous with charitable giving and prosocial behaviors, according to a study published June 14, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Joel H. Suss from the London School of Economics & Political Science and Bank of England, UK.
Many studies have attempted to assess whether the rich are more or less generous than the poor, and whether this shifts depending on the starkness of economic inequality. Thus far, the results have been inconclusive. Previous work in this vein has been conducted at a macro level, using state, region, and country-level aggregated data. In this study, Suss ...
2023-06-14
Marine heatwaves are emerging as a key impact of climate change and pose a particularly significant threat to corals that form the backbone of coral reefs. Researchers have now identified a phenomenon that could help coral reef managers better plan and act for the future.[1]
Every few years, the cyclic climate pattern called El Niño arises in the tropical Pacific, causing significant changes in winds, weather and ocean temperatures. From April 2015 to May 2016, the Central Pacific witnessed one of the strongest El Niño events ever recorded.
Coral reefs were so stressed by the warmer ocean temperatures that they experienced mass bleaching, whereby the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] ACSL4: Biomarker, mediator and target in quadruple negative breast cancer