(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Houston are working to make T-cell immunotherapy safer, developing a tool called CrossDome, which uses a combination of genetic and biochemical information to predict if T-cell immunotherapies might mistakenly attack healthy cells.
T-cell based immunotherapies hold tremendous potential in the fight against cancer and infectious diseases, thanks to their capacity to specifically target diseased cells, including cancer metastasis. Nevertheless, this potential has been tempered with safety concerns regarding the possible recognition of unknown off targets displayed by healthy cells.
In one case, scientists created special T-cells that were supposed to target a protein found in a type of skin cancer called melanoma. However, these T-cells also ended up attacking a different protein found in the heart cells of some patients. This caused severe damage to the heart.
“Our CrossDome tool helps predict the potential risks of T-cell-based immunotherapy. It uses a combination of different types of information (called multi-omics) to make predictions and identify whether the treatment might accidentally harm healthy cells in addition to targeting the intended diseased cells,” said Dinler Antunes, assistant professor of Computational Biology and member of the Center for Nuclear Receptors and Cell Signaling. His work is published in Frontiers in Immunology. “By analyzing various factors, CrossDome provides insights into the safety of T-cell-based immunotherapies and may help researchers develop safer treatments.”
To test the effectiveness of CrossDome, Antunes and Andre F. Fonseca, a postdoctoral fellow in Altunes’ lab, used it to predict potential mistakes in 16 well-known cases of T-cell cross-reactivity, including the melanoma-heart damage case. The tool successfully identified the heart protein as a potential target for the T-cells, ranking it as a high-risk candidate among thousands of other proteins.
Strengthening the results, Antunes combined information from different functional data sets to help assess how much certain genes are expressed and how likely they are to bind with a certain molecule called HLA, to trigger an immune response.
“This information helps us decide which potential off-target genes are worth testing in experiments,” said Antunes.
CrossDome users can be either technical or non-technical. It has features that allow more advanced control for those who know how to code, as well as an easy-to-use interface for those who don't have coding experience.
END
Making immunotherapy safer
New tool predicts if immunotherapy will mistakenly attack healthy cells
2023-06-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
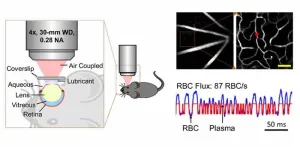
Eyeing the brain: Predicting cerebrovascular diseases with retinal imaging
2023-06-14
The brain is one of the most metabolically active organs in the human body. Although it represents only about 2 percent of the human body’s weight, it receives 15 to 20 percent of the body’s total blood supply. Disrupted blood flow to the brain over a long period of time, a condition known as “chronic cerebral hypoperfusion” (CCH), can lead to serious cerebrovascular diseases such as white matter disease.
CCH manifests as lesions in the white matter, a brain region vulnerable to problems with blood supply. Unfortunately, CCH has no available cure. An early diagnosis by visualizing the microvascular changes in the brain that occur prior to lesion ...
Phone Menu Test Detects Who May Be at Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease
2023-06-14
A new study by investigators from Mass General Brigham has found that a brief, simulated task of navigating a phone menu can detect the earliest changes in daily functioning in people at risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Investigators found that an older adult’s performance on the test, which can be completed in a matter of minutes, was associated with the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease pathology, including amyloid and tau depositions in the brain. The findings, which were published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, could help inform prevention trials testing treatments for Alzheimer’s disease before ...
When local economic inequality is high, the rich tend to be more generous
2023-06-14
Rich individuals living in communities with greater levels of economic inequality tend to be more generous with charitable giving and prosocial behaviors, according to a study published June 14, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Joel H. Suss from the London School of Economics & Political Science and Bank of England, UK.
Many studies have attempted to assess whether the rich are more or less generous than the poor, and whether this shifts depending on the starkness of economic inequality. Thus far, the results have been inconclusive. Previous work in this vein has been conducted at a macro level, using state, region, and country-level aggregated data. In this study, Suss ...
Ocean current comes to the rescue for Pacific island reefs
2023-06-14
Marine heatwaves are emerging as a key impact of climate change and pose a particularly significant threat to corals that form the backbone of coral reefs. Researchers have now identified a phenomenon that could help coral reef managers better plan and act for the future.[1]
Every few years, the cyclic climate pattern called El Niño arises in the tropical Pacific, causing significant changes in winds, weather and ocean temperatures. From April 2015 to May 2016, the Central Pacific witnessed one of the strongest El Niño events ever recorded.
Coral reefs were so stressed by the warmer ocean temperatures that they experienced mass bleaching, whereby the ...
'Smart' drugs can decrease productivity in people who don't have ADHD, study finds
2023-06-14
New research from the University of Cambridge and the University of Melbourne, published in Science Advances, shows neurotypical workers and students taking cognitive enhancers, or ‘smart’ drugs, may actually be inhibiting their performance and productivity.
Drugs such as methylphenidate, sold under the brand name Ritalin among others, are commonly prescribed for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), but are also taken by those without a diagnosis, in the belief that the drugs will enhance focus and cognitive performance.
In four double-blinded, ...
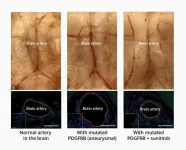
The mutant origin of brain aneurysms and the first drug treatment
2023-06-14
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan have discovered a set of related mutations that lead to intracranial aneurysms—weakened blood vessels in the brain that can burst at any time. The mutations all appear to act on the same biological signaling pathway, and the researchers report the first ever pharmaceutical treatment in a mouse model, which works by blocking this signal. The study was published in Science Translational Medicine on June 14.
About 5% of the population have unruptured intracranial aneurysms in blood vessels on the surface of the brain. Despite being ballooned arteries with ...
Massive hemorrhages are often deadly. Can a perfume ingredient stop the bleed and save lives?
2023-06-14
The chances of surviving massive blood loss from a traumatic injury such as a gunshot wound are around 50 percent. To survive, a patient needs two things to happen quickly: a large infusion of blood and coagulation at the wound to stop the bleeding.
The problem is one of these solutions prevents the other. Introducing a large amount of blood to those suffering a massive hemorrhage impairs the blood’s ability to clot, a condition known as coagulopathy.
Now, Tulane University researchers have uncovered the cause of coagulopathy in trauma victims receiving a blood infusion. They also found that a synthetic compound ...
Altered gut bacteria may be early sign of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-06-14
People in the earliest stage of Alzheimer’s disease — after brain changes have begun but before cognitive symptoms become apparent — harbor an assortment of bacteria in their intestines that differs from the gut bacteria of healthy people, according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
The findings, published June 14 in Science Translational Medicine, open up the possibility of analyzing the gut bacterial community to identify people at higher risk of developing dementia, and of designing microbiome-altering preventive treatments to stave off cognitive decline.
“We don’t yet know ...
Elimination of type of bacteria suggests treatment for endometriosis
2023-06-14
A research group from the Graduate School of Medicine and iGCORE at Nagoya University in Japan, has discovered that using an antibiotic to target Fusobacterium reduced the formation of lesions associated with endometriosis, a gynecological disorder characterized by endometrial tissue usually found inside the uterus being found outside it. Their findings suggest an alternative treatment for this disorder. The study was published in Science Translational Medicine.
Endometriosis affects one in ten women between the ages of 15 and 49. The disorder can cause lifelong health problems, including pelvic pain and infertility. ...
Newly planted vegetation accelerates dune erosion during extreme storms, research shows
2023-06-14
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Newly planted vegetation on coastal sand dunes can accelerate erosion from extreme waves, a study involving researchers from the Oregon State University College of Engineering suggests.
The authors note the findings run counter to the widely accepted paradigm that vegetation always acts to reduce erosion on dunes, the first line of storm defense for landscapes that are among the world’s most ecologically important and economically valuable.
The experiments involved building beach dune profiles 70 meters long and 4.5 meters high and subjecting ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Making immunotherapy saferNew tool predicts if immunotherapy will mistakenly attack healthy cells