New insights on bacteria that causes food poisoning
Latest research reveals the properties of a type of food poisoning bacteria, and paves way for establishment of preventive methods
2023-06-16
(Press-News.org)
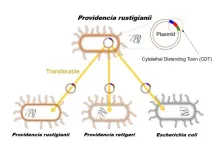
Recently, Providencia spp. which have been detected in patients with gastroenteritis, and similar to enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. O157 and Salmonella spp., have been attracting attention as causative agents of food poisoning. For children with low immunity, food poisoning can be lethal as it causes severe symptoms such as diarrhea and dehydration, so clarifying the source of infection and pathogenic factors of Providencia spp., and establishing preventive methods are urgent issues worldwide.
A joint research group led by Professor Shinji Yamasaki, Dr. Sharda Prasad Awasthi, a Specially Appointed Lecturer, and graduate student Jayedul Hassan from the Graduate School of Veterinary Science, Osaka Metropolitan University, determined how the pathogenic genes in some Providencia spp. such as Providencia alcalifaciens and Providencia rustigianii are transferred within bacterial cells of genus Providencia. The group has also elucidated that the pathogenic genes of Providencia rustigianii are also transferred to other bacterial cells belonging to Enterobacteriaceae.
Professor Yamasaki concluded, "This achievement is expected to provide new insights into the identification of infection routes of Providencia spp. and the establishment of preventive methods for food poisoning."
The findings were published in Infection and Immunity.
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is the third largest public university in Japan, formed by a merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University in 2022. OMU upholds "Convergence of Knowledge" through 11 undergraduate schools, a college, and 15 graduate schools. For more research news visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on Twitter: @OsakaMetUniv_en, or Facebook.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-16
Staying up late at night has little impact on how long ‘night owls’ live, according to new research published in the peer-reviewed journal Chronobiology International.
Data based on nearly 23,000 twins, however shows that evening types have a slightly increased risk of dying than morning types, but this is largely linked to smoking and drinking.
The study which tracked people over the course of more than 37 years in Finland suggests that lifestyle should be considered.
This is when analyzing the impact on health of chronotype – the body’s natural inclination to sleep at a certain time.
“Our ...
2023-06-16
A research team led by Dr. Minah Lee of the Energy Storage Research Center at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology(KIST) has developed a chemical activation strategy of magnesium metal that enables efficient operation of magnesium batteries in common electrolytes that are free of corrosive additives and can be mass-produced.
While the demand for lithium-ion batteries is exploding due to the rapid growth of the electric vehicle and energy storage system(ESS) markets, the supply and demand of their raw materials such as lithium and cobalt ...
2023-06-16
Fathers can make a huge difference in whether an infant is breastfed and placed to sleep safely, according to a recent survey of new fathers via the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS) for Dads. This new tool is modeled on the annual surveillance system that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and public health departments have used for more than 35 years to survey new mothers. By utilizing PRAMS for Dads, this article is the first to describe father-reported rates of infant breastfeeding and sleep practices in a state-representative sample. Findings are published in the journal Pediatrics.
Among fathers who wanted their infant’s ...
2023-06-16
Urine is one of the attractive sources for early and sensitive biomarker discovery since it can accumulate and reflect changes in the human body while being collected non-invasively. However, analysis of the urine proteome presents challenges due to its wide dynamic range, spanning approximately 10 orders of magnitude in protein concentrations. The presence of high-abundance proteins in urine can overshadow potential disease biomarkers, making their identification difficult. Fractionation and depletion ...
2023-06-16
CHICAGO—Exposure to dioxins can negatively impact thyroid function, according to a study presented Thursday at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Chicago, Ill.
Dioxins are highly toxic compounds that are primarily produced by industrial processes, and their persistence in the environment makes them a significant public health concern. They are produced through a variety of incineration processes, including improper municipal waste incineration and burning of trash. They can be released into the air during natural processes, such as forest fires and volcanoes. ...
2023-06-16
Adverse cognitive effects linked to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) exposure, a type of endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC), have the potential to be passed down through generations, according to an animal study being presented Thursday at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Chicago, Ill.
PCBs can mimic the effect of the hormone estrogen on the body, contributing to a variety of neuroendocrine, metabolic and reproductive problems.
“Endocrine-disrupting chemicals present in our food, air, water and personal products may cause cognitive-behavioral disorders like attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder or overeating in future generations,” ...
2023-06-16
In two new reports, IIASA researchers, with support from colleagues at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), examined the feasibility and fairness of emissions targets and considerations for the European Climate Law. Keywan Riahi, a member of the 15-strong EU Advisory Board and IIASA Energy, Climate, and Environment Program Director, took the lead in conducting the analyses.
The European Scientific Advisory Board on Climate Change is an independent board entrusted with the crucial responsibility of providing transparent and scientific guidance to the EU on setting a new emissions reduction target to be achieved by 2040, as well as budgets for greenhouse ...
2023-06-16
CRAG researchers have discovered that AtMC3 protein is exclusively located in a specific part of the plant vascular system.
Increased levels of AtMC3 are able to confer enhanced tolerance to severe water scarcity conditions, without affecting plant yield.
This knowledge will contribute to find tools to cope with increasing drought phenomena due to climate crisis.
Bellaterra (Barcelona), 16 June 2023
Researchers led by Núria Sánchez-Coll, CSIC researcher at the Centre ...
2023-06-15
SUMMARY
Treating a mouse model of multiple sclerosis with the pregnancy hormone estriol reversed the breakdown of myelin in the brain’s cortex, a key region affected in multiple sclerosis, according to a new UCLA Health study.
BACKGROUND
In multiple sclerosis, inflammation spurs the immune system to strip away the protective myelin coating around nerve fibers in the brain’s cortex, hampering electrical signals sent and received by the brain. Atrophy of the cortex in MS patients is associated with permanent worsening of disability, such as cognitive decline, visual impairment, weakness and sensory loss.
No currently available treatments ...
2023-06-15
INDIANAPOLIS — Researchers at the School of Science at IUPUI will lead two grants totaling $11.7 million from the U.S. Department of Defense to fund research on discovering a drug treatment for hydrocephalus, a condition commonly associated with complications from traumatic brain injury that causes cerebrospinal fluid to accumulate in the brain.
Using funds from a $7.8 million Department of Defense Focused Program grant, Bonnie Blazer-Yost and Teri Belecky-Adams, both professors in the Department of Biology, will team up with scientists from Johns Hopkins University to test the effectiveness of treatments for three types of hydrocephalus — genetic, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New insights on bacteria that causes food poisoning
Latest research reveals the properties of a type of food poisoning bacteria, and paves way for establishment of preventive methods