(Press-News.org) CHICAGO—People with obesity may have lower work productivity due to increased risk of illness, contributing to increased costs for employers, according to industry-supported research being presented Saturday at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting, in Chicago, Ill.
Obesity is a significant public health issue affecting approximately 42% of people in the United States. Employees with overweight or obesity are more likely to develop weight-related comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, cardiovascular disease, and cancer, which all contribute to lower work productivity.
“Employees with overweight and obesity may have higher loss of work productivity as measured by absenteeism, short and long-term disability, and worker’s compensation compared to employees with normal weight,” said Clare J. Lee, M.D., of Eli Lilly & Company in Indianapolis, Ind.
Co-author Shraddha Shinde M.B.A, also of Eli Lilly & Company, added that, "Given the substantial burden of overweight and obesity on employee health and function that was demonstrated by this study, employers should focus on building tailored interventions that could be beneficial in improving the health of these individuals.”
The researchers evaluated 719,482 employees with and without obesity in the MarketScan databases. They determined the percentage of employees with work loss, number of hours/days lost from work, and costs associated with productivity loss were higher among people with overweight or obesity. The loss of work productivity was greater with each higher Body Mass Index (BMI) category.
The researchers found costs associated with absenteeism, short and long-term disability, and worker’s compensation were $891, $623, $41, and $112 higher per year (respectively) for people with obesity compared to those with normal weight.
Funding for this study was provided by Eli Lilly and Company.
# # #
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world’s oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
END
Employees with obesity may have higher loss of work productivity than those with normal weight
2023-06-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gaps remain in identifying, treating obesity despite new treatment options
2023-06-17
CHICAGO—By being undiagnosed or untreated, a significant fraction of people with obesity or overweight are not getting the recommended care, despite an increase in new treatment options, according to research being presented on June 17 at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Chicago, Ill.
“The number of people with obesity is high and rising in the adult U.S. population. Obesity is a complex and expensive disease that has been implicated in many chronic conditions including high blood ...
Closed-loop insulin delivery systems may improve blood sugar control in children with type 1 diabetes
2023-06-17
CHICAGO—Closed-loop insulin delivery systems improve glucose control in children with type 1 diabetes without causing adverse effects, according to a study presented Saturday at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Chicago, Ill.
A closed-loop system consists of devices that use a continuous glucose monitor and insulin pump to automatically regulate blood sugar levels for people with diabetes. The system operates “closed-loop” because it continuously monitors and adjusts (starting and stopping) insulin delivery based on the person's ...
Study finds “robotic pill” can safely deliver injectable osteoporosis drug
2023-06-17
A proven and effective medication for osteoporosis, which is currently only available as an injection, can be administered orally using a novel “robotic pill,” according to a study presented Saturday at ENDO 2023, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting in Chicago, Ill.
“We believe this study provides the first clinical evidence of safe and successful delivery of the osteoporosis drug teriparatide through an oral robotic pill,” said Arvinder Dhalla, Ph.D., who leads Clinical Development at Rani Therapeutics, the San Jose, Calif.-based company that developed the technology and funded the study. “Data from this study are very encouraging ...
Wider search needed to improve outcomes for eosinophilic food allergy
2023-06-17
The good news: a monoclonal antibody treatment called benralizumab proved quite effective in a clinical trial at depleting the number of eosinophils found in the blood and digestive tract tissues of patients with eosinophilic gastritis.
The not-so-good news: eliminating eosinophils was not enough to stop the symptoms people feel with this uncommon and severe form of food allergy. Nor did the treatment affect key measures of gut tissue health and related gene expression patterns.
These paradigm-shifting Phase 2 clinical ...
University of Montana science unlocks secrets of high-elevation pregnancies
2023-06-17
MISSOULA – Pregnancy at high elevations often is associated with low birth weights and other complications. These challenges occur in a wide range of mammals, from deer mice to human beings.
Research conducted at the University of Montana revealed some of the genetic underpinnings that allow certain highland mouse populations to protect developing fetuses in higher areas. The work was published recently in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“Understanding how deer mice survive and thrive at high elevations not only informs our understanding of basic evolutionary processes, it may also one ...
ASU study: Jupiter’s moon Europa may have had a slow evolution
2023-06-16
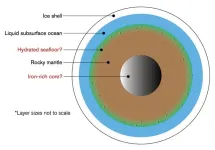
Jupiter's moon, Europa, is slightly smaller than Earth’s Moon and is one of the most promising places to search for alien life.
Amid the Jovian system, Europa is of particular interest to scientists because of the strong evidence for nutrients, water and energy to potentially provide a habitable environment for some form of life beyond Earth. In addition, Europa is believed to be made up into four layers (from surface to center): an ice shell, salt water ocean, rocky mantle, and metallic core.
Like Earth, Europa’s ...
Adagrasib effective for patients with KRAS G12C-mutant lung cancer and untreated brain metastases
2023-06-16
HOUSTON ― Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center found the KRAS G12C inhibitor adagrasib showed promising activity suppressing cancer growth not only within the lungs but also in brain metastases for patients with KRAS G12C-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Findings from the Phase Ib cohort of the KRYSTAL-1 trial, published today in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, represent the first prospective data of anti-tumor activity from a KRAS G12C inhibitor in brain metastases, providing continued evidence of the ...
ACQUIRE therapy framework shows results for intensive pediatric rehabilitation
2023-06-16
Virginia Tech researchers with the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC have demonstrated that children with a wide range of diagnoses that affect their motor function improve after receiving intensive pediatric neurorehabilitation called ACQUIRE Therapy.
The findings were published in June in Behavioral Sciences and will be included in an upcoming special issue of the journal devoted to “shifting the therapeutic paradigm for children with neuromotor disabilities to maximize development.”
“We ...
New research shows HIV can lie dormant in the brain
2023-06-16
As a part of its life cycle, the human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV) inserts a copy of its DNA into human immune cells. Some of these newly infected immune cells can then transition into a dormant, latent state for a long period of time, which is referred to as HIV latency.
Although current therapies, such current antiretroviral therapy (ART), can successfully block the virus from replicating further, it cannot eradicate latent HIV. If treatment is ever discontinued, the virus can rebound from latency and reignite the progression of HIV infection to AIDS.
Scientists from the HIV Cure Center at the UNC School of Medicine, University of California ...
For resistant breast cancers, two drugs may be better than one
2023-06-16
Cancer cells are even smarter than scientists previously believed, according to new CU Boulder research. When these cells are confronted with potent new drugs called CDK2 inhibitors, which are designed to prevent cancer from proliferating, they can trigger a workaround to survive the assault in as little as one to two hours.
But the study, published June 8 in the journal “Cell,” comes with a silver lining.
It reveals how cancer cells complete this adaption and shows that simultaneously administering a second, already widely ...