New study in Nature Water demonstrates a vastly more sustainable, cost-effective method to desalinate industrial wastewater
2023-06-21
(Press-News.org) Vanderbilt researchers are part of a team that has developed a cutting-edge method that seeks to make the removal of salt from hypersaline industrial wastewater far more energy-efficient and cost-effective.
While desalination through reverse osmosis has made tremendous strides—allowing for salt removal from seawater for less than a penny per gallon—it still falls short in eliminating saline in wastewater from industries like mining, oil and gas and power generation and in inland brackish water. The industrial brines are currently injected into deep geological formations or transferred to a evaporation ponds, and both disposal methods are facing more regulatory and environmental challenges.
Zero liquid discharge and minimal liquid discharge, which use engineered treatment systems to eliminate brines or minimize brine volume, are already required in some countries for certain industries, and they are expected to become more widely adopted soon. Current ZLD/MLD treatments typically involve a technology called mechanical vapor compression, which generates heat from electricity to evaporate brines until the salt is all that remains. Because of the high capital and operating costs of MVC, these processes are unaffordable to many users.
Associate professor of civil and environmental engineering and 2023 Chancellor Faculty Fellow Shihong Lin and his team, including researchers from Colorado State University, believe they have an answer to this dilemma.
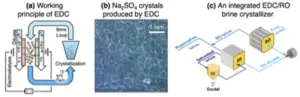
In a paper featured on the cover of the June 2023 issue of the journal Nature Water, Lin and his colleagues describe a novel brine treatment technology called electrodialytic crystallization that has the potential to reduce the energy consumption and cost of brine crystallization. The fundamental principle of EDC, according to the researchers, is like electrodialysis, a process that has been used in various industries for desalination and brine concentration.
In ED, an electric field is applied to pull ions through ion exchange membranes. By placing different types of IEMs in a certain way, ED can produce streams of deionized water and streams of concentrated brine. With some configuration changes to that process, the researchers say EDC keeps the brine within the integrated system and uses an electric field to induce salt crystallization without using costly evaporation methods.
“The elimination of evaporation is the key to developing potentially energy efficient brine crystallization processes,” according to the paper.
One major technical challenge is that when certain ions transport through the IEMs, they drag too much water across and reduce the effectiveness of the process in concentrating the brine stream. This phenomenon, called electro-osmosis, prevents some salts from being crystallized out effectively. The researchers said that better membrane design and optimized operation can potentially address this challenge and make EDC more universally applicable.
Nevertheless, for the salts that EDC can handle, the team performed a preliminary analysis and showed that EDC coupled with reverse osmosis can potentially consume much less energy than MVC for brine crystallization.
The study is funded by the National Alliance of Water Innovation, a public-private partnership that brings together world-class industry and academic partners to examine the critical technical barriers and research needed to radically lower the cost and energy of desalination. NAWI is led by DOE’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory in collaboration with National Energy Technology Laboratory, National Renewable Energy Laboratory and Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and it is funded by the Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy’s Industrial Efficiency and Decarbonization Office.
Earlier this year, Lin, who is also associate professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering, was awarded a Walter L. Huber Civil Engineering Research Prize by the American Society of Civil Engineers for his contributions to the field of water separation and resource sustainability.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-21
In a new paper published today in Nature, researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have outlined the structure and function of a protein complex which is required to repair damaged DNA and protect against cancer.
Every time a cell replicates, mistakes can happen in the form of mutations, but specialised proteins exist to repair the damaged DNA.
People with mutations in a DNA repair protein called BRCA2 are predisposed to breast, ovarian and prostate cancers, which often develop at a young age. In the clinic, these cancers are treated with a drug that inhibits PARP, ...
2023-06-21
The discovery of the quantum Hall effects in the 1980's revealed the existence of novel states of matter called "Laughlin states", in honor of the American Nobel prize winner who successfully characterized them theoretically. These exotic states specifically emerge in 2D materials, at very low temperature and in the presence of an extremely strong magnetic field. In a Laughlin state, electrons form a peculiar liquid, where each electron dances around its congeners while avoiding them as much as possible. Exciting such a quantum liquid generates collective states that physicists associate to fictitious particles, whose ...
2023-06-21
New research is increasing our understanding about why some women with the most lethal form of ovarian cancer respond much better to treatment than others.
Researchers at Imperial College London have confirmed that the tumours of some women with high-grade serious ovarian cancer (HGSOC) contain a type of lymphoid tissue – known as tertiary lymphoid structures, or TLS – and that the presence of this tissue gives women a significantly better prognosis. They have also identified genes in HGSOC ...
2023-06-21
An international team of scientists has discovered that Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*)1, the supermassive black hole at the centre of the Milky Way, emerged from a long period of dormancy some 200 years ago. The team, led by Frédéric Marin2, a CNRS researcher at the Astronomical Strasbourg Observatory (CNRS/University of Strasbourg), has revealed the past awakening of this gigantic object, which is four million times more massive than the Sun. Their work is published in Nature on 21 June. Over a period of one year at the beginning of the 19th century, the black ...
2023-06-21
New Haven, Conn. — Cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized treatment of many forms of cancer by unleashing the immune system response against tumors. Immunotherapies that block checkpoint receptors like PD-1, proteins that limit the capacity of T cells to attack tumors, have become the choice for the treatment of numerous types of solid cancer.
However, the introduction of PD-1-blocking agents can often result in T cells attacking healthy tissues in addition to cancer cells, causing severe, sometimes life-threatening, side effects that can blunt the benefits of immunotherapy.
A new study published by researchers ...
2023-06-21
New McMaster research has found that a disease-causing fungus — collected from one of the most remote regions in the world — is resistant to a common antifungal medicine used to treat infections.
The study, published today in mSphere, showed that seven per cent of Aspergillus fumigatus samples collected from the Three Parallel Rivers region in Yunnan, China were drug resistant.
Perched 6,000 metres above sea level and guarded by the staggering glaciated peaks of the Eastern Himalayas, the region is sparsely populated and undeveloped, which makes the presence of antimicrobial-resistant strains of A. fumigatus all the more striking for Jianping Xu, ...
2023-06-21
UPTON, NY— A new publication by the PHENIX Collaboration at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) provides definitive evidence that gluon “spins” are aligned in the same direction as the spin of the proton they’re in. The result, just published in Physical Review Letters, provides theorists with new input for calculating how much gluons—the gluelike particles that hold quarks together within protons and neutrons—contribute to a proton’s ...
2023-06-21
HOUSTON ― Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have uncovered a gene on the Y chromosome that is upregulated in KRAS-mutated colorectal cancer (CRC), increasing tumor cell invasiveness and reducing anti-tumor immunity in male patients.
The preclinical study, published today in Nature, provides novel insights into the longstanding mystery of molecular and cellular mechanisms that drive increased metastasis and poor prognosis in men with CRC. The results highlight the Y chromosome gene KDM5D, which codes for an epigenetic enzyme, as a potential therapeutic target and uncover ...
2023-06-21
‘Green’ farming policies may accelerate global biodiversity loss, two leading academics have warned.
Rewilding, organic farming and the ‘nature friendly farming’ measures included in some government conservation policies risk worsening the global biodiversity crisis by reducing how much food is produced in a region, driving up food imports and increasing environmental damage overseas.
In an article published today in the journal Nature, Professor Ian Bateman of the University of Exeter and Professor Andrew Balmford of the University of Cambridge urge policy-makers to consider a bolder approach known as ...
2023-06-21
Digital Science, a technology company serving stakeholders across the research ecosystem, is pleased to announce that Stellenbosch University (SU) has selected Symplectic Elements from Digital Science’s flagship products to support its goal of advancing knowledge in service of society.
Symplectic Elements will provide SU with a Researcher Profiles and Research Outputs Management Solution, supporting and streamlining DHET (Department of Higher Education and Training) submissions and providing a public profiling system for its researchers.
SU is one of South Africa’s leading tertiary institutions, and is recognised internationally ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study in Nature Water demonstrates a vastly more sustainable, cost-effective method to desalinate industrial wastewater