(Press-News.org) A new analysis suggests that wild, stray, and feral cats living in areas with higher human population density tend to release—or “shed”—a greater amount of the parasite that causes the disease toxoplasmosis. The study also draws links between environmental temperature variation and parasite shedding. Sophie Zhu of the University of California Davis, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 21.
Toxoplasmosis is a mild-to-severe disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, which can infect warm-blooded vertebrates, including humans and many wild or domestic animals; for instance, cats, sheep, mice, birds, and sea otters. Most T. gondii transmission is driven by wild and domestic cats shedding the parasite at a certain stage of its life cycle known as oocyst. However, prior research has primarily focused on T. gondii oocyst shedding from owned domestic cats, with less known about wild, stray, and feral cats.
To boost understanding of T. gondii shedding, Zhu and colleagues analyzed data from 47 previously published studies on both wildcats, such as cougars and bobcats, and unowned free-ranging domestic cats, including stray cats, unowned outdoor cats fed by humans, and feral cats that are not fed by humans. The data spanned regions around the world, and the researchers examined a variety of human- and climate-related factors that could potentially be associated with T. gondii oocyst shedding.
The analysis showed that a greater degree of T. gondii oocyst shedding was observed in places with higher human population density. It also showed that higher mean daily temperature fluctuations were associated with more shedding specifically from domestic cats, and that higher temperatures in the driest quarter of the year were associated with lower shedding from wildcats.
The researchers note that these findings do not prove any causal relationships. However, combined with evidence from other prior studies, they suggest that rising human population density and temperature fluctuations may create environmental conditions that exacerbate the spread of T. gondii and other infectious diseases.
On the basis of their findings, the researchers suggest that policymakers could focus on managing feral cat populations to help reduce T. gondii transmission.
The authors add: “Changes from climate or human activities can affect disease transmission in ways that we don't fully understand yet. In our study we can see how these factors may be associated with changes in Toxoplasma shedding by cats, which in turn can affect the risk of exposure to vulnerable people and wildlife.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0286808
Citation: Zhu S, VanWormer E, Shapiro K (2023) More people, more cats, more parasites: Human population density and temperature variation predict prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii oocyst shedding in free-ranging domestic and wild felids. PLoS ONE 18(6): e0286808. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286808
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
END
Wild and feral cats shed more toxoplasmosis parasites in areas densely populated by humans
Feral cat management might help reduce toxoplasmosis infection risk for humans
2023-06-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Young people learn gradually to reflect on mental states, peaking in young adulthood
2023-06-21
The capability to reflect on their own mental state and that of others continues to develop throughout adolescence, with mentalizing scores varying by gender and personality traits, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Alex Desatnik of University College London, UK, and colleagues.
It has been established that the human brain undergoes a number of important changes during adolescence, especially in the “social brain” regions associated with social cognition. One of the key constructs capturing multiple facets of social cognition is ...
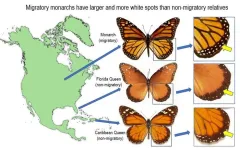
Monarch butterflies are more likely to survive their long migrations if they have more and larger white spots on their wings, possibly because it gives them an aerodynamic advantage
2023-06-21
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0286921
Article Title: How the monarch got its spots: Long-distance migration selects for larger white spots on monarch butterfly wings
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
One in ten NHS healthcare workers experienced suicidal thoughts during pandemic, study finds
2023-06-21
Approximately one in ten NHS healthcare workers experienced suicidal thoughts during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, finds a new University of Bristol-led study published in PLOS ONE today [21 June].
Concerns were raised about the risk of suicide among healthcare workers during the pandemic after a number of high-profile cases were reported in the media. Researchers from the University of Bristol, King’s College London and UCL (University College London), sought to investigate the prevalence and incidence of suicidal thoughts and behaviour among NHS healthcare workers in England and their relationship with occupational ...
Repurposed drug shows promise for treating cardiac arrhythmias
2023-06-21
Ruxolitinib, a drug that is already approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating certain cancers and skin conditions, is effective at inhibiting CaMKII, a protein kinase linked to cardiac arrhythmias.
In a new study published June 21, 2023, in Science Translational Medicine, researchers from Johns Hopkins University and the University of Chicago invented a new reporting technique to monitor activity of CaMKII while screening the effects of nearly 5,000 FDA approved drugs on human cells that expressed the ...
Urgent action needed to further improve child survival in Ethiopia: Study
2023-06-21
New global research on child mortality rates in Ethiopia shows while there has been a significant decline in these rates in past three decades, too many children under the age of five are still dying.
The analysis found the mortality rate in the under-five demographic decreased by almost 4.5 per cent every year between 1990 and 2019.
However, despite the progress, it’s still one of the highest rates in the world with an estimated 190,000 under 5 deaths in 2019 at the rate of 52 deaths per 1000 livebirths. The country’s neonatal mortality rate is 26.6 deaths per 1000 livebirths.
Lead author Dr Gizachew Tessema from the Curtin School of Population ...
Quantum interference can protect and enhance photoexcitation
2023-06-21
When a photon interacts with a material, an interaction occurs that causes its atoms to change their quantum state (a description of the physical properties of nature at the atomic level). The resulting state is called, aptly, photoexcitation. These photoexcitations are conventionally assumed to kill one another when they come near each other, radically limiting their density and mobility. This in turn limits how efficient tools that rely on photoexcitation such as solar cells and light-emitting devices can be.
But in a study published June 19 in the journal Nature Chemistry, scientists at Northwestern University and Purdue University challenge this assumption ...
Reducing bias and stigma associated with medication-assisted treatment improves care
2023-06-21
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT), such as naltrexone, is a well-documented successful treatment for opioid use disorder (OUD). However, there are multiple barriers for clinicians to use MAT, including clinician lack of confidence in using the treatment, their own misconceptions about the patient population, and, until recently, federally required training. Additionally, there is a stigma associated with MAT and the patients who would most benefit from it. Improving access to MAT training and integrating it into clinician programs and curriculums may remove identified barriers, decrease stigma, and enable newly trained clinicians to treat patients.
To address these barriers, ...
UNM researchers find medical cannabis patients who feel 'high' report greater symptom relief but increased negative side effects
2023-06-21
In a new study titled, “Understanding Feeling ‘High’ and Its Role in Medical Cannabis Patient Outcomes,” published in the journal, Frontiers in Pharmacology, researchers at The University of New Mexico, in collaboration with Releaf App™ found that patients who reported feeling “High” experienced 7.7% greater symptom relief and an increase in reporting of positive side effects such as “Relaxed” and “Peaceful.” However, these benefits must be weighed against a more than 20% increase in negative side effect reporting.
Senior author and Associate Professor of Psychology, ...
Screening newborns for "bubble-baby" disease saves lives
2023-06-21
Screening newborns for severe combined immunodeficiency disease (SCID) significantly increases the survival of children after bone marrow transplantation, a new North American study finds.
Published today in The Lancet with an accompanying editorial, the retrospective study was co-led by Elie Haddad, an Université de Montréal medical professor and clinician scientist, pediatrician and immunologist at the UdeM-affiliated CHU Sainte-Justine mother-and-child hospital.
The research shows that the gradual adoption of newborn screening for SCID since 2008 in North America has boosted the survival rate from 73 per cent between 1982 and 2009 to ...
Rain gardens could save salmon from toxic tire chemicals
2023-06-21
Specially designed gardens could reduce the amount of a toxic chemical associated with tires entering our waterways by more than 90 per cent, new research shows.
Tired toxins
The chemical 6PPD-quinone can form when car tires interact with the atmosphere. It enters rivers and streams when rain runs off roads into waterways. It is toxic to coho salmon, rainbow trout and some other fish.
“Rain gardens”, or bioretention cells, are gardens engineered to reduce flooding and soak up contaminants when road runoff is directed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Wild and feral cats shed more toxoplasmosis parasites in areas densely populated by humansFeral cat management might help reduce toxoplasmosis infection risk for humans