(Press-News.org) June 21, 2023 – For patients undergoing surgery for elbow trauma, treatment with the hemostatic drug tranexamic acid (TXA) is associated with a decreased incidence of heterotopic ossification (HO) – a common complication of abnormal bone formation, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
The findings "add new clinical evidence regarding the protective role of TXA with respect to the prevention of HO after elbow trauma," according to the report by Cunyi Fan, MD, PhD, of Shanghai Sixth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, China, and colleagues.
Fifty percent reduction in HO in patients receiving TXA
Heterotopic ossification refers to abnormal bone formation in the soft tissue. It is a common and potentially disabling complication following surgery for traumatic elbow fracture, with a reported prevalence of up to 40%. Inflammation is common after limb trauma and is an important factor in the initiation of HO.
TXA is increasingly used to reduce blood loss during orthopaedic surgery and has been shown to reduce inflammatory responses postoperatively. Dr. Fan and colleagues reviewed their experience to determine whether the use of TXA is associated with a lower risk of HO.
The retrospective study included two matched groups of patients with a mean age of 44 years who underwent surgery for traumatic elbow fracture. One group received TXA during surgery and the other group did not. The incidence and severity of HO were compared between groups, including adjustment for other characteristics.
The overall rate of postoperative HO was 8.71% in patients who received TXA compared with 16.18% in those who did not. On adjusted analysis, the incidence of HO was reduced by half in the TXA group, with an odds ratio of 0.49.
Anti-inflammatory effects of TXA may help to prevent HO
The incidence of clinically important HO, based on the presence of functional limitations, was 2.07% in patients who received TXA compared with 5.80% in those who did not. For this outcome, risk was reduced by two-thirds in the TXA group, with an odds ratio of 0.34. Tranexamic acid was associated with a lower risk of HO across patient subgroups with differing characteristics.
This study provides the first published evidence that using TXA during elbow trauma surgery can help lower the risk of postoperative HO. Previous reports have found that reducing inflammation can reduce HO formation – "indicating that the inflammatory response acts as a necessary starting factor for HO development," the researchers write. The authors discuss recent evidence suggesting the potential anti-inflammatory properties of TXA.
Dr. Fan and coauthors note the limitations of their retrospective analysis and highlight the need for larger studies, including those to assess laboratory markers of inflammation. In the meantime, the researchers conclude, "TXA prophylaxis may be an appropriate method for the prevention of HO following surgery for the treatment of elbow trauma."
Read [Association Between Tranexamic Acid Use and Heterotopic Ossification Prevalence After Elbow Trauma Surgery: A Propensity-Score-Matched Cohort Study]
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across healthcare. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
###
About The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery
The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (JBJS) has been the most valued source of information for orthopaedic surgeons and researchers for over 125 years and is the gold standard in peer-reviewed scientific information in the field. A core journal and essential reading for general as well as specialist orthopaedic surgeons worldwide, The Journal publishes evidence-based research to enhance the quality of care for orthopaedic patients. Standards of excellence and high quality are maintained in everything we do, from the science of the content published to the customer service we provide. JBJS is an independent, non-profit journal.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (EURONEXT: WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the healthcare, tax and accounting, financial and corporate compliance, legal and regulatory, and corporate performance and ESG sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with specialized technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2022 annual revenues of €5.5 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 20,000 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
For more information, visit www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube.
END
Early warning signs of diseases caused by dysfunctional levels of stress hormones could be spotted more easily thanks to a new wearable device developed by endocrine researchers.
This is the first time it has been possible to measure changes to people’s stress hormones as they go about normal daily activities, across both day and night. The new collaborative research led by the University of Bristol, University of Birmingham and University of Bergen has the potential to revolutionise how diseases of the stress hormone system are diagnosed and treated.
The technology, ...
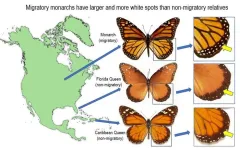
If you’ve ever wondered how the monarch butterfly got its spots, University of Georgia researchers may have just found the answer.
The new study suggests that the butterflies with more white spots are more successful at reaching their long-distance wintering destination. Although it’s not yet clear how the spots aid the species’ migration, it’s possible that the spots change airflow patterns around their wings.
“We undertook this project to learn how such a small animal can make such a successful ...
A new analysis suggests that wild, stray, and feral cats living in areas with higher human population density tend to release—or “shed”—a greater amount of the parasite that causes the disease toxoplasmosis. The study also draws links between environmental temperature variation and parasite shedding. Sophie Zhu of the University of California Davis, U.S., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 21.
Toxoplasmosis is a mild-to-severe disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, which can infect warm-blooded vertebrates, including humans and many wild or domestic animals; for instance, cats, sheep, mice, birds, ...
The capability to reflect on their own mental state and that of others continues to develop throughout adolescence, with mentalizing scores varying by gender and personality traits, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Alex Desatnik of University College London, UK, and colleagues.
It has been established that the human brain undergoes a number of important changes during adolescence, especially in the “social brain” regions associated with social cognition. One of the key constructs capturing multiple facets of social cognition is ...
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0286921
Article Title: How the monarch got its spots: Long-distance migration selects for larger white spots on monarch butterfly wings
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Approximately one in ten NHS healthcare workers experienced suicidal thoughts during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, finds a new University of Bristol-led study published in PLOS ONE today [21 June].
Concerns were raised about the risk of suicide among healthcare workers during the pandemic after a number of high-profile cases were reported in the media. Researchers from the University of Bristol, King’s College London and UCL (University College London), sought to investigate the prevalence and incidence of suicidal thoughts and behaviour among NHS healthcare workers in England and their relationship with occupational ...
Ruxolitinib, a drug that is already approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating certain cancers and skin conditions, is effective at inhibiting CaMKII, a protein kinase linked to cardiac arrhythmias.
In a new study published June 21, 2023, in Science Translational Medicine, researchers from Johns Hopkins University and the University of Chicago invented a new reporting technique to monitor activity of CaMKII while screening the effects of nearly 5,000 FDA approved drugs on human cells that expressed the ...
New global research on child mortality rates in Ethiopia shows while there has been a significant decline in these rates in past three decades, too many children under the age of five are still dying.
The analysis found the mortality rate in the under-five demographic decreased by almost 4.5 per cent every year between 1990 and 2019.
However, despite the progress, it’s still one of the highest rates in the world with an estimated 190,000 under 5 deaths in 2019 at the rate of 52 deaths per 1000 livebirths. The country’s neonatal mortality rate is 26.6 deaths per 1000 livebirths.
Lead author Dr Gizachew Tessema from the Curtin School of Population ...
When a photon interacts with a material, an interaction occurs that causes its atoms to change their quantum state (a description of the physical properties of nature at the atomic level). The resulting state is called, aptly, photoexcitation. These photoexcitations are conventionally assumed to kill one another when they come near each other, radically limiting their density and mobility. This in turn limits how efficient tools that rely on photoexcitation such as solar cells and light-emitting devices can be.
But in a study published June 19 in the journal Nature Chemistry, scientists at Northwestern University and Purdue University challenge this assumption ...
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT), such as naltrexone, is a well-documented successful treatment for opioid use disorder (OUD). However, there are multiple barriers for clinicians to use MAT, including clinician lack of confidence in using the treatment, their own misconceptions about the patient population, and, until recently, federally required training. Additionally, there is a stigma associated with MAT and the patients who would most benefit from it. Improving access to MAT training and integrating it into clinician programs and curriculums may remove identified barriers, decrease stigma, and enable newly trained clinicians to treat patients.
To address these barriers, ...