A recent study by scientists at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus reports the discovery of a molecular mechanism contributing to defective heart development in Down syndrome. The research team, led by Dr. Kunhua Song, associate professor of medicine, employed a combination of experiments using human cells with and without trisomy 21 and a mouse model of Down syndrome to illuminate the molecular basis of impaired heart formation.
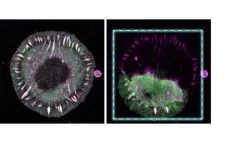
Using pluripotent stem cells obtained from research participants in the Human Trisome Project, a large study of people with Down syndrome led by the Linda Crnic Institute for Down syndrome at the University of Colorado, the team modeled the initial steps of heart formation, or cardiogenesis, in the laboratory. They observed that trisomy 21 impaired cardiogenesis, and this malfunction was associated with hyperactivity in the cellular response to viral infections, known as the interferon response. Then, using genetic and pharmacological approaches, they demonstrated that blocking the interferon response improved cardiogenesis in the laboratory.
“We were surprised to see strong activity of the interferon response during differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into heart muscle cells with trisomy 21. We now appreciate that an abnormally high interferon response could be detrimental to early heart development,” explains Dr. Song.
The researchers continued their investigation into how exactly interferon hyperactivity impaired cardiogenesis, which led them to discover that the interferon response inhibits a series of key molecular events required for heart development, such as the Wnt signaling pathway.
According to Dr. Congwu Li, lead author of the paper, “Too much interferon activity leads to too little Wnt signaling, which in turn impairs heart muscle cell function. Discovering this cascade of events illuminates potential strategies to ameliorate improper heart formation in Down syndrome by toning down interferon signaling and/or bumping up Wnt signaling.”
To test this therapeutic strategy in a mouse model of Down syndrome, the investigators treated pregnant female mice with a medicine that reduces the interferon response, known as a JAK inhibitor, and monitored the effects on heart development in the embryos carrying a genetic alteration equivalent to trisomy 21. Indeed, treatment of pregnant mice with the JAK inhibitor caused a remarkable improvement in cardiogenesis in mice.
“These are very important results, because they suggest a potential pharmacological strategy for pre-natal treatment of one of the most harmful impacts of trisomy 21. Babies born with Down syndrome and congenital heart defects face a number of challenges, from the need of heart surgery soon after birth to long lasting impacts on their physiology later in life. However, a lot of additional research will be needed to define the safety and efficacy of using JAK inhibitors during pregnancy,” explains Dr. Joaquin Espinosa, executive director of the Linda Crnic Institute for Down syndrome and co-author of the paper.
Dr. Espinosa and his team are currently leading clinical trials studying the benefits of JAK inhibitors in older children and adults with Down syndrome.
These findings expand on a growing body of evidence demonstrating the harmful effects of interferon hyperactivity in Down syndrome, even during early stages of embryonic development. The results also support the idea that many of the hallmarks of Down syndrome are driven by lifelong dysregulation of the immune system and that restoring immune balance could provide therapeutic benefits.
“This body of work is proof of the rapid scientific advances that can take place with the right investment of resources and the willingness of individuals with Down syndrome to participate in research,” says Dr. Espinosa. “We are experiencing a true renaissance in the field of Down syndrome research, fueled by strong support from the National Institutes of Health INCLUDE Project, which is the culmination of many years of advocacy by the Global Down Syndrome Foundation. Thanks to these efforts, we are confident that people with Down syndrome will live longer, healthier lives.”
About the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus
The University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is a world-class medical destination at the forefront of transformative science, medicine, education and patient care. The campus encompasses the University of Colorado health professional schools, more than 60 centers and institutes and two nationally ranked independent hospitals - UCHealth University of Colorado Hospital and Children's Hospital Colorado - that treat more than two million adult and pediatric patients each year. Innovative, interconnected and highly collaborative, the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus delivers life-changing treatments, patient care and professional training and conducts world-renowned research fueled by over $690 million in research grants. For more information, visit www.cuanschutz.edu.
About the Linda Crnic Institute for Down Syndrome
The Linda Crnic Institute for Down Syndrome is one of the only academic research centers fully devoted to improving the lives of people with Down syndrome through advanced biomedical research, spanning from basic science to translational and clinical investigations. Founded through the generous support and partnership of the Global Down Syndrome Foundation, the Anna and John J. Sie Foundation, and the University of Colorado, the Crnic Institute supports a thriving Down syndrome research program involving over 50 research teams across four campuses on the Colorado Front Range. To learn more, visit www.crnicinstitute.org or follow us on Facebook and Twitter @CrnicInstitute.
About Global Down Syndrome Foundation
The Global Down Syndrome Foundation (GLOBAL) is the largest non-profit in the U.S. working to save lives and dramatically improve health outcomes for people with Down syndrome. GLOBAL has donated more than $32 million to establish the first Down syndrome research institute supporting over 400 scientists and over 2,200 patients with Down syndrome from 33 states and 10 countries. Working closely with Congress and the National Institutes of Health, GLOBAL is the lead advocacy organization in the U.S. for Down syndrome research and care. GLOBAL has a membership of over 120 Down syndrome organizations worldwide, and is part of a network of Affiliates – the Crnic Institute for Down Syndrome, the Sie Center for Down Syndrome, and the University of Colorado Alzheimer’s and Cognition Center – all on the Anschutz Medical Campus.
GLOBAL’s widely circulated medical publications include Global Medical Care Guidelines for Adults with Down Syndrome, Prenatal Testing and Information about Down Syndrome, and the award-winning magazine Down Syndrome World TM. GLOBAL also organizes the Be Beautiful Be Yourself Fashion Show, the largest Down syndrome fundraiser in the world. Visit globaldownsyndrome.org and follow us on social media (Facebook & Twitter: @GDSFoundation, Instagram: @globaldownsyndrome).
###
END