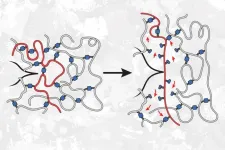
(Press-News.org) CAMBRIDGE, MA -- A team of chemists from MIT and Duke University has discovered a counterintuitive way to make polymers stronger: introduce a few weaker bonds into the material.
Working with a type of polymer known as polyacrylate elastomers, the researchers found that they could increase the materials’ resistance to tearing up to tenfold, simply by using a weaker type of crosslinker to join some of the polymer building blocks.
These rubber-like polymers are commonly used in car parts, and they are also often used as the “ink” for 3D-printed objects. The researchers are now exploring the possible expansion of this approach to other types of materials, such as rubber tires.
“If you could make a rubber tire 10 times more resistant to tearing, that could have a dramatic impact on the lifetime of the tire and on the amount of microplastic waste that breaks off,” says Jeremiah Johnson, a professor of chemistry at MIT and one of the senior authors of the study, which appears today in Science.
A significant advantage of this approach is that it doesn’t appear to alter any of the other physical properties of the polymers.
“Polymer engineers know how to make materials tougher, but it invariably involves changing some other property of the material that you don’t want to change. Here, the toughness enhancement comes without any other significant change in physical properties — at least that we can measure — and it is brought about through the replacement of only a small fraction of the overall material,” says Stephen Craig, a professor of chemistry at Duke University who is also a senior author of the paper.
This project grew out of a longstanding collaboration between Johnson, Craig, and Duke University Professor Michael Rubinstein, who is also a senior author of the paper. The paper’s lead author is Shu Wang, an MIT postdoc who earned his PhD at Duke.
The weakest link
Polyacrylate elastomers are polymer networks made from strands of acrylate held together by linking molecules. These building blocks can be joined together in different ways to create materials with different properties.
One architecture often used for these polymers is a star polymer network. These polymers are made from two types of building blocks: one, a star with four identical arms, and the other a chain that acts as a linker. These linkers bind to the end of each arm of the stars, creating a network that resembles a volleyball net.
In a 2021 study, Craig, Rubinstein, and MIT Professor Bradley Olsen teamed up to measure the strength of these polymers. As they expected, they found that when weaker end-linkers were used to hold the polymer strands together, the material became weaker. Those weaker linkers, which contain cyclic molecules known as cyclobutane, can be broken with much less force than the linkers that are usually used to join these building blocks.
As a follow-up to that study, the researchers decided to investigate a different type of polymer network in which polymer strands are cross-linked to other strands in random locations, instead of being joined at the ends.
This time, when the researchers used weaker linkers to join the acrylate building blocks together, they found that the material became much more resistant to tearing.
This occurs, the researchers believe, because the weaker bonds are randomly distributed as junctions between otherwise strong strands throughout the material, instead of being part of the ultimate strands themselves. When this material is stretched to the breaking point, any cracks propagating through the material try to avoid the stronger bonds and go through the weaker bonds instead. This means the crack has to break more bonds than it would if all of the bonds were the same strength.
“Even though those bonds are weaker, more of them end up needing to be broken, because the crack takes a path through the weakest bonds, which ends up being a longer path,” Johnson says.
Tough materials
Using this approach, the researchers showed that polyacrylates that incorporated some weaker linkers were nine to 10 times harder to tear than polyacrylates made with stronger crosslinking molecules. This effect was achieved even when the weak crosslinkers made up only about 2 percent of the overall composition of the material.
The researchers also showed that this altered composition did not alter any of the other properties of the material, such as resistance to breaking down when heated.
“For two materials to have the same structure and same properties at the network level, but have an almost order of magnitude difference in tearing, is quite rare,” Johnson says.
The researchers are now investigating whether this approach could be used to improve the toughness of other materials, including rubber.
“There’s a lot to explore here about what level of enhancement can be gained in other types of materials and how best to take advantage of it,” Craig says.
###
The group’s work on polymer strength is part of a National Science Foundation-funded center called the Center for the Chemistry of Molecularly Optimized Networks. This mission of this center, directed by Craig, is to study how the properties of the molecular components of polymer networks affect the physical behavior of the networks.
END
Surprise! Weaker bonds can make polymers stronger
By adding weak linkers to a polymer network, chemists dramatically enhanced the material’s resistance to tearing
2023-06-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The clue is in the glue - Nature’s secret for holding it together
2023-06-22
An obscure aquatic plant has helped to explain how plants avoid cracking up under the stresses and strains of growth.
The finding by researchers Dr Robert Kelly-Bellow and Karen Lee in the group of Professor Enrico Coen at the John Innes Centre, started with a curious observation in a dwarf mutant of the carnivorous plant Utricularia gibba.
The stems of this floating plant are filled with airspaces and this hollowness means that the vascular column inside the stem can buckle when under stress. This effect would not be apparent in most plants, which have solid stems.
The researchers saw that in a dwarf mutant the central column was wavy instead of straight. They hypothesised that ...
Generative AI models are encoding biases and negative stereotypes in their users
2023-06-22
The likes of ChatGPT, Google’s Bard and Midjourney can also help spread incorrect, nonsensical information
Marginalised groups are disproportionately affected
Children are at particular risk
In the space of a few months generative AI models, such as ChatGPT, Google’s Bard and Midjourney, have been adopted by more and more people in a variety of professional and personal ways. But growing research is underlining that they are encoding biases and negative stereotypes in their users, as well as mass generating and spreading seemingly accurate but nonsensical information. Worryingly, marginalised groups are disproportionately affected by the fabrication of this nonsensical information.
In ...
Bringing the power of "multiplex" imaging to clinical pathology
2023-06-22
June 22, 2023, NEW YORK – Researchers at the Ludwig Center at Harvard have developed a platform technology for imaging that enables integration of the methods of microscopic analysis long employed in pathology laboratories with the visualization of multiple molecular markers in individual cells that is now rapidly advancing in research labs. The latter capability, known as “multiplex” imaging, promises to revolutionize cancer diagnostics by exposing molecular traits associated with ...
NF researchers, clinicians and patients gather for annual conference in Scottsdale
2023-06-22
From June 21 through June 27, the largest gathering of NF researchers, clinicians, and patients in the world will take place at the Fairmont Scottsdale Princess in Scottsdale, Arizona. NF is a group of genetic disorders that causes tumors to grow on nerves throughout the body, and affects 1 in 2,000 births of all populations equally. As such, NF affects millions worldwide, but is underrecognized. While there is one approved treatment for a small subgroup of NF patients with plexiform neurofibromas, there is no cure yet, and the vast majority of NF patients face serious health issues because of the condition. ...
Argonne installs final components of Aurora supercomputer
2023-06-22
The installation of Aurora’s 10,624th and final “blade” marked a major milestone for the highly anticipated exascale supercomputer at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory.
After years of diligent work and planning, the system now contains all the hardware that will make it one of the most powerful supercomputers in the world when it is opened up for scientific research. Built by Intel and Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), Aurora will be theoretically capable ...
Being able to tell parents about sexuality plays important role in mental health of Black sexual minority men and transgender women
2023-06-22
Black sexual minority men (BSMM) and transgender women (BTW) face racial and sexuality-based discrimination, and disproportionately high depression compared to Black heterosexual men and Black cisgender women, respectively. Though previous studies have demonstrated the relationship between discrimination and depression among racial and sexual minorities, few studies explore the extent to which openness with parents impacts this relationship.
A new study by College of Public Health Assistant Professor Rodman Turpin found that sexual identity ...
Transforming Anthropology joins the University of Chicago Press journals program in 2024
2023-06-22
We are honored to announce that Transforming Anthropology will join the University of Chicago Press journals program beginning in 2024 (vol. 32, no. 1). Transforming Anthropology is the flagship journal of the Association of Black Anthropologists (ABA), which is a section of the American Anthropological Association (AAA). All 8,000+ members of the AAA receive online access to Transforming Anthropology through their membership, and that benefit will continue in this new partnership.
“Thanks to the vision and dedication of our editor, Aisha Beliso-De Jesús, the journal will maintain its tradition of supporting and nurturing ...
Lehigh Industrial Assessment Center to expand into regional energy audit, workforce development role
2023-06-22
The Lehigh University Industrial Assessment Center (IAC) will expand into the Mid-Atlantic Regional IAC Center of Excellence (MARICE) with newly awarded funding from the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE).
Lehigh’s IAC was established in 2001 as part of the DOE’s nationwide Industrial Assessment Center Program to reduce energy and waste and enhance productivity for manufacturing plants in Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and New York. The center, which was most recently renewed in 2021, is led by mechanical engineering and mechanics (MEM) faculty Professor Alparslan ...
Stem cell model of human brain development suggests embryonic origins of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-06-22
Alzheimer's disease (AD) mainly affects the older population. Recent research found early disease signs in cell culture models of early human brain development, raising the possibility that the disease has its origins much earlier in life, possibly during embryogenesis – the formation and development of an embryo.
Alzheimer’s disease is a highly prevalent, debilitating, and potentially fatal neurodegenerative disease with limited treatment options. Patients are typically diagnosed at an advanced disease stage, limiting the possibilities for early therapeutic intervention. Although for most patients ...
Chronic stress-related neurons identified
2023-06-22
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have identified a group of nerve cells in the mouse brain that are involved in creating negative emotional states and chronic stress. The neurons, which have been mapped with a combination of advanced techniques, also have receptors for oestrogen, which could explain why women as a group are more sensitive to stress than men. The study is published in Nature Neuroscience.
Just which networks in the brain give rise to negative emotions (aversion) and chronic stress have long been unknown to science.
By using ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Putting some ‘muscle’ into material design
House fires release harmful compounds into the air
Novel structural insights into Phytophthora effectors challenge long-held assumptions in plant pathology
Q&A: Researchers discuss potential solutions for the feedback loop affecting scientific publishing
A new ecological model highlights how fluctuating environments push microbes to work together
Chapman University researcher warns of structural risks at Grand Renaissance Dam putting property and lives in danger
Courtship is complicated, even in fruit flies
Columbia announces ARPA-H contract to advance science of healthy aging
New NYUAD study reveals hidden stress facing coral reef fish in the Arabian Gulf
36 months later: Distance learning in the wake of COVID-19
Blaming beavers for flood damage is bad policy and bad science, Concordia research shows
The new ‘forever’ contaminant? SFU study raises alarm on marine fiberglass pollution
Shorter early-life telomere length as a predictor of survival
Why do female caribou have antlers?
How studying yeast in the gut could lead to new, better drugs
Chemists thought phosphorus had shown all its cards. It surprised them with a new move
A feedback loop of rising submissions and overburdened peer reviewers threatens the peer review system of the scientific literature
Rediscovered music may never sound the same twice, according to new Surrey study
Ochsner Baton Rouge expands specialty physicians and providers at area clinics and O’Neal hospital
New strategies aim at HIV’s last strongholds
Ambitious climate policy ensures reduction of CO2 emissions
Frontiers in Science Deep Dive webinar series: How bacteria can reclaim lost energy, nutrients, and clean water from wastewater
UMaine researcher develops model to protect freshwater fish worldwide from extinction
Illinois and UChicago physicists develop a new method to measure the expansion rate of the universe
Pathway to residency program helps kids and the pediatrician shortage
How the color of a theater affects sound perception
Ensuring smartphones have not been tampered with
Overdiagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer
Association of dual eligibility and medicare type with quality of postacute care after stroke
Shine a light, build a crystal
[Press-News.org] Surprise! Weaker bonds can make polymers strongerBy adding weak linkers to a polymer network, chemists dramatically enhanced the material’s resistance to tearing