(Press-News.org) Background
COVID-19 survivors may experience persistent neuropsychological disruptions such as lower satisfaction with life (SWLS), depression, and anxiety. While student-athletes are at low risk for severe COVID complications, the effect of COVID on mental health remains to be elucidated.
Objective
Compare patient-reported mental health outcomes for incoming collegiate athletes who did (COVID+) and did not (COVID-) have COVID-19.
Methods
79 COVID+ (79/178, 44.4%, 18.90±0.16 years) and 99 COVID- (99/178, 55.6%,18.95±0.16 years) completed SWLS, anxiety (HADS anxiety, STAI), depression (HADS depression). Unadjusted One-way ANOVAs were conducted across all patient-reported outcomes. ANCOVAs were conducted to determine the interaction of COVID history, sex, and race/ethnicity on outcomes. Post-hoc Bonferroni testing was performed to determine specific differences between groups. Chi-square analyses were used to compare the number of athletes who met the standard of clinical cut points for both groups.
Results
We observed a significant difference between groups for HADS depression (p=0.047), whereby athletes in the COVID+ group had significantly higher depression ratings (2.9±0.3). There was a significant group difference for SWLS (p=0.019), HADS anxiety (p=0.003), and STAI state anxiety (p=0.014) such that SWLS, HADS anxiety, and trait anxiety was higher for the COVID+ group in the adjusted model. Post-hoc testing revealed that COVID+ females had significantly worse HADS anxiety (p=0.011) and STAI trait anxiety (p=0.002). There were no significant differences in the percentage of responses below established diagnostic thresholds between groups.
Conclusions
Incoming collegiate student-athletes who reported prior COVID diagnosis reported significantly higher depression scores suggesting clinicians may need to be aware of the potential need to intervene with appropriate mental health identification and referral. However, it was encouraging that most participants, regardless of prior COVID diagnosis, had mental health scores that did not exceed established diagnostic threshold values.
END
Research links increase in depression, COVID diagnosis in student-athletes
“On average, student-athletes who had COVID reported slightly higher feelings of depression,” Anderson said
2023-06-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Heat spots reveal growth rate of a galaxy 12 billion years ago
2023-06-22
An international team of astronomers has drawn a temperature map of the dust drifting within one of the oldest spiral galaxies of the Universe which provides new insights into how fast the galaxy is growing. Until now researchers have only been able to measure the temperature of most distant galaxies in broad terms, without showing how temperatures vary in individual areas.
This research, described in a paper published today in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS) shows unambiguous temperature variation within the distant galaxy indicating two distinct heat sources – a supermassive black hole at the centre of the galaxy, and the heat generated ...
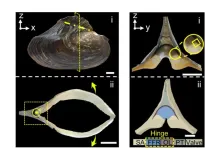
Scientists learn from hinge in bivalve about fatigue resistance of materials
2023-06-22
Recently, flexible and foldable devices have developed at a dramatic rate. More and more foldable devices appear in people's lives. Long-term service requires the folded parts to endure repeated deformation which might cause fatigue damage to the devices. Consequently, the damage will affect the normal function of the devices. Inspired by the hinge of bivalve Cristaria plicata, which experiences hundreds of thousands of repeating opening-and-closing valve motions throughout the bivalve’s lifetime, a research team led by Prof. YU Shuhong collaborating with Prof. WU Hengan from the University of Science and Technology of China ...
Bias in AI algorithms could be mitigated by implementing new checklist
2023-06-22
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Digital Health: https://journals.plos.org/digitalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pdig.0000278
Article Title: Bias in artificial intelligence algorithms and recommendations for mitigation
Author Countries: Jordan, United States, Canada
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
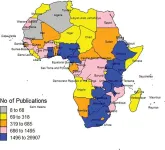
Africa's share of global HIV research output has increased from 5.1% to 31.3% over the last 35 years, but is still low compared to its relative burden of infections
2023-06-22
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0000544
Article Title: HIV research output in African Countries between 1986–2020
Author Countries: Nigeria, USA, UK
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
How might generative AI models distort human beliefs?
2023-06-22
Generative AI models such as ChatGPT, DALL-E, and Midjourney all have features that may distort human beliefs through their transmission of false information and stereotyped biases, according to Celeste Kidd and Abeba Birhane. In this Perspective, they discuss how research on human psychology can explain why generative AI could be particularly powerful in distorting beliefs. The capabilities of generative AI have been exaggerated at this point, they suggest, leading to a belief that these models exceed human capabilities. People are predisposed to adopt the information of knowledgeable, confident agents like generative AI ...
Large herbivores slow Arctic tundra diversity losses associated with sea ice decline
2023-06-22
Tundra diversity, including plants, lichens and fungi, declined over a 15-year experiment in the Arctic due to warming temperatures mediated by the disappearance of sea ice, according to Eric Post and colleagues. However, the presence of large herbivores such as caribou and musk oxen slowed this decline, by affecting the plant understory with their different browsing behaviors, the researchers concluded. Their findings offer support for the idea that encouraging herbivore diversity in the tundra could temper some of the impacts of climate warming. Post et al. observed the interacting effects of warming temperatures, sea ice changes, tundra diversity and herbivore exclusion in ...
Hard and soft materials form a fatigue-resistant fan in the mussel’s hinge
2023-06-22
How does a mussel shell open and shut easily and without damage for hundreds of thousands of cycles during the bivalve’s lifetime? Such fatigue-resistant materials would be useful in electronics, aerospace and tissue engineering designs, where components need to operate repeatedly without failure. Xiang-Sen Meng and colleagues took a closer look at the hinge on the shell of the bivalve Cristaria plicata, and found that the answer lies in a combination of design and materials that resist brittle fracture over time. Microscopic observations by Meng et al. show that the hinge gets its ...
Laws restricting abortion have ethical, legal and practical impacts for research on people who may become pregnant
2023-06-22
In this Policy Forum, Jeremy Sugarman and colleagues describe the risks that increasingly limited access to abortion may pose to clinical research participants and staff, one year after the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Woman’s Health Organization. People who may become pregnant are already an understudied population in clinical research. The authors suggest that new laws restricting abortion access may lead to ethical, legal and practical problems that make the risk of conducting research with this population unreasonable ...
Are viruses keeping sea lice at bay in wild salmon?
2023-06-22
More than 30 previously unknown RNA viruses in sea lice have been identified by University of British Columbia (UBC) researchers. Sea lice are parasitic copepods (small crustaceans) found in many fresh and saltwater habitats, and have been implicated in the decline of wild salmon populations. The research sheds greater light on the types of viruses being carried by sea lice, and how the viruses and host are interacting.
“We found many more types of viruses than are known in sea lice or their distant relatives; the lice are mounting an immune defense response to many of these viruses indicating that they are replicating,” says UBC marine microbiologist Dr. Curtis Suttle, ...
The molecular control centre of our protein factories
2023-06-22
Based on genetic blueprints, individual amino acids are assembled into long amino acid chains, the proteins, in the protein factories of our cells, the ribosomes. Each newly formed protein starts with the amino acid methionine. This amino acid is often split off again during protein synthesis, as soon as the growing amino acid chain leaves the protein factory through the "ribosomal tunnel". In these cases, the excision of methionine is essential to ensure the subsequent function of the corresponding ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Research links increase in depression, COVID diagnosis in student-athletes“On average, student-athletes who had COVID reported slightly higher feelings of depression,” Anderson said