(Press-News.org) Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/globalpublichealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgph.0000544
Article Title: HIV research output in African Countries between 1986–2020
Author Countries: Nigeria, USA, UK
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
END
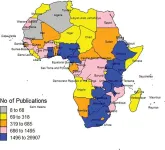
Africa's share of global HIV research output has increased from 5.1% to 31.3% over the last 35 years, but is still low compared to its relative burden of infections
2023-06-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How might generative AI models distort human beliefs?
2023-06-22
Generative AI models such as ChatGPT, DALL-E, and Midjourney all have features that may distort human beliefs through their transmission of false information and stereotyped biases, according to Celeste Kidd and Abeba Birhane. In this Perspective, they discuss how research on human psychology can explain why generative AI could be particularly powerful in distorting beliefs. The capabilities of generative AI have been exaggerated at this point, they suggest, leading to a belief that these models exceed human capabilities. People are predisposed to adopt the information of knowledgeable, confident agents like generative AI ...
Large herbivores slow Arctic tundra diversity losses associated with sea ice decline
2023-06-22
Tundra diversity, including plants, lichens and fungi, declined over a 15-year experiment in the Arctic due to warming temperatures mediated by the disappearance of sea ice, according to Eric Post and colleagues. However, the presence of large herbivores such as caribou and musk oxen slowed this decline, by affecting the plant understory with their different browsing behaviors, the researchers concluded. Their findings offer support for the idea that encouraging herbivore diversity in the tundra could temper some of the impacts of climate warming. Post et al. observed the interacting effects of warming temperatures, sea ice changes, tundra diversity and herbivore exclusion in ...
Hard and soft materials form a fatigue-resistant fan in the mussel’s hinge
2023-06-22
How does a mussel shell open and shut easily and without damage for hundreds of thousands of cycles during the bivalve’s lifetime? Such fatigue-resistant materials would be useful in electronics, aerospace and tissue engineering designs, where components need to operate repeatedly without failure. Xiang-Sen Meng and colleagues took a closer look at the hinge on the shell of the bivalve Cristaria plicata, and found that the answer lies in a combination of design and materials that resist brittle fracture over time. Microscopic observations by Meng et al. show that the hinge gets its ...
Laws restricting abortion have ethical, legal and practical impacts for research on people who may become pregnant
2023-06-22
In this Policy Forum, Jeremy Sugarman and colleagues describe the risks that increasingly limited access to abortion may pose to clinical research participants and staff, one year after the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Woman’s Health Organization. People who may become pregnant are already an understudied population in clinical research. The authors suggest that new laws restricting abortion access may lead to ethical, legal and practical problems that make the risk of conducting research with this population unreasonable ...
Are viruses keeping sea lice at bay in wild salmon?
2023-06-22
More than 30 previously unknown RNA viruses in sea lice have been identified by University of British Columbia (UBC) researchers. Sea lice are parasitic copepods (small crustaceans) found in many fresh and saltwater habitats, and have been implicated in the decline of wild salmon populations. The research sheds greater light on the types of viruses being carried by sea lice, and how the viruses and host are interacting.
“We found many more types of viruses than are known in sea lice or their distant relatives; the lice are mounting an immune defense response to many of these viruses indicating that they are replicating,” says UBC marine microbiologist Dr. Curtis Suttle, ...
The molecular control centre of our protein factories
2023-06-22
Based on genetic blueprints, individual amino acids are assembled into long amino acid chains, the proteins, in the protein factories of our cells, the ribosomes. Each newly formed protein starts with the amino acid methionine. This amino acid is often split off again during protein synthesis, as soon as the growing amino acid chain leaves the protein factory through the "ribosomal tunnel". In these cases, the excision of methionine is essential to ensure the subsequent function of the corresponding ...
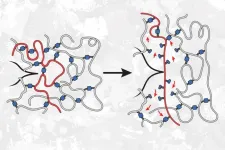
Surprise! Weaker bonds can make polymers stronger
2023-06-22
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- A team of chemists from MIT and Duke University has discovered a counterintuitive way to make polymers stronger: introduce a few weaker bonds into the material.
Working with a type of polymer known as polyacrylate elastomers, the researchers found that they could increase the materials’ resistance to tearing up to tenfold, simply by using a weaker type of crosslinker to join some of the polymer building blocks.
These rubber-like polymers are commonly used in car parts, and they are also often used as the “ink” for ...
The clue is in the glue - Nature’s secret for holding it together
2023-06-22
An obscure aquatic plant has helped to explain how plants avoid cracking up under the stresses and strains of growth.
The finding by researchers Dr Robert Kelly-Bellow and Karen Lee in the group of Professor Enrico Coen at the John Innes Centre, started with a curious observation in a dwarf mutant of the carnivorous plant Utricularia gibba.
The stems of this floating plant are filled with airspaces and this hollowness means that the vascular column inside the stem can buckle when under stress. This effect would not be apparent in most plants, which have solid stems.
The researchers saw that in a dwarf mutant the central column was wavy instead of straight. They hypothesised that ...
Generative AI models are encoding biases and negative stereotypes in their users
2023-06-22
The likes of ChatGPT, Google’s Bard and Midjourney can also help spread incorrect, nonsensical information
Marginalised groups are disproportionately affected
Children are at particular risk
In the space of a few months generative AI models, such as ChatGPT, Google’s Bard and Midjourney, have been adopted by more and more people in a variety of professional and personal ways. But growing research is underlining that they are encoding biases and negative stereotypes in their users, as well as mass generating and spreading seemingly accurate but nonsensical information. Worryingly, marginalised groups are disproportionately affected by the fabrication of this nonsensical information.
In ...
Bringing the power of "multiplex" imaging to clinical pathology
2023-06-22
June 22, 2023, NEW YORK – Researchers at the Ludwig Center at Harvard have developed a platform technology for imaging that enables integration of the methods of microscopic analysis long employed in pathology laboratories with the visualization of multiple molecular markers in individual cells that is now rapidly advancing in research labs. The latter capability, known as “multiplex” imaging, promises to revolutionize cancer diagnostics by exposing molecular traits associated with ...