(Press-News.org) A combination of radiotherapy followed by immunotherapy is a promising strategy for the treatment of oral malignant melanomas in dogs.
Melanomas are the most common oral cancers in dogs. It is highly metastatic and conventional chemotherapy does not increase survival time. Canine oral melanomas are similar to human melanomas; thus, research is being conducted into adapting treatments developed for human melanomas for dogs.
A particularly effective therapy for treating human melanomas is a combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors and radiotherapy. A team of researchers led by Professor Satoru Konnai at Hokkaido University has investigated the effects of this therapy in dogs. Their findings were published in the journal Cancers.
“One of the means that tumors employ to protect themselves is by inducing overexpression of molecules that suppress the immune response, such as PD-1 and PD-L1,” explained Konnai. “Immunotherapy that targets these molecules and blocks their function has a response rate of 14.3% for canine oral malignant melanoma (OMM). Studies in humans have shown that combining anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy with radiotherapy—where the radiation is focused on the tumor—increases survival in humans, and we wanted to examine if this was true in dogs as well.”
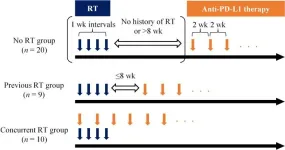
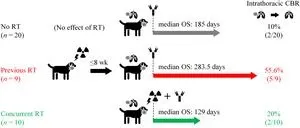
The team analyzed data from 39 canine patients with Stage IV pulmonary OMM treated with the anti-PD-L1 antibody c4G12 between March 2016 and September 2021. Of these, twenty had either never been treated with radiotherapy or had not received such treatment for at least 8 weeks; nine had received radiotherapy within 8 weeks prior to c4G12 treatment; and the remaining ten received c4G12 and radiotherapy concurrently.
The most important metric the team measured was the overall survival time, the duration between the first dose of c4G12 and death. “The group that had received radiotherapy prior to c4G12 had better overall survival compared to the group that received just c4G12,” Konnai elaborated. “Concurrent treatment had no benefits compared to prior radiotherapy. We also observed that there was no statistical difference between the three groups in terms of side effects from treatment.”
This study shows that sequential treatment of canine pulmonary OMM with radiotherapy followed by c4G12 is a promising antitumor strategy. Future work will need to examine the validity of these findings in larger sample sizes, and will also focus on pinning down the optimal protocol (combination of timing, dose and fractionation of radiotherapy) to increase overall survival.
END
Combination therapy effective against canine melanoma
2023-06-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Building the semiconductor workforce of the future
2023-06-23
The University of Utah is one of thirteen founding partner members of the Northwest University Semiconductor Network, a partnership with and created by Micron Technology, Inc. whose goal is to help develop the next generation of the United States’ semiconductor industry’s workforce.
Micron, one of the world’s largest semiconductor companies, made the announcement on Monday. In a press release the company stated the Northwest University Semiconductor Network will “drive foundational and emerging research to increase students’ ...
New rapid viral plaque detection system, aided by deep learning and holographic imaging, can help accelerate vaccine and drug development
2023-06-23
Findings
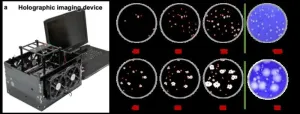
In a new paper published in Nature Biomedical Engineering, a team of scientists led by Professor Aydogan Ozcan from the Electrical and Computer Engineering Department at UCLA and an associate director of the California NanoSystems Institute, developed a rapid, stain-free, and automated viral plaque detection system enabled by holography and deep learning. This system incorporates a cost-effective and high-throughput holographic imaging device that continuously monitors the unstained virus-infected cells during their incubation process. At each imaging cycle, these ...
New ruling on care of dying will force some to live life “of machine-related suffering”
2023-06-23
The newly revised ruling on advance medical directives and withholding/withdrawing medical support for the dying in India will inevitably force some terminally ill patients to “live a life of machine-related suffering” and deprive them of their autonomy and dignity in death, suggest specialist doctors in a letter published online in the journal BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care.
While a progressive step, the 2023 ruling still has important shortcomings, they add.
In the absence of any specific legislation ...
Global diabetes cases to soar from 529 million to 1.3 billion by 2050
2023-06-23
***Embargo: 23.30 UK time / 18:30 ET / 15:30 PT Thursday, 22 June 2023***
SEATTLE, Wash. June 22, 2023 – More than half a billion people are living with diabetes worldwide, affecting men, women, and children of all ages in every country, and that number is projected to more than double to 1.3 billion people in the next 30 years, with every country seeing an increase, as published today in The Lancet.
The latest and most comprehensive calculations show the current global prevalence rate is 6.1%, making diabetes one of the top 10 leading causes of death and disability. At the super-region level, the ...
Surrey expert recognized on International Women in Engineering Day
2023-06-23
The Women’s Engineering Society has named the University of Surrey’s Dr Kelly Kousi as one of the finalists in its Top 50 Women in Engineering Awards (WE50) 2023: Safety and Security. The announcement coincides with International Women in Engineering Day 2023, a celebration of women in engineering.
Dr Kousi, a lecturer in the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, leads a research group of scientists and engineers who work on emission control, synthetic fuel production ...
Gloss is less effective camouflage in beetles compared to matte, according to latest study
2023-06-23
When combined with iridescent colouration, a matt target surface appearance confers greater survival benefits in beetles than a glossy surface, scientists at the University of Bristol have found.
The findings, published in Behavioural Ecology, suggest that iridescence provides camouflage independent of glossiness, which means that it is the colour of iridescent surfaces and its changeability, that is the most important aspect of iridescence in enabling camouflage.
Iridescence is a type of structural colouration that produces bright, vibrant hues. These are often angle-dependent, meaning the observed colour appears to ...
UW–Madison researchers reveal how key protein might help influenza A infect its hosts
2023-06-23
Influenza A is one of two influenza viruses that fuel costly annual flu seasons and is a near constant threat to humans and many other animals. It's also responsible for occasional pandemics that, like the one in 1918, leave millions dead and wreak havoc on health systems and wider society.
Influenza A was first identified as a health threat nearly a century ago, but only in the last decade have scientists identified one of the virus’s key proteins for infiltrating host cells and short-circuiting their defenses. Now, a team of researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison have taken a major step toward ...
CU professor leads study on discontinuing therapy for MS patients over 55
2023-06-23
AURORA, Colo. (June 22, 2023) – An article published today in the journal Lancet Neurology evaluates the risk of recurrence of active disease in older patients with multiple sclerosis after discontinuing disease-modifying therapies.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic illness, often presenting in young adulthood. Most commonly, at onset, individuals have acute attacks, or relapses, of intermittent new neurological symptoms such as vision changes, numbness, and weakness that may come and go, seemingly randomly, and then remit completely or incompletely. ...
Mystery of how leaf-cutting ants gauge leaf portion size revealed
2023-06-23
They might not be able to leap tall buildings with a single bound, but leaf-cutting ants are insect superheroes, capable of carrying leaf pieces up to six times their body mass to cultivate fungus in their borrows. But how do the charismatic creatures determine the size of the fragments they carve with their mandibles? Do they use their bodies as a simple ruler, or do they use information about the position of their bodies to adjust how far they cut, adapting to the thickness of a leaf while dismembering it? Knowing that the insects alter the trajectory of a cut when sculpting ®Parafilm of different thicknesses, Flavio ...
Ramón Barthelemy wins 2023 LGBTQ+ Educator of the Year
2023-06-22
Out to Innovate is proud to announce the winners of its 2023 recognition awards for lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ+) professionals in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM). Out to Innovate has recognized exemplary individuals with LGBTQ+ Educator, Engineer, and Scientist of the Year for over 15 years.
2023 LGBTQ+ Educator of the Year: Ramón S. Barthelemy, Ph.D
The LGBTQ+ Educator of the Year award recognizes an educator who has significantly impacted STEM students through teaching, ...