(Press-News.org) Have you ever wondered what the earliest ancestors of today’s dolphins looked like? Then look no further, meet Olympicetus thalassodon, a new species of early odontocete, or toothed whale, that swam along the North Pacific coastline around 28 million years ago. This new species is one of several that are helping us understand the early history and diversification of modern dolphins, porpoises and other toothed whales. The new species is described in a new study published in the open access journal PeerJ Life and Environment by Puerto Rican paleontologist Jorge Velez-Juarbe of the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County.
“Olympicetus thalassodon and its close relatives show a combination of features that truly sets them apart from any other group of toothed whales. Some of these characteristics, like the multi-cusped teeth, symmetric skulls, and forward position of the nostrils makes them look more like an intermediate between archaic whales and the dolphins we are more familiar with,” says Dr. Velez-Juarbe, Associate Curator of Marine Mammals at NHMLAC.
But Olympicetus thalassodon was not alone, the remains of two other closely related odontocetes were described in the same paper. The fossils were all collected from a geologic unit called the Pysht Formation, exposed along the coast of the Olympic Peninsula in Washington State and dated to between 26.5–30.5 million years.
The study further revealed that Olympicetus and its close kin belonged to a family called Simocetidae, a group so far known only from the North Pacific and one of the earliest diverging groups of toothed whales. Simocetids formed part of an unusual fauna represented by fossils found in the Pysht Formation and which included plotopterids (an extinct group of flightless, penguin-like birds), the bizarre desmostylians, early relatives of seals and walruses, and toothed baleen whales.
Differences in body size, teeth and other feeding-related structures suggest that simocetids showed different forms of prey acquisition and likely prey preferences. “The teeth of Olympicetus are truly weird, they are what we refer to as heterodont, meaning that they show differences along the toothrow”, notes Dr. Velez-Juarbe, “this stands out against the teeth of more advanced odontocetes whose teeth are simpler and tend to look nearly the same.”
However, other aspects of the biology of these early toothed whales remain to be elucidated, such as whether they could echolocate like their living relatives, or not. Some aspects of their skull can be related to the presence of echolocating-related structures, such as a melon. An earlier study had suggested that neonatal individuals could not hear ultrasonic sounds, so the next step would be to investigate the earbones of subadult and adult individuals to test whether this changed as they grew older.
END
A new species of early toothed whale
2023-06-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Yearly re-scanning not needed for common brain tumor detected in 1 in 10 people
2023-06-23
People with a common type of benign brain tumour detected in around 1 in 10 don’t require annual scans, a new national study has found.
The largest study of its kind has been published in the European Journal of Endocrinology and looks at clinical data on a type of tumour growth in the pituitary gland in the brain. The common growth, called a non-functioning pituitary microadenoma (NFPA), is less than 1cm across, is predicted to affect around 10% of the population and usually doesn’t cause any symptoms.
In the ...
Women with common heart rhythm disorder have faster cognitive decline than men
2023-06-23
Edinburgh, UK – 23 June 2023: Women with atrial fibrillation progress more rapidly to cognitive impairment and dementia than men with the heart rhythm condition, according to research presented today at ACNAP 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)1 and published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.
“Symptoms of atrial fibrillation in women are often ignored by healthcare providers or attributed to stress or anxiety so it can go undiagnosed for long period of time, while men are more likely to be diagnosed and ...
Race-neutral testing could have given access to life-saving lung transplants for more black patients
2023-06-23
June 21, 2023 – NEW YORK, NY— Race-neutral lung function interpretation could increase access to lung transplants for Black patients with respiratory disease, according to new research published in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society online ahead of print.
In “Race-Specific Interpretation of Spirometry: Impact on the Lung Allocation Score,” lead researcher J. Henry Brems, MD, MBE of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, and colleagues investigated how race-specific versus race-neutral equations alter the lung allocation score (LAS) and the priority for lung transplant across races. The lung allocation score determines ...
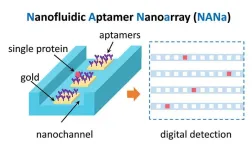
Bridging the gap for precision medicine: nanofluidic aptamer nanoarray measures individual proteins
2023-06-23
In the evolving world of precision medicine, the need for methods that can measure biomolecules with supreme accuracy and specificity is paramount. Recognizing this, Associate Professor Yan Xu of the Graduate School of Engineering at Osaka Metropolitan University and his international research team have made a great stride in this direction. They have developed an innovative nanofluidic device capable of capturing single proteins stochastically and detecting them digitally at their naturally high concentrations. This breakthrough could potentially ...
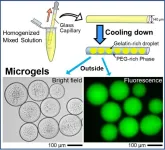
Smart yet simple – creating uniform DNA-encapsulating microgels that mimic a living cell
2023-06-23
The living cell harbors physiologically relevant components such as the genetic material (DNA) and proteins in a ‘self-organized’ setting. Understanding this process of self-assembly can reveal the underlying mechanism of self-organization of living matter. Water/oil (w/o) or water/water (w/w) droplets may be used as prototypes or “models” that mimic cells and can be used to study cellular self-assembly. These models also have major implications in the field of biomedical research. Although cell mimetics can be generated using complicated and high-cost equipment, the associated methods are costly, ...
Even a modest reduction in kidney function increases health risks in young adults
2023-06-23
A study of more than 8 million adults in Ontario, Canada suggests that even a modest loss of kidney function is associated with increased health risks. The study, published in The BMJ, could lead to better approaches to prevent chronic kidney disease and related conditions, particularly in younger adults.
“The dogma is that healthy, young adults don’t need to worry about kidney function unless it drops to around 50% of the normal level, but our research suggests that even a more modest 20-30% drop may have consequences and we may want to have earlier conversations ...
Forensic bitemark analysis for court trials is not supported by sufficient data and “is leading to wrongful convictions”
2023-06-23
The commonly-used evidence in trials, bitemark analysis, is not backed up by scientific research – an analysis of current literature, and 12 new studies, shows.
Published in the peer-reviewed Journal of the California Dental Association, the research suggests 26 people have been wrongfully convicted, and some even sentenced to death, from the use of this forensic science.
“The scientific community does not uphold the underlying premises that human teeth are unique and their unique features transfer to human skin,” states lead author Mary Bush, Associate Professor at the State University of New York in Buffalo, NY.
“We find bitemark transfer ...
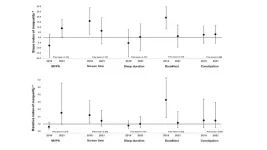
COVID-19's impact on socioeconomic inequality in health behaviors among Japanese adolescents
2023-06-23
Key Findings
This study is the first worldwide to investigate time trend in socioeconomic inequality in various health behaviors among adolescents before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The study found widening socioeconomic inequality among Japanese adolescents in achieving recommended physical activity levels before and during the pandemic, alongside narrowing inequality in breakfast intake. Specifically, despite no observed differences in physical activity by income in 2019, by 2021, adolescents from families with lower equivalent household incomes were less likely to engage in physical activity.
Research is needed to continue monitoring the impact these phenomena will have ...
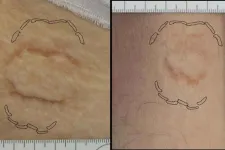
More exposure needed for cosmetic breast enhancement risks
2023-06-23
Complications after cosmetic breast augmentation are more common than other cosmetic plastic surgery yet many women who undergo such procedures are often in the dark about the associated risks say QUT researchers.
The authors of a new paper argue the need for more disclosure early (and in much simpler terms) of those risks and the high likelihood of revision surgery being required so when women give their consent, they have a greater understanding of what may happen.
“The Australian cosmetic surgery industry is worth billions but there are concerns inside the industry on potential issues surrounding whether patients ...
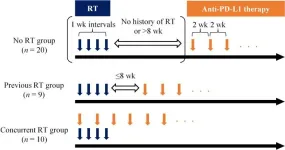
Combination therapy effective against canine melanoma
2023-06-23
A combination of radiotherapy followed by immunotherapy is a promising strategy for the treatment of oral malignant melanomas in dogs.
Melanomas are the most common oral cancers in dogs. It is highly metastatic and conventional chemotherapy does not increase survival time. Canine oral melanomas are similar to human melanomas; thus, research is being conducted into adapting treatments developed for human melanomas for dogs.
A particularly effective therapy for treating human melanomas is a combination of immune checkpoint inhibitors and radiotherapy. A team of researchers led by Professor Satoru Konnai at Hokkaido University has investigated ...