(Press-News.org) The 17 SDGs are the blueprint to achieve a better and more sustainable future for all. They address the global challenges we face, including climate change, environmental degradation, and inequality. The achievement of the SDGs depends on the ability to accurately measure progress towards meeting the associated targets based on timely, relevant, and reliable data. Citizen science offers an innovative approach to complement and enhance official statistics. Additionally, citizen science can help raise awareness, mobilize action, and therefore achieve transformative change.
The collection brings together academic papers that offer insights into the contributions of citizen science to the SDGs and other international frameworks. The call for abstracts for this collection attracted 40 submissions, from which 21 papers were reviewed and accepted for publication.
“The interest in contributing to this collection reflects the importance and popularity of Citizen Science,” notes Dilek Fraisl, a researcher in the Novel Data Ecosystems for Sustainability Research Group of the Advancing Systems Analysis Program, who is leading the collection. “We received high-quality submissions from a diverse community, including citizen science researchers and practitioners, National Statistical Offices (NSOs), and international organizations, from both the Global North and South.”
Core themes that run across the set of diverse papers include monitoring and data collection, and the transformative potential of citizen science. The collection also reflects on the progress achieved in the scientific literature and through practical implementation over the past few years.
An example of a paper showcasing the potential of citizen science for monitoring the SDGs is the paper by Proden et al (2023), to which Fraisl contributed together with Linda See, who is also associated with the Novel Data Ecosystems for Sustainability Research Group at IIASA.
“This paper focuses on the views and experiences of the official statistics community, including representatives from NSOs, on citizen science data, along with the opportunities and challenges that these data present,” explains See. “Despite the widely recognized value of citizen science for monitoring the SDGs, we have discovered a conspicuous lack of awareness with this approach among members of the official statistics community.”
The collection serves as a comprehensive compilation, gathering the latest research, findings, and practical recommendations from a diverse set of actors. Additionally, it explores the development of this emerging field of study, providing a roadmap for future research and proposing tangible actions. It is worth noting that, even after eight years of pursuing the SDGs, nearly half of the 92 environmental SDG indicators still lack data. The collection demonstrates that citizen science has vast untapped potential for driving progress towards achieving the SDGs and other international frameworks, highlighting its capacity for collaborative problem solving.
“With this collection, we call for stronger cooperation between all citizen science actors, and for the Citizen Science Global Partnership (CSGP), to help bridge the gap between the citizen science and official statistics communities and stakeholders. We urge the official statistics community to consider the inclusiveness and relevance of their practices and encourage funders to reassess their strategies, to go beyond short-term pilot studies, and to provide genuine financial support to citizen science initiatives focused on monitoring and achieving sustainable development,” concludes Fraisl.
Note: Citizen Science: Theory and Practice is an international peer-reviewed journal focused on impacts and effective practices associated with public participation in scientific endeavors in all disciplines and across the globe. This open-access journal is a publication of the Citizen Science Association.
References
Fraisl, D., See, L., Campbell, J., Andrianandrasana, H., Danielsen, F. (2023). Special Collection: Contributions of Citizen Science to the SDGs and International Development Frameworks. Citizen Science: Theory and Practice https://theoryandpractice.citizenscienceassociation.org/collections/contributions-of-citizen-science
Fraisl, D., See, L., Campbell, J., Danielsen, F., Andrianandrasana H. (2023). Editorial: The Contributions of Citizen Science to the United Nationals Sustainable Development Goals and Other International Agreements and Frameworks. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5334/cstp.643
Researcher contact
Dilek Fraisl
Researcher
Novel Data Ecosystems for Sustainability Research Group
Advancing Systems Analysis Program
Tel: +43 2236 807 398
fraisl@iiasa.ac.at
Linda See
Senior Researcher
Novel Data Ecosystems for Sustainability Research Group
Advancing Systems Analysis Program
Tel: +43 2236 807 423
see@iiasa.ac.at
Press Officer
Bettina Greenwell
IIASA Press Office
Tel: +43 2236 807 282
greenwell@iiasa.ac.at
About IIASA:
The International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) is an international scientific institute that conducts research into the critical issues of global environmental, economic, technological, and social change that we face in the twenty-first century. Our findings provide valuable options to policymakers to shape the future of our changing world. IIASA is independent and funded by prestigious research funding agencies in Africa, the Americas, Asia, and Europe.
END
LAS VEGAS – June 27, 2023 – Bariatric surgery, also called weight-loss or metabolic surgery, was associated with a 42% lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), including heart failure, heart attack, stroke, and atrial fibrillation in patients with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), according to a new study from Cleveland Clinic and presented here today at the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting. Researchers also report metabolic surgery ...
LAS VEGAS – June 27, 2023 – Patients with diabetes and a history of metabolic surgery had significantly fewer heart attacks, strokes, hospitalizations and death compared to matched patients who did not have the surgery, according to a new study* presented here today at the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting.
Patients reduced their chances of winding up in a hospital with a heart attack by more than 35%, a stroke by more than 25% and congestive heart failure by nearly ...
LAS VEGAS – June, 27, 2023 – Patient eligibility for bariatric surgery, also called weight-loss or metabolic surgery, has expanded over the last decade and its safety and effectiveness even further established in clinical studies and professional guidelines, but relatively few patients with a body mass index (BMI) below 35 actually get the surgery in any given year, according to new studies presented here at the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting.
In one study*, University of Southern California (USC) researchers found only 3.5% of the more than one million bariatric ...
LAS VEGAS – June 27, 2023 – More than half of patients with diabetes and a history of metabolic surgery (51%) experienced remission of their diabetes even if they did not achieve significant weight loss after surgery, according to a new study* presented here today at the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting.
Researchers from Mayo Clinic in Rochester, University of California San Francisco in Fresno, and Stony Brook University Medical Center in New York performed a multicenter retrospective study of patients with diabetes who underwent gastric ...
Copenhagen, Denmark: More women are having just one embryo transferred per cycle of fertility treatment to get pregnant, according to research presented at the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1].
Preliminary data from the ESHRE European IVF-monitoring Consortium (EIM) [2] shows that nearly three in five (57.6%) out of all in vitro fertilisation (IVF) and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) procedures in 2020 in Europe involved the transfer ...
Copenhagen, Denmark: A new artificial intelligence (AI) tool can identify sperm in severely infertile men in seconds compared to the hours it takes scientists, according to results presented today (Tuesday) at the 39th annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE) [1].
The study authors say the algorithm they have developed brings hope to men who want a biological child but have no sperm in their semen.
Currently, these patients must undergo a procedure where a portion of their testes is removed to help them become fathers. Embryologists extract sperm manually from this biopsy sample to fertilise the partner’s eggs ...
Recurrent bouts of systemic lupus erythematosus, marked by the body’s immune system attack of its own tissues, closely tracked with measureable upticks in growth in the gut of a certain species of bacteria.
New research from NYU Grossman School of Medicine shows that bacterial blooms of the gut bacterium Ruminococcus blautia gnavus occurred at the same time as disease flare-ups in five of 16 women with lupus of diverse racial backgrounds studied over a four-year period. Systemic lupus erythematosus involves damaging inflammation, especially in the kidneys, but also in joints, skin, and blood vessels. ...
EL PASO, Texas (June 27, 2023) – Step aside self-driving cars, self-driving boats are here — and they can do more than take you on a cruise.
Researchers at The University of Texas at El Paso have constructed a fully autonomous boat that can carry out bathymetric surveys — surveys of the depth and terrain of bodies of water like oceans, rivers and lakes. The team hopes the robotic boat can help simplify the survey process, which usually takes a crew of individuals to complete, as well as assist ...
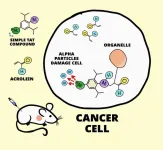
Researchers led by Katsunori Tanaka at the RIKEN Cluster for Pioneering Research (CPR) in Japan and Hiromitsu Haba at the RIKEN Nishina Center for Accelerator-Based Science (RNC) have developed a new technique that has the potential to generically treat several kinds of cancer, with fewer negative side effects than currently available methods. Published on June 27 in Chemical Science, the proof-of-concept study showed that tumors in mice grew almost three times less and survival was 100% after just one injection of a compound that is designed to emit small amounts of alpha radiation from the inside of cancer cells, thus killing them but sparing ...
In October, the excavation work for the superlative construction project began. What some consider an ideal ecological city, others call a promotional gimmick. Researchers from the Complexity Science Hub now show why The Line should not be a showcase for future cities.
"It's the embodiment of the dream to start from scratch and completely rethink a city," says Rafael Prieto-Curiel, who researches cities at the Complexity Science Hub. The Line is planned to be a city built from nothing in the desert. It is to consist of two gigantic, unbroken rows of skyscrapers, with living space in between. 170 kilometers long. 200 meters wide. 500 meters high, higher ...