(Press-News.org)
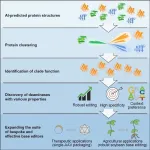
GAO Caixia's group from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has pioneered the use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted methods to discover novel deaminase proteins with unique functions through structural prediction and classification.
This approach has opened up a range of applications for the discovery and creation of desired plant genetic traits.
The results were published in Cell.
The discovery of new proteins and the exploitation of diverse engineered enzymes have contributed to the rapid advancement of biotechnology. Currently, efforts to mine novel proteins generally rely on amino acid sequences, which cannot provide a robust link between protein structural information and function.
Base editing is a new precision genome editing technology that has the potential to revolutionize molecular crop breeding by introducing desired traits into elite germplasm. The discovery of several deaminases has expanded the capability of cytosine base editing. Although traditional sequence-based efforts have identified many proteins for use as base editors, limitations in editing specific DNA sequences or species still remain.
Canonical efforts based solely on protein engineering and directed evolution have helped to diversify base editing properties, but challenges persist. By predicting the structures of proteins within the deaminase protein family using AlphaFold2, the researchers clustered and analyzed deaminases based on structural similarities. They identified five new deaminase clusters with cytidine deamination activity in the context of DNA base editors.
Using this approach, they further reclassified a group of cytidine deaminases, called SCP1.201 and previously thought to act on dsDNA, to perform deamination primarily on ssDNA. Through subsequent protein profiling and engineering efforts, they developed a suite of new DNA base editors with remarkable features. These deaminases exhibit properties such as higher efficiency, lower generation of off-target editing events, editing at different preferred sequence motifs, and much smaller size.
The researchers emphasized that the development of a suite of base editors would enable future tailor-made applications for various therapeutic or agricultural breeding efforts. They developed the smallest single-strand specific cytidine deaminase, enabling the first efficient cytosine base editor to be packaged in a single adeno-associated virus.
They also discovered a highly effective deaminase from this clade specifically for soybean plants, a globally significant agricultural crop that previously exhibited poor editing by cytosine base editors.
In general, the recent advent of protein structure prediction using growing genomic databases will greatly accelerate the development of new bioengineering tools.
This study highlights an approach that uses just the cytidine deaminase superfamily to develop a suite of new technologies and uncover new protein functions. These newly discovered deaminases, based on AI-assisted structural predictions, greatly expand the utility of base editors for therapeutic and agricultural applications.
In addition, this study will be of broad interest to the larger research community in phylogenetics, metagenomics, protein engineering and evolution, genome editing, and plant breeding.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, and the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China, among others.
END
Key points:
Scientists have been mystified as to why animals are missing in much of the fossil record;
Researchers have developed a new method to determine if animals really were absent during certain geological eras, or if they were present but too fragile to be preserved;
The findings establish a new maximum point at which animals first evolved on Earth.
A study led by the University of Oxford has brought us one step closer to solving a mystery that has puzzled naturalists since Charles Darwin: when did animals first appear in the history of Earth? The results have been published ...
About The Study: Neighborhood and household contexts were associated with white matter development in children, and findings suggested that obesity and cognitive performance were possible mediators in these associations. Future research on children’s brain health may benefit from considering these factors from multiple socioeconomic perspectives.
Authors: Scott Marek, Ph.D., and Tamara Hershey, Ph.D., of the Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
A Cretaceous origin for placental mammals, the group that includes humans, dogs and bats, has been revealed by in-depth analysis of the fossil record, showing they co-existed with dinosaurs for a short time before the dinosaurs went extinct.
The catastrophic destruction triggered by the asteroid hitting the Earth resulted in the death of all non-avian dinosaurs in an event termed the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) mass extinction. Debate has long raged among researchers over whether placental mammals were present alongside the dinosaurs before the mass extinction, ...
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis suggests that growing up in poverty may influence the wiring of a child’s brain.
The study, published June 27 in JAMA Network Open, indicates a link between both neighborhood and household poverty and the brain’s white matter tracts, which allow for communication between brain regions. White matter plays a critical role in helping the brain process information.
The findings stem from the largest long-term study of brain development and child health conducted in the U.S. — ...
WASHINGTON, D.C., June 27, 2023 – A trove of more than 160 eBooks in insect science is now available on the BioOne Digital Library, through an extension of BioOne’s partnership with the Entomological Society of America (ESA).
With the launch of the ESA eBook Collection, BioOne and ESA have partnered to source, digitize, and make fully searchable critical books from ESA’s catalog. Through this collaboration, BioOne and ESA share a commitment to make scientific research more accessible with the preservation of over 100 years ...
Cambridge scientists have created a stem cell-derived model of the human embryo in the lab by reprogramming human stem cells. The breakthrough could help research into genetic disorders and in understanding why and how pregnancies fail.
Published today in the journal Nature, this embryo model is an organised three-dimensional structure derived from pluripotent stem cells that replicate some developmental processes that occur in early human embryos.
Use of such models allows experimental modelling ...
(WASHINGTON, June 27, 2023) – Ask the average American what their blood type is, and you will likely receive a blank look. For most people, blood type only becomes an issue if they need a blood transfusion. Beginning in the earliest days of the COVID-19 pandemic, however, results from previous work published in Blood Advances suggested that people with blood group A (about a third of the US population) seemed to be more vulnerable to infection with the novel coronavirus, while those with blood group O (about 38% of the population) seemed to be somewhat less susceptible. Until now, however, ...
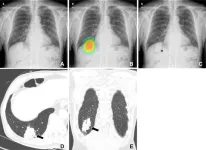
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Assistance from an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm with high diagnostic accuracy improved radiologist performance in detecting lung cancers on chest X-rays and increased human acceptance of AI suggestions, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
While AI-based image diagnosis has advanced rapidly in the medical field, the factors affecting radiologists’ diagnostic determinations in AI-assisted image reading remain underexplored.
Researchers at Seoul National University looked at how these factors might influence the detection of malignant lung nodules during ...
Orangutans can make two separate sounds simultaneously, much like songbirds or human beatboxers, according to a study led by the University of Warwick.
Academics say the findings provide clues around the evolution of human speech, as well as human beatboxing.
Scientists observed two populations of vocalising orangutans in Borneo and Sumatra across a total of 3800 hours and found primates within both groups used the same vocal phenomenon.
Dr Adriano Lameira, Associate Professor of Psychology at the University of Warwick said: “Humans use the lips, tongue, and jaw to make the unvoiced sounds ...
Orangutans can make two separate sounds simultaneously, much like songbirds or human beatboxers, according to a study. Adriano Lameira and Madeleine Hardus observed vocalizing orangutans in the wild. Humans use the lips, tongue, and jaw to make the unvoiced sounds of consonants, while activating the vocal folds in the larynx with exhaled air to make the voiced, open sounds of vowels. Orangutans are capable of producing both types of sounds—and both at once. For example, large male orangutans in Borneo will produce noises known as “chomps” in combination with “grumbles” in combative situations. Females in Sumatra produce “kiss squeaks” atop ...