Birds aren’t the only creatures who flock together
Virginia Tech researchers will work to increase access and inclusivity in ornithology as part of a collaborative effort funded by the National Science Foundation
2023-06-27
(Press-News.org)
Virginia Tech researchers are working to increase access and inclusivity in ornithology as part of a collaborative effort funded by the National Science Foundation.
The Leading Cultural Change Through Professional Societies of Biology program has awarded $500,000 to help researchers in the co-creation of affinity groups to facilitate diverse and inclusive ornithological societies. The program supports the design, implementation, and evaluation of projects that leverage the work of professional societies to advance diversity, equity, and inclusion in the biological sciences.
Goals of the project
Understand the climate of three ornithological societies with respect to diversity and culture in order to recommend changes and resources needed to foster more welcoming and supportive organizations.
Design a process for co-creating affinity groups, or “flocks” — identity-based groups created by and for members of these communities — that will facilitate “transformative resilience” for historically marginalized groups.
Why it matters
The landscape of science is changing: people from increasingly varied backgrounds, identities, cultures, and genders are pursuing careers in STEM fields. Support for this more diverse population of scientists needs to extend beyond “one size fits all” to better meet the today's needs. Expanding support and strengthening the sense of community for individuals and groups who have not been historically welcomed in a discipline can foster a deeper sense of belonging and meaningfully broaden representation within that field.
Professional scientific associations and societies can guide and shape the culture within their respective fields, cultivating supportive communities and providing relevant resources to ensure that all scientists have the professional and personal support they need to succeed on their chosen career paths. This initiative will use an internal culture assessment conducted by the American Ornithological Society in 2022 as its starting point and seeks to build a scientific field that fosters a greater sense of belonging among society members from historically excluded communities.
How Hokies are leading
Ashley Dayer of the College of Natural Resources and Environment is the co-principle investigator for the project. Dayer is an associate professor in the Department of Fish and Wildlife Conservation and an affiliated faculty member of the Center for Coastal Studies and the Global Change Center, both part of the Fralin Life Sciences Institute. As a conservation social scientist, her research program focuses on 1) involving private landowners in durable working lands conservation, 2) managing coastal lands for birds and people, and 3) engaging underserved, marginalized, and uninvolved audiences in conservation, community science, and wildlife management.
“As a social scientist focused on bird conservation, inclusive research, and diversifying the field of science, I’m excited about this opportunity to work with the societies to co-produce evidence-based affinity groups,” Dayer said. “I look forward to working with Nathan Thayer to conduct surveys, focus groups, and workshops with members of the societies and build these affinity groups from the bottom up to meet ornithologists’ needs.”
Nathan Thayer, a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Fish and Wildlife Conservation, will collaborate with Dayer.
The project also will provide educational and professional development opportunities for a postdoctoral scholar and undergraduate researchers in the university’s Multicultural Academic Opportunities Program.
Partners
University of Nebraska–Lincoln
American Ornithological Society
Association of Field Ornithologists
Wilson Ornithological Society
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-06-27
For many, neighborhoods that offer children access to better resources, less crime and less violence often result in better opportunities for healthier and more prosperous lives. Indeed, researchers studying the effects of moving to “opportunity neighborhoods” argue that very point and many policymakers have taken notice. However, so far, researchers have only accounted for the neighborhoods where children grow up, ignoring the long-term effects that parents’ childhood neighborhoods have on children’s adult economic well-being.
Expanding ...
2023-06-27
Chicago, Illinois (Embargoed until 2:15 p.m. CDT, Tuesday, June 27, 2023)—A novel PET perfusion radiotracer, 18F-flurpiridaz, can diagnose coronary artery disease (CAD) in obese patients with a higher sensitivity and specificity compared to 99mTc-SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI), according to research presented at the 2023 Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Annual Meeting. 18F-flurpiridaz PET MPI obtained images at a lower radiation dose than 99mTc-SPECT MPI and performed similarly in both obese and non-obese patients.
Obese individuals frequently have medical ...
2023-06-27
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) — the country’s largest interdisciplinary organization devoted to the field of aging — is proud to acknowledge the work of 20 outstanding individuals through its prestigious awards program.
GSA salutes outstanding research, recognizes distinguished leadership in teaching and service, and fosters new ideas through a host of awards. Nominated by their peers, the recipients’ achievements serve as milestones in the history and development of gerontology.
The award presentations will take place at GSA’s 2023 Annual Scientific Meeting, which will be held from November 8 to 12 in Tampa, Florida.
Society-Wide
Donald ...
2023-06-27
Fascination surrounding spaceflight and rockets is at an all-time high. Sites near launchpads draw crowds of spectators, eager to witness the flash of fire and feel the vibrations as the rumble of the motor becomes a roar. People, squinting and craning their necks to watch the rocket hurtle out of sight, aren’t likely thinking about the science behind the propulsion that makes it all possible.
What are the key elements that influence the combustion process? Are there advantages to utilizing solid propellants versus liquid? Simplicity, lower cost, and ease of storage and handling make solid fuel sources ideal for military and space ...
2023-06-27
A team led by scientists at The University of Texas at Austin has filled a major gap in the state’s fossil record – describing the first known Jurassic vertebrate fossils in Texas.
The weathered bone fragments are from the limbs and backbone of a plesiosaur, an extinct marine reptile that would have swum the shallow sea that covered what is now northeastern Mexico and far western Texas about 150 million years ago.
The bones were discovered in the Malone Mountains of West Texas during two fossil hunting missions led by Steve May, a research associate at UT Austin’s Jackson School of Geosciences Museum of Earth ...
2023-06-27
The Department of Energy (DOE) today signed an implementation agreement with Sweden to further promote and facilitate basic science research in energy and related fields.
The agreement reflects the United States and Sweden’s commitment to advancing scientific knowledge. It aims to foster joint research, shared facilities and exchanges of scientists in topics such as scientific computing, high energy physics, nuclear physics, fusion, basic energy sciences, and biological and environmental research.
Present at the ...
2023-06-27
FROM: James Urton
University of Washington
206-543-2580
jurton@uw.edu
(Note: researcher contact information at the end)
For immediate release
June 27, 2023
Researchers make a quantum computing leap with a magnetic twist
Quantum computing could revolutionize our world. For specific and crucial tasks, it promises to be exponentially faster than the zero-or-one binary technology that underlies today’s machines, from supercomputers in laboratories to smartphones in our pockets. But developing quantum computers hinges on building a stable network of qubits — or quantum ...
2023-06-27
A University of Texas at Arlington faculty member is pioneering a transformative technique aimed at enhancing the utilization of tungsten in additive manufacturing processes, specifically overcoming significant challenges presented by tungsten’s high melting point, intrinsic brittleness and high susceptibility to cracking.
Narges Shayesteh, assistant professor in the Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Department and director of the Innovative Additive Manufacturing Laboratory, has earned a five-year, $582,358 Faculty Early Career Award Development Program (CAREER) grant from the National Science Foundation to advance her research and education initiatives.
The ...
2023-06-27
DURHAM, N.C. – What people say they’ve eaten and what they’ve actually eaten are often two very different lists of foods. But a new technique using DNA barcoding to identify the plant matter in human feces may get at the truth, improving clinical trials, nutrition studies and more.
Building on earlier studies that attempted to compare DNA found in feces with reported diets, researchers in the lab of Lawrence David, an associate professor of molecular genetics and microbiology in the Duke ...
2023-06-27
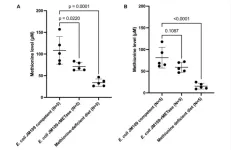
“This is the first report that showed the efficacy of methionine restriction to reverse old-age-induced obesity.”
BUFFALO, NY- June 27, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 11, entitled, “Old-age-induced obesity reversed by a methionine-deficient diet or oral administration of recombinant methioninase-producing Escherichia coli in C57BL/6 mice.”
Obesity increases with aging. Methionine restriction ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Birds aren’t the only creatures who flock together
Virginia Tech researchers will work to increase access and inclusivity in ornithology as part of a collaborative effort funded by the National Science Foundation