EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, JUNE 28, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a degenerative brain disease linked to repeated head impacts that athletes get from contact sports. However, the definitive diagnosis of the disease can be made only after death through an autopsy.
New research criteria for identifying who may be more likely to develop the disease proved accurate in distinguishing a group who would have changes in brain volume and cognitive skills years later, according to a study published in the June 28, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
The criteria define a condition called traumatic encephalopathy syndrome, where CTE is suspected based on cognitive impairment, behavior changes and other factors.
“These findings suggest that this new diagnosis of traumatic encephalopathy syndrome may be useful in professional sports such as boxing and mixed martial arts and may be helpful in predicting who may experience cognitive decline,” said study author Brooke D. Conway Kleven, PT, DPT, PhD, of the University of Nevada, Las Vegas School of Public Health.
The study involved a cohort of 130 active and retired professional fighters in boxing, martial arts and mixed martial arts as a part of Cleveland Clinic Lou Ruvo Center for Brain Health’s longitudinal Professional Athletes Brain Health Study. Participants had brain scans and took cognitive tests at the beginning of the study. A total of 52 people, or 40%, met the criteria for traumatic encephalopathy syndrome. Over 80% of those who met the criteria reported that boxing was their only form of fighting.
Then participants had annual brain scans and cognitive tests for up to six years.
The people who met the criteria for traumatic encephalopathy syndrome had greater declines in brain volume than those who did not meet the criteria. They also had a faster annual rate of decline in brain volume. For example, in the hippocampus area of the brain that plays a role in memory, those with traumatic encephalopathy syndrome had volumes 385 cubic millimeters (mm³) smaller than those without the syndrome. Those with the syndrome were losing volume at an average rate of 41 mm3 per year faster than those without the syndrome.
The people with traumatic encephalopathy syndrome had slower reaction times and lower scores on all the cognitive tests than those without the syndrome. These differences remained after researchers adjusted for age, education and other factors that could affect test scores.
“Our results suggest that the criteria for traumatic encephalopathy syndrome can identify people who are more likely to have worsening brain shrinkage and cognitive issues over time, while those who do not meet the criteria for the syndrome remain relatively stable,” Conway Kleven said. “Further research is needed to validate the accuracy of these criteria in detecting CTE.”
A limitation of the study was that athletes reported their own information, so it could not be verified for accuracy.
Learn more about brain health at BrainandLife.org, home of the American Academy of Neurology’s free patient and caregiver magazine focused on the intersection of neurologic disease and brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
When posting to social media channels about this research, we encourage you to use the hashtags #Neurology and #AANscience.
The American Academy of Neurology is the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals, with over 40,000 members. The AAN is dedicated to promoting the highest quality patient-centered neurologic care. A neurologist is a doctor with specialized training in diagnosing, treating and managing disorders of the brain and nervous system such as Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, migraine, multiple sclerosis, concussion, Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy.
For more information about the American Academy of Neurology, visit AAN.com or find us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn and YouTube.
END
Among professional fighters, new criteria can identify who may develop CTE
2023-06-28
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Blood test aids in predicting lung cancer mortality risk
2023-06-28
HOUSTON ― A blood-based test developed by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center can efficiently predict an individual’s risk of dying from lung cancer when combined with a personalized risk model.
According to new data published today in the Journal of Clinical Oncology, a blood-based four-protein panel (4MP), when combined with a lung cancer risk model (PLCOm2012), can better identify those at high risk of dying from lung cancer than the current U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) criteria.
These findings build upon previous MD Anderson research demonstrating the ...
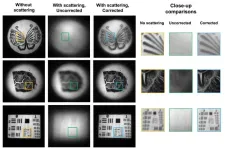
NeuWS camera answers ‘holy grail problem’ in optical imaging
2023-06-28
HOUSTON – (June 28, 2023) – Engineers from Rice University and the University of Maryland have created full-motion video technology that could potentially be used to make cameras that peer through fog, smoke, driving rain, murky water, skin, bone and other media that reflect scattered light and obscure objects from view.
“Imaging through scattering media is the ‘holy grail problem’ in optical imaging at this point,” said Rice’s Ashok Veeraraghavan, co-corresponding author of an open-access study published today in Science Advances. ...
Research reveals sources of CO2 from Aleutian-Alaska Arc volcanoes
2023-06-28
Scientists have wondered what happens to the organic and inorganic carbon that Earth’s Pacific Plate carries with it as it slides into the planet’s interior along the volcano-studded Ring of Fire.
A new study suggests a notable amount of such subducted carbon returns to the atmosphere rather than traveling deep into Earth’s mantle.
The finding can improve long-term projections about Earth’s climate.
A study led by a University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute scientist has shown that volcanoes of the Aleutian-Alaska Arc return more subducted slab carbon to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide than previously thought. This occurs ...
Cancerous brain tumor cells may be at ‘critical point’ between order and disorder, study suggests
2023-06-28
Glioblastoma is the most aggressive form of brain cancer. Despite decades of major efforts and clinical trials, the tumor’s survival rate has remained stagnant.
For years, scientists understood the cells in these tumors as static and relatively fixed. But recent studies have uncovered that glioblastomas contain active cells moving in complex patterns known as “oncostreams”, which determine how aggressively the tumors grow.
Research led by Michigan Medicine and the University of Michigan, published in Science Advances, suggests that glioblastoma ...
A dog’s breed can affect pain sensitivity, but not necessarily the way your vet may think
2023-06-28
Dog breeds differ in pain sensitivity, but these differences don’t always match up with the beliefs people – including veterinarians – hold about breed-specific pain sensitivity. The results appear in a new study from North Carolina State University, which also found that a dog’s temperament (specifically in the way they interact with strangers) may influence the way veterinarians view breed pain sensitivity.
“Veterinarians have a fairly strong consensus in their ratings of pain sensitivity ...
Controversy in Facebook posts linked to speed of spread among users
2023-06-28
A new analysis of nearly 60 million Facebook posts investigates how users’ interest in posts evolves over time, suggesting that the amount of controversy generated by a post is strongly linked to the speed with which it reaches a broad audience—regardless of the specific topic being discussed. Gabriele Etta of Sapienza Università di Roma, Italy, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on June 28, 2023.
This study adds to mounting research examining the influence ...
Kindness meditation helps people with depression recall positive memories, study finds
2023-06-28
A meditation that guides people to practice unconditional kindness to themselves and others helps people with a history of depression recall specific personal memories, according to a new study published this week in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Amanda Lathan and Barbara Dritschel of the University of St. Andrews, UK.
Autobiographic memory is essential to human functioning in areas such as self-concept, emotion regulation and problem-solving. Research has suggested that, among the cognitive processes disrupted by depression, the retrieval of autobiographical memory is often impaired.
In the new ...
Intranasal insulin treatment might boost cognition in people with mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer's Disease, according to meta-analysis of 29 studies across multiple disorders
2023-06-28
Intranasal insulin treatment might boost cognition in people with mild cognitive impairment or Alzheimer's Disease, according to meta-analysis of 29 studies across multiple disorders
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0286887
Article Title: Outcomes and clinical implications of intranasal insulin on cognition in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Author Countries: Canada
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
In animal assisted therapy, horses may aid the treatment of patients with substance use disorders by boosting mood and quality of life
2023-06-28
In animal assisted therapy, horses may aid the treatment of patients with substance use disorders by boosting mood and quality of life
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0286867
Article Title: An evaluation of the effect of equine-facilitated psychotherapy on patients with substance use disorders
Author Countries: Czech Republic
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Turning old maps into 3D digital models of lost neighborhoods
2023-06-28
Embargoed until 2 p.m. ET, Wednesday June 28, 2023
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Imagine strapping on a virtual reality headset and “walking” through a long-gone neighborhood in your city – seeing the streets and buildings as they appeared decades ago.
That’s a very real possibility now that researchers have developed a method to create 3D digital models of historic neighborhoods using machine learning and historic Sanborn Fire Insurance maps.
But the digital models will be more than just a novelty – they will give researchers a resource to conduct studies that would have been nearly ...