(Press-News.org) In light of climate change and the impending transition to clean energy, many long-standing programs to address energy insecurity need to be refreshed. A new paper published online in the journal Health Affairs provides growing documentation of the connections between energy insecurity and poor health. The paper, by Diana Hernandez, PhD, associate professor of sociomedical sciences at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, also offers an overview of current policy initiatives and discusses ways that current policies can be improved upon.
The average U.S. household allocates 3.1 percent of its income to energy expenses but for low-income households, this figure is upward of 8.1 percent, according to Hernandez. “This financial hardship often means that for low-income households there are fewer financial resources available for other basic needs such as housing, food, clothing, child care, medical expenses, digital access, and transportation.”
Disconnection of electric or gas service is considered the crisis point of energy insecurity and is disproportionately high among households below the poverty level and headed by persons of color. Nearly 15 percent of households received at least one disconnection notice during the prior twelve months, Earlier research by Hernandez was the first known prevalence study of shutoffs in the U.S.
Energy insecurity or the “inability to adequately meet basic household energy needs has profound implications for health and health equity,” says Dr. Hernandez, who is also managing director of the Energy Opportunity Lab’s Domestic Program at the Center for Global Energy Policy in Columbia’s School of International and Policy Affairs. “Energy insecurity encompasses much more than electricity, gas, or other power sources used for lighting, cooling, and heating. Instead, there are three primary dimensions of energy insecurity—the physical, economic, and coping which reflect financial hardship, housing quality issues and the adaptive strategies people use to manage unaffordable bills and subpar living conditions.”
Hernandez makes the following key points:
As of 2020 more than thirty million U.S. households were energy insecure.
Low-income households and those comprised of people of color are disproportionately affected by energy insecurity.
Structural racism, poor housing conditions, inflation, climate change, and the clean energy transition contribute to and exacerbate energy insecurity.
Energy insecurity adversely affects physical and mental health and can be fatal.
Policy and programmatic solutions exist to reduce and eliminate energy insecurity.
Home renters, rural dwellers, residents of houses built before 1980 with inadequate insulation, and people living in the Northeast and Southern regions were at greatest risk of experiencing energy insecurity as well as mobile home occupants and households with children compared to those with an elderly resident, according to Dr. Hernandez. “The latter is, in part, because of shutoff protections for seniors.”
“The somewhat good news is that there is hope for addressing energy insecurity now with recent world events including the COVID-19 pandemic, global social unrest and the war in Ukraine which may spur further investments in renewable energy,” noted Hernandez.
The policy brief was supported by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (grants 78975 and 84643); Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, and National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences Center for Environmental Health and Justice in Northern Manhattan (grant P30 ES009089).
Addendum: This energy insecurity dashboard: https://energyinsecuritydashboard.shinyapps.io/shinyappDeploy/ provides state level estimates on energy insecurity using government sponsored survey data (the Census' Household Pulse Survey, which has been tracking EI regularly throughout the pandemic; and the Residential Energy Consumption Survey, which was administered in 2020 and is the basis of the estimates reported in the policy brief and fact sheet.
Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health
Founded in 1922, the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health pursues an agenda of research, education, and service to address the critical and complex public health issues affecting New Yorkers, the nation and the world. The Columbia Mailman School is the fourth largest recipient of NIH grants among schools of public health. Its nearly 300 multi-disciplinary faculty members work in more than 100 countries around the world, addressing such issues as preventing infectious and chronic diseases, environmental health, maternal and child health, health policy, climate change and health, and public health preparedness. It is a leader in public health education with more than 1,300 graduate students from 55 nations pursuing a variety of master’s and doctoral degree programs. The Columbia Mailman School is also home to numerous world-renowned research centers, including ICAP and the Center for Infection and Immunity. For more information, please visit www.publichealth.columbia.edu
END
Energy insecurity is an underappreciated social and environmental determinant of health
The clean energy economy is out of reach for many households
2023-06-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Current developments in nutrition debuts strong with its first impact factor
2023-06-29
Rockville, MD – The latest journal impact factors and rankings reflect the high-quality research that is published each year by the American Society for Nutrition (ASN).
Scopus recently ranked Advances in Nutrition the number one journal in the Nutrition and Dietetics field. The Society’s newest journal, Current Developments in Nutrition, surpassed expectations with an excellent inaugural impact factor of 4.8 confirming its promising future.
“I am delighted to receive such a superb first impact factor,” stated Jack Odle, PhD, William Neal Reynolds Distinguished Professor at North Carolina State University and Editor-in-Chief of Current ...
CHEST releases clinical practice guideline on antithrombotic therapy in arterial thrombosis and thromboembolism in COVID-19
2023-06-29
Glenview, Illinois – The American College of Chest Physicians® (CHEST) recently released a new clinical guideline on antithrombotic therapy in arterial thrombosis andthromboembolism in COVID-19. Published in the journal CHEST®, the guideline contains 11 evidence-based recommendations to improve risk-evaluation and to assist in determining the course of treatment.
While there are guidelines for the management of COVID-19-related coagulopathy for venous thromboembolism (VTE), a recent large cohort study showed ...
UTHSC College of Pharmacy rises to No. 6 in research funding from National Institutes of Health
2023-06-29
The College of Pharmacy at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center is now ranked No. 6 in annual research funding from the National Institutes of Health, according to a new listing published by the American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy of its approximately 140 member institutions.
“The ranking of No. 6 in NIH funding for federal fiscal year 2022 is external validation for the UTHSC College of Pharmacy’s standing as one of the leading institutions in research among the 142 U.S. pharmacy schools,” said Bernd Meibohm, ...
New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks
2023-06-29
WASHINGTON — Researchers report a new single-photon Raman lidar system that operates underwater and can remotely distinguish various substances. They also show that the new system can detect the thickness of the oil underwater up to 12 m away, which could be useful for detecting oil spills.
“Differentiating substances in water and detecting their distribution characteristics in the ocean are of great significance for marine monitoring and scientific research,” said research team leader Mingjia Shangguan from Xiamen University in China. “For instance, the remote sensing of underwater oil that we ...
Faster, safer target prep
2023-06-29
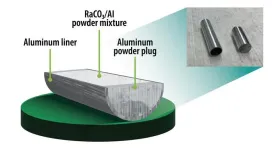
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have developed a method to simplify one step of radioisotope production — and it’s faster and safer.
ORNL produces several radionuclides from irradiated radium-226 targets, including actinium-227 and thorium-228, both used in cancer treatments. Continuously improving isotopes for human health is one of the lab’s missions.
Currently, it takes workers two weeks to prepare radium-226 targets for irradiation in the High Flux Isotope Reactor. The targets are exposed to radiation throughout the process, which involves pressing radium carbonate aluminum composite into 10 pellets — one each day — and sealing ...
Health care utilization following interventions to improve social well-being
2023-06-29
About The Study: This systematic review and meta-analysis including 41 studies and 7,800 participants found that psychosocial interventions were associated with decreased health care use in most health services and increased use of outpatient care. The greatest health care decrease was among caregivers and individuals with mental illnesses and in interventions delivered 1-on-1 by health professionals.
Authors: Neta HaGani, M.S.W., of the University of Sydney in Sydney, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Transferring data with many colors of light simultaneously
2023-06-29
New York, NY—June 29, 2023—The data centers and high-performance computers that run artificial intelligence programs, such as large language models, aren’t limited by the sheer computational power of their individual nodes. It’s another problem — the amount of data they can transfer among the nodes — that underlies the “bandwidth bottleneck” that currently limits the performance and scaling of these systems.
The nodes in these systems can be separated by more than one kilometer. Since metal wires dissipate electrical signals as heat when transferring data at high speeds, these systems transfer data via fiber-optic ...
An early predictor of cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease
2023-06-29
Have you ever felt the strong sensation that someone is behind you, so intense that you turn around, only to see that no-one is there? This is a 'presence hallucination’. Presence hallucinations are particularly frequent but underreported in patients with Parkinson’s disease and may appear early on in the course of the disease. They are sometimes ignored by the patient, by clinicians, or brushed off as a simple side-effect of medication.
Now, EPFL scientists have found that patients recently diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease and who have early hallucinations are ...
Cracking the tubulin code
2023-06-29
Tubulin is a protein that plays a crucial role in the structure and function of cells. It is the main component of microtubules, which are long, hollow fibers that provide structural support, help the cell divide, give it its shape, and act as tracks for moving molecular cargo around inside the cell.
There are two types of tubulin: alpha-tubulin and beta-tubulin. Together, they form dimeric (two-part) building blocks, spontaneously assembling into microtubules that undergo further continuous cycles of assembly and disassembly.
The tubulin code
To fine-tune microtubules, the dimers undergo various post-translational modifications (PTMs), which are chemical modifications that occur ...
Amander T. Clark takes on new role as President of the ISSCR
2023-06-29
Skokie, IL – The ISSCR is pleased to announce Amander T. Clark, PhD, Professor of Molecular, Cell and Developmental Biology, University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), USA, as its President. Dr. Clark’s one-year term of office leading the global society begins 1 July 2023.
“I will work to ensure that the society continues to defend stem cell science and the researchers working to transform lives,” Dr. Clark said at the ISSCR 2023 Annual Meeting in Boston this month. “We will expand our engagement with the public ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] Energy insecurity is an underappreciated social and environmental determinant of healthThe clean energy economy is out of reach for many households