(Press-News.org) Protein aggregates accumulate during aging and are linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease. A new study by the Nyström lab at Gothenburg University, in collaboration with the Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing in Germany, describes a novel, engineered approach that makes protein aggregates amenable to spatial manipulations in both budding yeast and human cells.
Many neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease are associated with the aggregation of misfolded proteins but whether or not these aggregates contribute to these diseases is not clear.
The research group of Professor Thomas Nyström from Gothenburg University was able to export such protein aggregates from cells in an engineered manner, which was published in the journal Nature Communications. The system was first developed in the widely-used model organism, budding yeast, but was extended also for use in human cells.
Free of protein aggregates
The authors achieved this synthetic cellular export system by fusing an aggregate-binding protein to a daughter-cell-targeting factor such that when the daughter cell is pinched off, the mother cell is free of protein aggregates. This approach was effective in dealing with endogenous, age-associated protein aggregates, as well as with mutant Huntingtin aggregates associated with the Huntington’s disease.
Using this daughter targeting system, they showed that the export of mutant Huntingtin protected yeast mother cells from cell death suggesting that large Huntingtin aggregates may be highly toxic and contribute to the disease, a trait that has been widely debated.
Potential future therapy
“To our knowledge this is the first demonstration that protein aggregates can be exported from cells in a controlled, engineered manner. Other kinds of cellular damage might be also exported from cells with adapted versions of our targeting system”, says Dr. Arthur Fischbach, postdoc and the lead author of the study.
“Although we currently lack supporting data, there is a possibility that the ATS concept could be employed in the future as a potential novel therapeutic approach for neurodegenerative diseases or at least for gaining a better understanding of them. Given the urgency, there is a strong demand for innovative therapies in this area”, he concludes.
END
Engineered approach to remove protein aggregates from cells
2023-06-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
BGI Genomics leads in industry to obtain BSI ISO 37301 Compliance Management System Certification
2023-06-30
As businesses become increasingly global, changes are also taking place at an extraordinary pace. Compliance is critical for large economies, industry regulations, and enterprise operations.
BGI Genomics prioritizes compliance management and strictly follow laws, regulations, and international practices while conducting business globally. BGI Genomics recently completed the rigorous evaluation of BSI, a major worldwide standard, testing, and certification authority. It was awarded the GB/T 35770-2022/ISO 37301:2021 Compliance Management System accreditation, making it the first enterprise in the industry to do so. ...
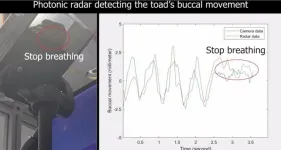
The device that can remotely and accurately monitor breathing: as tested on cane toads
2023-06-30
Constant monitoring of vital health signs is needed in a variety of clinical environments such as intensive care units, for patients with critical health conditions, health monitoring in aged care facilities and prisons, or in safety monitoring situations where drowsiness can cause accidents.
This is now mostly achieved via wired or invasive contact systems. However, these are either inconvenient or, for patients with burns or for infants with insufficient skin area, are unsuitable.
Scientists at the University of Sydney Nano Institute and the NSW Smart Sensing ...
Rising monkey and pig populations pose human disease risk
2023-06-30
Exploding populations of wild pigs and macaque monkeys in Southeast Asia are threatening native forests and disease outbreaks in livestock and people, according to research led by The University of Queensland.
Dr Matthew Luskin, from UQ’s School of the Environment, and his team collated and analysed species population data from across the region, some of it collected with a network of cameras.
“Macaques and wild pigs are taking over Southeast Asia’s disturbed forests,” Dr Luskin said.
“Humans are largely to blame for this by altering forests with logging ...
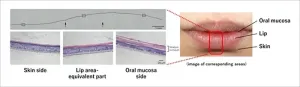
KOSÉ and Niigata University develop a three-dimensional epithelial model that reproduces the human lip area
2023-06-30
Niigata, Japan - KOSÉ Corporation (Headquarters: Chuo-ku, Tokyo; President: Kazutoshi Kobayashi) has developed in collaborative research with Professor Kenji Izumi and his colleagues at Niigata University Graduate School of Medical and Dental Sciences (Faculty of Dentistry) a three-dimensional epithelial model that reproduces the human lip area from the oral mucosa to the lips and surrounding skin, using cell culture.
The lips are one of the most important elements that determine the impressions of the face, and they are also an area where many people suffer from problems, ...
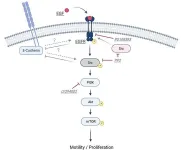
Revolutionizing regenerative medicine: Unlocking the healing power of oral keratinocytes
2023-06-30
Niigata, Japan—Scientists have made significant progress in understanding the signals involved in regulating oral keratinocyte cell motility and proliferative capacity, offering new insights into potential pharmacological manipulation for regenerative medicine. A recent study, published in FEBS Open Bio, elucidated the role of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) and its downstream signaling cascade in controlling the behavior of oral keratinocytes.
Oral keratinocytes, which play a crucial role in the formation of the oral mucosa epithelial cell sheet, have long been enigmatic in terms of their signaling ...
Long COVID is not a single condition, study finds
2023-06-30
Long COVID is not a single condition, and should not be treated as such, according to new data collected in nationwide study released May 31 in the Open Forum of Infectious Diseases.
The study looked at persistent symptoms experienced by patients with COVID-19 both at three- and six-month intervals. In all, 5,963 patients participated in the study, with 4,504 of the participants testing positive for COVID-19 and 1,459 testing negative. Many of the participants, 2,000 in all, came from King County through the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The four major symptom categories for people who tested positive for COVID-19 included:
Minimal ...
Loneliness linked with elevated risk of cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes
2023-06-30
Sophia Antipolis, 30 June 2023: Loneliness is a bigger risk factor for heart disease in patients with diabetes than diet, exercise, smoking and depression, according to research published today in European Heart Journal, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“The quality of social contact appears to be more important for heart health in people with diabetes than the number of engagements,” said study author Professor Lu Qi of Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, New Orleans, US. “We should not downplay the important of loneliness ...
TGI-led research finds climate change, increasing population put Kenya at risk of famine
2023-06-30
ST. LOUIS - Research published in Outlook on Agriculture has shown that the population relative to available climate-suitable areas in Kenya has increased, posing a threat to the country’s economy and food security.
The study, “Spatial changes to climate suitability and availability of agropastoral farming systems across Kenya (1980-2020),” was published online on May 29.
The research team analyzed Kenya’s farming systems and climate zones between 1980-2020. Over that time, the population ...
Status of biobased production of succinic acid and derivatives
2023-06-30
The current status and future perspectives on the successful industrialization of biobased succinic acid are discussed in a comprehensive review article in the peer-reviewed journal Industrial Biotechnology. Click here to read the article now.
Succinic acid is one of the most important platform chemicals, with applications as a pharmaceutical ingredient, food additive, precursor of various chemicals, and raw material for biobased polymers. There is increasing demand for the sustainable production of succinic acid and its derivatives.
Sang Yup Lee, from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), and coauthors, review ...
Nearly half of tuberculosis cases in prisons worldwide go undetected
2023-06-30
In the first global assessment of TB among incarcerated people, a new study found consistently high TB case rates and low case detection in prisons, suggesting the need for health organizations to increase efforts to reduce the spread of TB among this high-risk population.
In 2019, incarcerated people across the globe developed tuberculosis (TB) at nearly 10 times the rate of people in the general population, according to a new study led by Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH).
Published in The Lancet Public Health, the study found that 125,105 of the 11 million people incarcerated worldwide developed tuberculosis in 2019, ...