Planting seeds: FSU researchers dig into how chemical gardens grow
2023-07-03
(Press-News.org)
EMBARGOED UNTIL JULY 3 AT 3 P.M. ET
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
CONTACT: Kathleen Haughney, University Communications
(850) 644-1489; khaughney@fsu.edu
July 2023
PLANTING SEEDS: FSU RESEARCHERS DIG INTO HOW CHEMICAL GARDENS GROW
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — Since the mid-1600s, chemists have been fascinated with brightly colored, coral-like structures that form by mixing metal salts in a small bottle.
Until now, researchers have been unable to model how these deceptively simple tubular structures —called chemical gardens — work and the patterns and rules that govern their formation.
In a paper published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Florida State University researchers lay out a model that explains how these structures grow upward, form different shapes and how they go from a flexible, self-healing material to a more brittle one.
“In a materials context, it’s very interesting,” said FSU Professor of Chemistry and Biochemistry Oliver Steinbock. “They don’t grow like crystals. A crystal has nice sharp corners and grows atom layer by atom layer. And when a hole occurs in a chemical garden, it’s self-healing. These are really early steps in learning how to make materials that can reconfigure and repair themselves.”
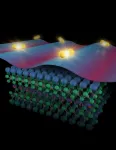
Typically, chemical gardens form when metal salt particles are put in a silicate solution. The dissolving salt reacts with the solution to create a semipermeable membrane that ejects upward in the solution, creating a biological-looking structure, similar to coral.
Scientists observed chemical gardens for the first time in 1646 and for years have been fascinated with their interesting formations. The chemistry is related to the formation of hydrothermal vents and the corrosion of steel surfaces where insoluble tubes can form.
“People realized these were peculiar things,” Steinbock said. “They have a very long history in chemistry. It became more like a demonstration experiment, but in the past 10-20 years, scientists became interested in them again.”
Inspiration for the mathematical model developed by Steinbock, along with postdoctoral researcher Bruno Batista and graduate student Amari Morris, came from experiments that steadily injected a salt solution into a larger volume of silicate solution between two horizontal plates. These showed distinct growth modes and that the material starts off as stretchy, but as it ages, the material becomes more rigid and tends to break.
The confinement between two layers allowed the researchers to simulate a number of different shape patterns, some looking like flowers, hair, spirals and worms.
In their model, the researchers described how these patterns emerge over the course of the chemical garden’s development. Salt solutions can vary a lot in chemical makeup, but their model explains the universality in formation.
For example, the patterns can consist of loose particles, folded membranes, or self-extending filaments. The model also validated observations that fresh membranes expand in response to microbreaches, demonstrating the material’s self-healing capabilities.
“The good thing we got is we got into the essence of what is needed to describe the shape and growth of chemical gardens,” Batista said.
To read the full paper, visit pnas.org. This work was supported by NASA and the National Science Foundation.
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-03
Gene expression within the apicoplast, an organelle in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum, is regulated by melatonin (the circadian signaling hormone) in host blood, and intrinsic parasite cues, via a factor called ApSigma, as identified by a recent study aided by Tokyo Tech’s World Research Hub Initiative. The regulatory system highlighted in this study might be a future target for malaria treatment.
Malaria is one of the biggest public health risks, with around 240 million people from across the globe contracting it every year. However, this life-threatening disease is ...
2023-07-03
Regular physical exercise, such as resistance training, can prevent Alzheimer’s disease, or at least delay the appearance of symptoms, and serves as a simple and affordable therapy for Alzheimer’s patients. This is the conclusion of an article published in Frontiers in Neuroscience by Brazilian researchers affiliated with the Federal University of São Paulo (UNIFESP) and the University of São Paulo (USP).
Although older people and dementia patients are unlikely to be able to do long daily runs or perform other high-intensity aerobic exercises, these activities are the focus for most scientific studies on ...
2023-07-03
UPTON, NY—In the field of superconductivity—the phenomenon in which electrons can flow through a material with essentially zero resistance—the “holy grail” of discovery is a superconductor that can perform under everyday temperatures and pressures. Such a material could revolutionize modern life. But currently, even the “high-temperature” (high-Tc) superconductors that have been discovered must be kept very cold to function—too cold for most applications.
Scientists still have much to learn before room-temperature ...
2023-07-03
Artificial Intelligence, Space Food & Polyphenols: 2 Ambitious Projects
Polyphenols Applications 2023 World Congress, which will be held on September 28-29 in Malta, will support 2 projects in order to advance in the polyphenols innovations:
1- Polyphenols & Artificial Intelligence:
This project aims to leverage artificial intelligence techniques to enhance the understanding and utilization of polyphenols. You will utilize machine-learning algorithms to analyze large datasets on polyphenols, including their chemical structures, bioactivities, and health effects. ...
2023-07-03
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- While formula-feeding babies is a safe and convenient option, research studies have shown natural breastfeeding is linked to numerous health benefits for both mother and child. For mothers, breastfeeding can improve recovery after giving birth and lower the risks of cancer. For babies, the nutrients strengthen their immune system and help lower their risk of developing obesity and diabetes.
Now, a new study at the University of Missouri Sinclair School of Nursing is helping researchers better understand the factors that influence moms, particularly in rural areas where breastfeeding is less common, when deciding how to feed their babies.
In the study, ...
2023-07-03
People with dementia still have the ability to learn new things despite their illness. This is the conclusion of a doctoral thesis recently presented at Linköping University, Sweden. Its findings debunk the general belief that people with dementia are empty shells, according to Elias Ingebrand, who conducted the study.
Elias Ingebrand let ten dementia sufferers, eight of whom lived in care facilities, try using computer tablets for the first time in their lives. A staff member or a loved one was there for support, but the only instruction given to participants ...
2023-07-03
Summary
An El Niño event has officially begun. The climate phenomenon, which originates in the tropical Pacific and occurs in intervals of a few years will shape weather across the planet for the next year or more and give rise to various climatic extremes. El Niño-like conditions can also occur on longer time scales of decades or centuries. This has been shown to have occurred in the recent past by an international research team led by Ana Prohaska of the University of Copenhagen and Dirk Sachse of the German Research Centre for Geosciences (GFZ). Their analysis of biomarkers – organic molecules or molecular fossils from vascular plants – in ...
2023-07-03
Nadine Kabbani, Associate Professor, School of Systems Biology, is set to receive $100,000 from Charles Morgan for: "Mitochondrial Targeting and Regulation." This funding will begin in July 2023 and will end in July 2025.
Regarding the importance of the project, Kabbani said, "Studies suggest an important role for mitochondrial regulation in many human diseases. The targeting of mitochondrial processes has thus emerged as an important strategy in drug design and biomarker discovery. In addition, mitochondrial responses are especially useful in toxicity testing for medical and environmental applications. The goal of this project is to identify mitochondrial ...
2023-07-03
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – July 03, 2023) Gene therapy that alters hemoglobin genes may be an answer to curing sickle cell disease (SCD) and beta thalassemia. These two common life-threatening anemias afflict millions of individuals across the globe. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard used a next-generation genome editing technology, adenosine base editing, to restart fetal hemoglobin expression in SCD patient cells. The approach raised the expression of fetal hemoglobin to higher, more stable, and more uniform levels than other genome editing technologies that use ...
2023-07-03
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL JULY 3, 2023 AT NOON ET) – The median length of survival after diagnosis of glioblastoma is 14 months, but some of these brain tumors are more aggressive and resistant to treatment than others, and a new study from Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine suggests reactivation of an ancient retrovirus may be at least partly to blame.
“Our lab found that an evolutionary dormant retrovirus from 6 million years ago – HML-2, a subtype of HERV-K– contributes to brain tumor formation. We demonstrated for the first time that this virus, when reactivated, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Planting seeds: FSU researchers dig into how chemical gardens grow