(Press-News.org) Rising global temperatures are making it harder for birds to know when it’s spring and time to breed according to a new study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
A large collaboration led by scientists at UCLA and Michigan State University has found that birds produce fewer young if they start breeding too early or late in the season. With climate change resulting in earlier springlike weather, the researchers report, birds have been unable to keep pace.
And, the authors write, the mismatch between the start of spring and birds’ readiness to reproduce is likely to become worse as the world warms, which could have large-scale consequences that would be catastrophic for many bird populations. Birds’ breeding seasons begin whenever the first green plants and flowers appear, which is happening earlier and earlier as the climate warms.
“By the end of the 21st century, spring is likely to arrive about 25 days earlier, with birds breeding only about 6.75 days earlier,” said the study’s first author, Casey Youngflesh, who led the research as a postdoctoral researcher at UCLA and is now a postdoctoral fellow at Michigan State. “Our results suggest that breeding productivity may decrease about 12% for the average songbird species.”
The authors stress that conservation strategies should address bird species’ responses to climate-driven shifts.
Determining if the earlier springs will pose problems for migratory birds has been a major goal of biologists for decades.
“For nearly 30 years, scientists have hypothesized that animals could become mismatched from plants as springs begin earlier,” said Morgan Tingley, a UCLA associate professor of ecology and evolutionary biology and the study’s senior author. “While there have been a few very good case studies of this phenomenon, it has remained a major mystery whether advancing springs will pose a general problem for the majority of species.”
When it comes to raising their young, timing matters for birds. If they breed too early or too late, harsh weather could harm their eggs or newborns. But timing relative to food sources matters too: If birds are looking for food before or after its natural availability, they might not have the resources to keep their young alive.
“Critically, we found evidence for impacts on bird reproduction of both the absolute and the relative timing of birds,” Tingley said.
Using data from a large-scale collaborative bird banding program run by the Institute for Bird Populations, the researchers calculated the timing of breeding and the number of young produced for 41 migratory and resident bird species at 179 sites near forested areas throughout North America between 2001 and 2018.
Then, the authors used satellite imaging to determine when vegetation emerged around each site. They found that each species had an optimal time to breed, and that the number of young produced decreased when spring arrived very early, or when breeding occurred early or late relative to when plants emerged.
While the majority of birds were adversely affected by variations in the start of spring, several species — the northern cardinal, Bewick’s wren and wrentit among them — countered the trend, demonstrating improved breeding productivity when spring began earlier. Those species are mostly non-migratory species that can respond more quickly to the emergence of spring plants that signal the start of the breeding season.
By breeding earlier and without the time constraints imposed by migration, the study noted, non-migratory species may also be able to reproduce more than once per season.
But those species were the exceptions to the rule. Even most non-migratory species couldn’t keep up with earlier spring arrivals. Overall, for every four days earlier that leaves appeared on trees, species bred only about one day earlier.
For migratory species, that discrepancy means that the time between when they arrive at their breeding sites and breeding itself is likely to get shorter as springlike conditions begin earlier. Birds need time to establish territories and prepare physiologically for egg-laying and rearing their young, so that change could cause even greater disturbances to reproduction.
“North America has lost nearly a third of its bird populations since the 1970s,” Tingley said. “While our study demonstrates that the worst impacts of timing mismatch likely won’t occur for several decades yet, we need to focus now on concrete strategies to boost bird populations before climate change takes its toll.”
The study received primary funding from the National Science Foundation and was supported by researchers from the University of Florida; Pennsylvania State University; University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill; and the Institute for Bird Populations.
END
Birds raise fewer young when spring arrives earlier in a warming world
Study led by UCLA, Michigan State scientists finds conservation strategies should address avian responses to climate-driven shifts
2023-07-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Chemists discover why photosynthetic light-harvesting is so efficient
2023-07-03
When photosynthetic cells absorb light from the sun, packets of energy called photons leap between a series of light-harvesting proteins until they reach the photosynthetic reaction center. There, cells convert the energy into electrons, which eventually power the production of sugar molecules.
This transfer of energy through the light-harvesting complex occurs with extremely high efficiency: Nearly every photon of light absorbed generates an electron, a phenomenon known as near-unity quantum efficiency.
A new study from MIT chemists offers a potential explanation for how proteins of the light-harvesting complex, also called the antenna, achieve that ...
Planting seeds: FSU researchers dig into how chemical gardens grow
2023-07-03
EMBARGOED UNTIL JULY 3 AT 3 P.M. ET
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
CONTACT: Kathleen Haughney, University Communications
(850) 644-1489; khaughney@fsu.edu
July 2023
PLANTING SEEDS: FSU RESEARCHERS DIG INTO HOW CHEMICAL GARDENS GROW
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. — Since the mid-1600s, chemists have been fascinated with brightly colored, coral-like structures that form by mixing metal salts in a small bottle.
Until now, researchers have been unable to model how these deceptively simple tubular structures —called chemical gardens — work and the patterns and rules that ...
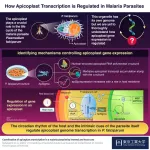
Understanding the regulation of apicoplast gene expression in the malaria parasite
2023-07-03
Gene expression within the apicoplast, an organelle in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum, is regulated by melatonin (the circadian signaling hormone) in host blood, and intrinsic parasite cues, via a factor called ApSigma, as identified by a recent study aided by Tokyo Tech’s World Research Hub Initiative. The regulatory system highlighted in this study might be a future target for malaria treatment.
Malaria is one of the biggest public health risks, with around 240 million people from across the globe contracting it every year. However, this life-threatening disease is ...
Study suggests resistance training can prevent or delay Alzheimer’s disease
2023-07-03
Regular physical exercise, such as resistance training, can prevent Alzheimer’s disease, or at least delay the appearance of symptoms, and serves as a simple and affordable therapy for Alzheimer’s patients. This is the conclusion of an article published in Frontiers in Neuroscience by Brazilian researchers affiliated with the Federal University of São Paulo (UNIFESP) and the University of São Paulo (USP).
Although older people and dementia patients are unlikely to be able to do long daily runs or perform other high-intensity aerobic exercises, these activities are the focus for most scientific studies on ...
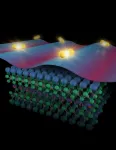
First direct visualization of a zero-field pair density wave
2023-07-03
UPTON, NY—In the field of superconductivity—the phenomenon in which electrons can flow through a material with essentially zero resistance—the “holy grail” of discovery is a superconductor that can perform under everyday temperatures and pressures. Such a material could revolutionize modern life. But currently, even the “high-temperature” (high-Tc) superconductors that have been discovered must be kept very cold to function—too cold for most applications.
Scientists still have much to learn before room-temperature ...
Polyphenols Applications 2023 paves the way for artificial intelligence-enhanced therapeutics and space food
2023-07-03
Artificial Intelligence, Space Food & Polyphenols: 2 Ambitious Projects
Polyphenols Applications 2023 World Congress, which will be held on September 28-29 in Malta, will support 2 projects in order to advance in the polyphenols innovations:
1- Polyphenols & Artificial Intelligence:
This project aims to leverage artificial intelligence techniques to enhance the understanding and utilization of polyphenols. You will utilize machine-learning algorithms to analyze large datasets on polyphenols, including their chemical structures, bioactivities, and health effects. ...
Supportive communities can help increase breastfeeding rates for moms, MU study finds
2023-07-03
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- While formula-feeding babies is a safe and convenient option, research studies have shown natural breastfeeding is linked to numerous health benefits for both mother and child. For mothers, breastfeeding can improve recovery after giving birth and lower the risks of cancer. For babies, the nutrients strengthen their immune system and help lower their risk of developing obesity and diabetes.
Now, a new study at the University of Missouri Sinclair School of Nursing is helping researchers better understand the factors that influence moms, particularly in rural areas where breastfeeding is less common, when deciding how to feed their babies.
In the study, ...
Dementia is not the end of learning
2023-07-03
People with dementia still have the ability to learn new things despite their illness. This is the conclusion of a doctoral thesis recently presented at Linköping University, Sweden. Its findings debunk the general belief that people with dementia are empty shells, according to Elias Ingebrand, who conducted the study.
Elias Ingebrand let ten dementia sufferers, eight of whom lived in care facilities, try using computer tablets for the first time in their lives. A staff member or a loved one was there for support, but the only instruction given to participants ...
New study reveals abrupt shift in tropical Pacific climate during Little Ice Age
2023-07-03
Summary
An El Niño event has officially begun. The climate phenomenon, which originates in the tropical Pacific and occurs in intervals of a few years will shape weather across the planet for the next year or more and give rise to various climatic extremes. El Niño-like conditions can also occur on longer time scales of decades or centuries. This has been shown to have occurred in the recent past by an international research team led by Ana Prohaska of the University of Copenhagen and Dirk Sachse of the German Research Centre for Geosciences (GFZ). Their analysis of biomarkers – organic molecules or molecular fossils from vascular plants – in ...
Kabbani to receive funding for study of mitochondrial targeting and regulation
2023-07-03
Nadine Kabbani, Associate Professor, School of Systems Biology, is set to receive $100,000 from Charles Morgan for: "Mitochondrial Targeting and Regulation." This funding will begin in July 2023 and will end in July 2025.
Regarding the importance of the project, Kabbani said, "Studies suggest an important role for mitochondrial regulation in many human diseases. The targeting of mitochondrial processes has thus emerged as an important strategy in drug design and biomarker discovery. In addition, mitochondrial responses are especially useful in toxicity testing for medical and environmental applications. The goal of this project is to identify mitochondrial ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
[Press-News.org] Birds raise fewer young when spring arrives earlier in a warming worldStudy led by UCLA, Michigan State scientists finds conservation strategies should address avian responses to climate-driven shifts