(Press-News.org) CAMBRIDGE, MD (July 5, 2023)—Researchers have found that one method of reducing greenhouse gas emissions is available, affordable, and capable of being implemented right now. Nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas and ozone-depleting substance, could be readily abated with existing technology applied to industrial sources.
“The urgency of climate change requires that all greenhouse gas emissions be abated as quickly as is technologically and economically feasible,” said lead author Eric Davidson, a professor with the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science. “Limiting nitrous oxide in an agricultural context is complicated, but mitigating it in industry is affordable and available right now. Here is a low-hanging fruit that we can pluck quickly.”
When greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere, they trap the heat from the sun, leading to a warming planet. In terms of emissions, nitrous oxide is third among greenhouse gases, topped only by carbon dioxide and methane. Also known as laughing gas, it has a global warming potential nearly 300 times that of carbon dioxide and stays in the atmosphere for more than 100 years. It also destroys the protective ozone layer in the stratosphere, so reducing nitrous oxide emissions provides a double benefit for the environment and humanity.
Nitrous oxide concentration in the atmosphere has increased at an accelerating rate in recent decades, mostly from increasing agricultural emissions, which contribute about two-thirds of the global human-caused nitrous oxide. However, agricultural sources are challenging to reduce. In contrast, for the industry and energy sectors, low-cost technologies already exist to reduce nitrous oxide emissions to nearly zero.
Industrial nitrous oxide emissions from the chemical industry are primarily by-products from the production of adipic acid (used in the production of nylon) and nitric acid (used to make nitrogen fertilizers, adipic acid, and explosives). Emissions also come from fossil fuel combustion used in manufacturing and internal combustion engines used in cars and trucks.
“We know that abatement is feasible and affordable. The European Union’s emissions trading system made it financially attractive to companies to remove nitrous oxide emissions in all adipic acid and nitric acid plants,” said co-author Wilfried Winiwarter of the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis. “The German government is also helping to fund abatement of nitrous oxide emissions from nitric acid plants in several low-income and middle-income countries.”
The private sector could also play a key role in nitrous oxide emissions reduction, encouraged by trends in consumer preferences for purchasing climate-friendly products. For example, 65% of the nitrous emissions embodied in nylon products globally are used in passenger cars and light vehicles. Automobile manufacturers could require supply chains to source nylon exclusively from plants that deploy efficient nitrous oxide abatement technology.
“Urgent abatement of industrial sources of nitrous oxide” is published in Nature Climate Change by Eric Davidson of the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science, Spark Climate Solutions, Wilfried Winiwarter of the International Institute of Applied Systems Analysis, Austria, and the Institute for Environmental Engineering, University of Zielona Góra, Poland.
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND CENTER FOR ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE
The University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science leads the way toward better management of Maryland’s natural resources and the protection and restoration of the Chesapeake Bay. From a network of laboratories located across the state, UMCES scientists provide sound evidence and advice to help state and national leaders manage the environment, and prepare future scientists to meet the global challenges of the 21st century. www.umces.edu
# # #
END
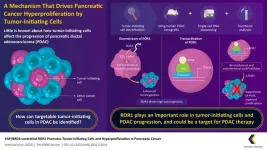
Tumor-initiating cells, or cancer stem cells, are gaining attention in cancer therapy, as they can travel through the body and cause cancerous tumors at other sites through metastasis. These cells also may cause resistance to chemotherapy. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a type of cancer that has a poor prognosis. The problem of metastasis is particularly prominent in this type of cancer. Though the tumor-initiating cells are implicated in the disease progression of some cancers, their specific role, unique traits, and the underlying signaling pathways of their action in pancreatic adenocarcinoma remain poorly understood. ...
WASHINGTON (July 5, 2023) – A new multicenter, single-arm, open-label study is the first to exclusively assess bleeding complications in patients undergoing high-risk percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) with Impella with independent adjudication via a clinical events adjudication committee and will gather meaningful real-world data based on contemporary practice. The design and rationale of the study was published online today in the Journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (JSCAI).
Nearly one in every five patients1 will experience a bleeding complication during a large-bore endovascular procedure. Periprocedural ...
SAN ANTONIO — July 5, 2023 —The Southwest Research Institute-led Ultraviolet Spectrograph (UVS) aboard ESA’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) spacecraft has successfully completed its initial commissioning following the April 14 launch. The UVS instrument is one of three instrument projects comprising NASA’s contribution to the JUICE mission. The mission’s science goals focus on Jupiter and its system, making multiple flybys of the planet’s large, ocean-bearing satellites with a particular emphasis on investigating Ganymede ...
The first clinical trial of a three-month tuberculosis (TB) treatment regimen is closing enrollment because of a high rate of unfavorable outcomes with the investigational course of treatment. AIDS Clinical Trials Group 5362, also known as the CLO-FAST trial, sought to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a three-month clofazimine- and high-dose rifapentine-containing regimen. An interim data analysis showed that participants taking the investigational regimen experienced ongoing or recurring TB at rates above thresholds set in the study protocol. Based on these findings, ...
Voters in North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) member states are far more willing to militarily defend another country if the country joins NATO, versus if the same country does not join NATO, according to a study. To explore the possible consequences of expanding NATO membership, Michael Tomz and colleagues surveyed 14,000 voters in 13 NATO countries. Each survey participant was presented with a hypothetical Russian attack on one of four possible targets: Bosnia, Finland, Georgia, or Sweden—the four countries (other than Ukraine) furthest along in their bids for NATO accession at the time of ...
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has launched the Center for Ophthalmic Artificial Intelligence and Human Health, the first of its kind in New York and one of the first in the United States. The Center is dedicated to advancing artificial intelligence (AI) in the field of ophthalmology, further positioning the Mount Sinai Health System as a leader in providing patient care through pioneering innovations and technologies.
In partnership with the Windreich Department of Artificial Intelligence and Human Health at Icahn Mount Sinai, the Center aims to ...
New research reveals that sunscreen contamination may be less harmful to wildlife than previously thought. This study by Aaron Boyd, a PhD candidate at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Canada, demonstrates how exposure to sunscreen is actually a low risk for small aquatic animals compared to some of the suncream’s individual chemicals.
Sunscreens contain ultraviolet filters (UVFs) which have been found to be toxic to marine life such as corals, leading to the ban of some UVFs in Hawaii and Palau. If sunscreen is applied to the skin before swimming in lakes and rivers, these UVFs and other chemicals will leach into surrounding waters.
Mr ...
Researchers have been testing real-life Batman-style gadgets to eradicate moth pests from greenhouses, including bat-inspired flying drones that hunt down and destroy moths – but new research reveals that the noise from drones can alter moth flight behaviour.
“The idea of using drones as an alternative solution to eliminating moths all started in the bedroom of one of the co-owners of the PATS startup company,” says Dayo Jansen, a PhD student from student from Wageningen University and Research in the Netherlands. ...
Embargoed until 8 a.m. ET/ 7 a.m. CT on Wednesday, July 5, 2023
DALLAS, July 5, 2023 — The COVID-19 pandemic radically changed the way health care professionals serve their patients. Over the past three years, a huge proportion of care has shifted to the virtual landscape as clinicians and patients search for a safe, reliable way to receive needed care.[1]
As part of its longstanding commitment to ensuring equitable access to high-quality health care, the American Heart Association has launched its first individual ...
Imagine a world where computers can unravel the mysteries of quantum mechanics, enabling us to study the behavior of complex materials or simulate the intricate dynamics of molecules with unprecedented accuracy.
Thanks to a pioneering study led by Professor Zoe Holmes and her team at EPFL, we are now closer to that becoming a reality. Working with researchers at Caltech, the Free University of Berlin, and the Los Alamos National Laboratory, they have found a new way to teach a quantum computer how to understand and predict the behavior of quantum systems, even with a few simple examples.
Quantum neural networks (QNNs)
The researchers worked on “quantum neural networks” ...