(Press-News.org)
Fukuoka, Japan—In research that could lead to a new age in illumination, researchers from Japan and Germany have developed an eco-friendly light-emitting electrochemical cells using new molecules called dendrimers combined with biomass derived electrolytes and graphene-based electrodes. Their findings were published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
Electroluminescence is the phenomenon where a material emits light in response to a passing electric current. Everything from the screen you're using to read this sentence to the lasers used in cutting edge scientific research are results of the electroluminescence of different materials. Due to its ubiquity and necessity in the modern age, it is only natural that extensive resources go into research and development to make this technology better.
"One such example of an emerging technology is 'light-emitting electrochemical cells' or LECs," explains Associate Professor Ken Albrecht from Kyushu University's Institute for Materials Chemistry and Engineering and one of the leads of the study. "They have been attracting attention because of their cost advantage over organic light emitting diodes, or OLEDs. Another reason for LECs popularity is their simplified structure."
OLED devices generally require the carful layering of multiple organic films, making it tricky and costly to manufacture. LECs on the other hand can be made with a single layer of organic film mixed with light-emitting materials and an electrolyte. The electrode that connects it all together can even be made from inexpensive materials unlike the rare or heavy metals used in OLEDs. Moreover, LECs have lower driving voltage, meaning they consume less energy.
"Our research teams have been exploring new organic materials that can be used in LECs. One such candidate are dendrimers," explains Prof. Rubén D. Costa of the Technical University of Munich, who led the research team in Germany. "These are branched symmetric polymeric molecules whose unique structure has led to their utility in everything from medicine to sensors, and now in optics."
Building upon their past work on developing dendrimers, the research team began modifying their materials for LECs.
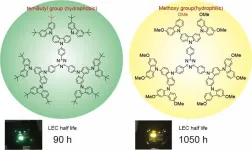
"The dendrimer we developed initially had hydrophobic, or water repelling, molecular groups. By replacing this with hydrophilic, or water liking, groups we found that the lifetime of the LEC device could be extended to over 1000 hours, more than 10-fold from the original," explains Albrecht. "What makes it even better is that thanks to our collaboration with Dr Costa's team the device is very eco-friendly."
For years, Costa's team in Germany had been working on developing cheaper and more environmentally friendly materials in light-emitting devices. One material they have been experimenting with is cellulose acetate, a common organic compound used in everything from clothing fibers and eyeglass frames.
"We used biomass derived cellulose acetate as the electrolyte in our new LEC device, and confirmed that it has the same long-life span," continues Costa. "Moreover, we also found that graphene can be used as an electrode as well. This is a vital step toward making flexible light-emitting devices using environmentally friendly materials."
The team explains that while their work is promising more research is necessary before the devices can be made to market.
"The device we made here only illuminates in yellow, so we need to develop it to illuminate in the three primary light colors: blue, green, and red. Luminescence efficiency, how bright the light is, also needs work," concludes Albrecht. "Though thanks to our international collaboration, the future looks bright."
###
For more information about this research, see "Dendri-LEC Family: Establishing the Bright Future for Dendrimer Emitters in Traditional and Graphene-Based Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cells," Luca M. Cavinato, Keiko Yamaoka, Sophia Lipinski, Vladimir Calvi, Dominique Wehenkel, Richard van Rijn, Ken Albrecht, and Rubén D. Costa Advanced Functional Materials, https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202302483
About Kyushu University
Kyushu University is one of Japan's leading research-oriented institutes of higher education since its founding in 1911. Home to around 19,000 students and 8,000 faculty and staff, Kyushu U's world-class research centers cover a wide range of study areas and research fields, from the humanities and arts to engineering and medical sciences. Its multiple campuses—including one of the largest in Japan—are located around Fukuoka City, a coastal metropolis on the southwestern Japanese island of Kyushu that is frequently ranked among the world's most livable cities and historically known as Japan's gateway to Asia. Through its Vision 2030, Kyushu U will 'Drive Social Change with Integrative Knowledge.' Its synergistic application of knowledge will encompass all of academia and solve issues in society while innovating new systems for a better future.
END
The mitochondrial genome of cybrid citrus (G1 + HBP) is from the CMS callus parent ‘Guoqing No. 1’ Satsuma mandarin (G1), while the nuclear and chloroplast genomes of G1 + HBP are from the fertile mesophyll parent Hirado Buntan pummelo (HBP). The tree of G1+HBP resembles HBP, as well as fruit appearance and flavor, while G1+HBP showed typical male sterility including degenerated petals and stamens and aborted pollen which resulted in seedless fruit. The interaction of mitochondrion from CMS parent G1and nucleus from HBP might attribute to male sterility of G1+HBP. The male sterility candidate genes of the cybrid were identified using comparation analysis of ...
Reduced fertility prolongs the interval from calving to conception in dairy cows, resulting in significant economic losses to dairy farms. Up to 25% of cows are culled due to reproductive failure, and this accounts for a larger proportion than that caused by other major factors, including mastitis and lameness.
A variety of factors are considered to cause low fertility in cows, including farm management factors like estrus detection, nutritional control, and cowshed environment, as well as cow-specific ...
Researchers from Nagoya University and the National Institute of Polar Research in Japan have found that dust from land without snow cover in the Arctic is a major source of particles that form ice crystals in low-level clouds of the Arctic (at altitudes below about 3 km) during summer and fall.
The formation of ice crystals in low-level clouds is considered to affect climate because it can cause ice particles to grow at the expense of liquid droplets and then fall as precipitation, resulting in a lower sunlight reflectance and a shorter lifetime for clouds.
“The Arctic is said to be heating up two to four times faster than the rate ...
Financial materiality pertains to crucial and pertinent data that a company is obligated to reveal in its financial statements. It provides companies with the insights necessary to discern elements influencing their performance and profitability, thereby enabling them to mitigate risks and captivate potential investors. There have been conflicts between shareholders and stakeholders regarding issues that are not directly related to finances, like environmental and social concerns. However, ignoring these factors like ESG (environmental, social and governance) could pose risks to both ...
In a new study, National Institutes of Health (NIH) researchers found that altered B cell function in children with mitochondrial disorders led to a weaker and less diverse antibody response to viral infections. The study, published in Frontiers in Immunology was led by researchers at the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), who analyzed gene activity of immune cells in children with mitochondrial disorders and found that B cells, which produce antibodies to fight viral infections, are less able to survive cellular stress.
“Our work is one of the first examples to study how B cells are affected in mitochondrial disease by looking at human ...
Board games based on numbers, like Monopoly, Othello and Chutes and Ladders, make young children better at math, according to a comprehensive review of research published on the topic over the last 23 years.
Board games are already known to enhance learning and development including reading and literacy.
Now this new study, published in the peer-reviewed journal Early Years, finds, for three to nine-year-olds, the format of number-based board games helps to improve counting, addition, and the ability to recognize if a number is higher or lower than another.
The researchers say children benefit from ...
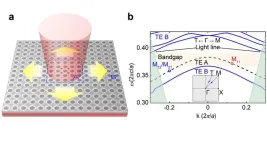
Lasers with ultra-low threshold and compact size are highly desirable in photonic integrated circuits, aiming at the application of optical communications, chip-scale solid-state LIDAR and quantum information. The general approach to realizing such lasers is to effectively trap light and boost light-matter interaction by embedding gain materials into few- or sub-wavelength scale optical cavities with high quality (Q) factor and/or small mode volume (V-mode).
Low-threshold lasing has been realized on planar photonic crystal via introducing defect-type PhC modes or ...
Using Cryo-EM, a powerful microscopy technique, researchers at IISc and collaborators have decoded the molecular architecture of a transporter protein controlling the movement of a key neurotransmitter.
Neurons or nerve cells communicate by releasing chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Each neurotransmitter can activate specific sets of proteins called receptors that in turn either excite or inhibit neural communication. A balance between excitation and inhibition is vital for the neural circuitry to maintain normal structure and function. Imbalances in excitatory or inhibitory inputs can result in disorders like seizures, anxiety, and schizophrenia.
The inhibitory neurotransmitter ...
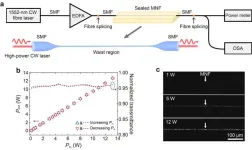
Optical MNFs are cylindrical optical waveguides with diameter below or close to the wavelength of the light. Since its first experimental demonstration [Nature 426, 816 (2003)], low-loss silica MNF has been attracting increasing attention in wide applications from optical sensors, atom optics, nonlinear optics to optomechanics. Generally, increasing the waveguiding mode power is the most effective approach to enhance light-matter interaction, and explore new opportunities for both scientific research and technological applications. However, the highest CW mode power reported so far in a MNF is ~0.4 W [AIP Adv. 4, 067124 (2014)], with typical waveguiding ...
There are obvious differences between cancerous cells and normal cells in morphology, chemical properties and mechanical properties. The detection of cytochemical and mechanical properties of tumor tissues can provide multi-dimensional information for the pathological process of cells and human tissues. Among the existing detection methods for the morphology, mechanics and chemical properties of tissue and cells, confocal Raman spectroscopy can detect the chemical properties of micro-regions of samples without contact and label, and confocal Brillouin spectroscopy can detect ...