(Press-News.org) UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A team of Penn State researchers investigated how seeing frightening news about climate change day after day may shape the way people feel about the phenomenon and how willing they are to take action to address it.
Christofer Skurka, Jessica Myrick and graduate student Yin Yang found that seeing bad news about climate change can make people more afraid over time, but it also may encourage audiences to think about what society can do to address the problem. They published the results of two separate studies in an article titled “Fanning the flames or burning out? Testing competing hypotheses about repeated exposure to threatening climate change messages,” which appeared in the journal Climatic Change.
“The public is surrounded by media coverage about climate change, and this messaging tends to be negative in tone, focusing on the threats that climate change poses to human prosperity and ecological health,” said Skurka, the paper’s lead author and an assistant professor of media studies in the Donald P. Bellisario College of Communications. “We know from years of research in the field of communication that media messaging can impact our emotions, our beliefs and, in turn, sometimes our behavior.”
The first study involved exposing participants to three days of negative news stories about climate change. A follow-up study consisted of participants reading negative news headlines about climate change in the form of Twitter posts for seven consecutive days.
“We found that three days in a row of reading doom-and-gloom news stories about climate change was linked to greater fear and less hope, which can potentially hurt an audience’s attitude that they can do anything to tackle the problem,” said Myrick, the Donald P. Bellisario Professor of Health Communication and co-funded faculty member of the Institutes of Energy and the Environment. “However, our follow-up study had people look only at headlines and not full news stories for a longer period of seven days in a row. In that study, we found that fear peaked after a few days and then held steady.”
The researchers reported that over time, people who repeatedly saw climate change headlines started to feel like they could do more to affect change and that the topic of climate change was important.
“You would think that as people are repeatedly exposed to threatening climate news devoid of solutions content that their efficacy beliefs will decrease over time,” Skurka said. “We saw the opposite pattern in our second study. People’s efficacy beliefs increased over time. In other words, the more exposure people had to these threatening news stories each day, they were increasingly likely to think that they can make a difference in addressing climate change.”
Skurka said one possibility is that as the public copes with unpleasant feelings about the enormous threat climate change presents, they may convince themselves that they have control over the situation, which translates into greater efficacy beliefs that their actions will make a difference.
“Our findings suggest that people have gotten used to doom-and-gloom reporting around climate change and what may be more important for motivating them to take action is that they see coverage of it on a daily basis,” Myrick said. “This is called an agenda-setting effect, where a topic that is covered more often in the news is then viewed as more important by people who consume the news.”
According to Skurka, decades of research in communication and psychology show that under certain circumstances, fear can be motivating.
“We found that people exposed to the high-threat headlines, which tended to evoke more fear, generally expressed greater intentions to share the information than people exposed to the low-threat headlines, which means there may be an advantage to evoking fear,” Skurka said. “However, people’s responses over time were essentially the same regardless of whether they were shown the high-threat or low-threat news headlines. That tells us that when it comes to over-time responses to repeated media exposure, simply mentioning climate change in the news activates pre-existing emotions and thoughts associated with climate change.”
Myrick added that this does not mean that fear-appeals should be used for all climate change communication. Instead, the more important factor may be communicating hope and solutions.
“For communication to be most impactful, people need to feel like there is still something we can do about it to make a difference,” Myrick said. “That should hopefully motivate reporters and strategic communicators to include information about solutions to climate change in their messaging.”
END
Doom-and-gloom climate news may scare but also encourage audiences
2023-07-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Name of Portuguese astrophysicist shines in the night sky
2023-07-07
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) has named an asteroid after Pedro Machado, astrophysicist at Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences (IA), at the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon (Portugal). Along with the nomination of Pedro Machado, there were over a hundred other nominations of asteroids and other small bodies.
It is almost three kilometers in diameter and takes four and a half years to complete its orbit around the sun. We’re talking about 2001 QL160, or rather the asteroid 32599 Pedromachado. Pedro Machado has been honored by the Work group for the Nomenclature of Small Bodies (WGSBN 2) of the International Astronomical ...
Charles 'Chipper' Griffith named dean of UK College of Medicine
2023-07-07
LEXINGTON, Ky. (July 6, 2023) — Charles “Chipper” Griffith III, M.D., has been named dean of the University of Kentucky College of Medicine.
Pending approval from the Board of Trustees, Griffith will begin his appointment July 15, 2023. He has served as acting dean of the college since July 2021.
Through the years, he has played an instrumental role in the health and well-being of Kentuckians, and in the academic success of thousands of students.
“Dr. Griffith understands Kentucky needs the UK College of Medicine,” said Provost Robert ...
Updating pulse oximeters
2023-07-07
Updating pulse oximeters
A portable device used to detect blood oxygen levels revolutionized the medical field 50 years ago and is now receiving essential updates
Efforts to improve the accuracy of pulse oximetry readings for diverse groups of patients and in multiple settings are underway. Joel Moss, M.D., Ph.D., a senior investigator in NHLBI’s Laboratory of Translational Research, and Bennett Yang, a postbaccalaureate fellow in Dr. Moss’s lab, describe this process and the future of pulse oximetry research.
Q: Why are portable pulse ...
July issues of American Psychiatric Association journals cover advances in social determinants of mental health, youth mental health screening, AI in psychotherapy and more
2023-07-07
The latest issues of three of the American Psychiatric Association’s journals, The American Journal of Psychiatry, Psychiatric Services and The American Journal of Psychotherapy are now available online.
The July issue of The American Journal of Psychiatry features articles on social determinants of health relevant to racial and ethnic disparities as well as postmortem molecular studies. Highlights include:
Recent Advances on Social Determinants of Mental Health: Looking Fast Forward.
Differences in Social Determinants of Health Underlie Racial/Ethnic Disparities in Psychological Health and Well-Being: Study of 11,143 Older Adults.
The Nature ...
Breakthrough identifies new state of topological quantum matter
2023-07-07
ITHACA, N.Y. -- Cornell scientists have revealed a new phase of matter in candidate topological superconductors that could have significant consequences for condensed matter physics and for the field of quantum computing and spintronics.
Researchers at the Macroscopic Quantum Matter Group at Cornell have discovered and visualized a crystalline yet superconducting state in a new and unusual superconductor, Uranium Ditelluride (UTe2), using one of the world’s most powerful millikelvin Scanned Josephson Tunnelling Microscopes (SJTM). This “spin-triplet electron-pair crystal” is a previously unknown state of topological quantum matter.
The findings, ...
Fecal transplants show promise in improving melanoma treatment
2023-07-07
LONDON, ON – In a world-first clinical trial published in the journal Nature Medicine, a multi-centre study from Lawson Health Research Institute, the Centre hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal (CHUM) and the Jewish General Hospital (JGH) has found fecal microbiota transplants (FMT) from healthy donors are safe and show promise in improving response to immunotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma.
Immunotherapy drugs stimulate a person’s immune system to attack and destroy cancer. While they can significantly improve survival outcomes in those with melanoma, they are only ...
Privacy-preserving collaborative data collection and analysis with many missing values
2023-07-07
To control pandemics like the novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19), data such as the age, gender, family composition, and medical history of infected individuals are required. While patients themselves may provide this information to medical institutions, these details are highly confidential. If the data is properly handled for privacy protection, it can be shared with researchers worldwide without identifying the infected individual, which can help clarify the state of the pandemic and more accurately predict its progression.
There ...
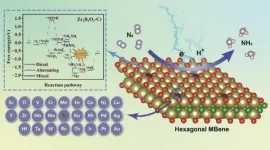
Hexagonal MBene: A promising platform for the electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction reaction
2023-07-07
They published their work on July. 6 in Energy Material Advances.
"In 2017, we reported a new family of 2D transition metal borides as analogues to MXenes and coined a catchy name for them, MBenes," said paper author Zhimei Sun, professor of the School of Materials Science and Engineering at Beihang University. "Up till now, MBenes have been widely studied as catalysts or substrates of various reactions, including HER, ORR/OER, NRR and CO2RR. Notably, the exploration of electrocatalytic performance for MBenes mainly focuses on those with orthorhombic structures, while there are few studies on applying ...
AI tool decodes brain cancer’s genome during surgery
2023-07-07
Scientists have designed an AI tool that can rapidly decode a brain tumor’s DNA to determine its molecular identity during surgery — critical information that under the current approach can take a few days and up to a few weeks.
Knowing a tumor’s molecular type enables neurosurgeons to make decisions such as how much brain tissue to remove and whether to place tumor-killing drugs directly into the brain — while the patient is still on the operating table.
A report ...
Spider mite males undress maturing females to win the first mating
2023-07-07
In males of many species, it pays to identify females that are nearing maturity to be the first in line for mating. Now researchers reporting in the journal iScience on July 7 have found a remarkable example: male spider mites guard and then actively strip off the skin of premature females that are soon to molt and mature to make them accessible for mating sooner.
“Our study documents an exceptional male behavior in the animal kingdom, namely that male spider mites strip off the skin of premature females that are close to molting into adulthood,” said Peter Schausberger ...