(Press-News.org) Researchers have known that a lack of quality sleep can increase a person’s risk of diabetes. What has remained a mystery, however, is why.
Now, new findings from a team of sleep scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, are closer to an answer. The researchers have uncovered a potential mechanism in humans that explains how and why deep-sleep brain waves at night are able to regulate the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which in turn improves blood sugar control the next day.
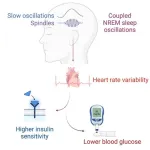
“These synchronized brain waves act like a finger that flicks the first domino to start an associated chain reaction from the brain, down to the heart, and then out to alter the body’s regulation of blood sugar,” said Matthew Walker, a UC Berkeley professor of neuroscience and psychology and senior author of the new study. “In particular, the combination of two brain waves, called sleep spindles and slow waves, predict an increase in the body’s sensitivity to the hormone called insulin, which consequentially and beneficially lowers blood glucose levels.”
The researchers say this is an exciting advance because sleep is a modifiable lifestyle factor that could now be used as part of a therapeutic and painless adjunct treatment for those with high blood sugar or Type 2 diabetes.
Scientists also noted an additional benefit besides the potential new mechanistic pathway.
“Beyond revealing a new mechanism, our results also show that these deep-sleep brain waves could be used as a sensitive marker of someone’s next-day blood sugar levels, more so than traditional sleep metrics,” said Vyoma D. Shah, a researcher at Walker’s Center for Human Sleep Science and co-author of the study. “Adding to the therapeutic relevance of this new discovery, the findings also suggest a novel, non-invasive tool — deep-sleep brain waves — for mapping and predicting someone’s blood sugar control.”
The team’s findings were published today in the journal Cell Reports Medicine.
For years, researchers have studied how the coupling of non-rapid eye movement sleep spindles and deep, slow brain waves corresponded to an entirely different function — that of learning and memory. Indeed, the same team of UC Berkeley researchers previously found that deep-sleep brain waves improved the ability of the hippocampus — the part of the brain associated with learning — to retain information.
But this new research builds on a 2021 rodent study and reveals a novel and previously unrecognized role for these combined brain waves in humans when it comes to the critical bodily function of blood sugar management.
The UC Berkeley researchers first examined sleep data in a group of 600 individuals. They found that this particular coupled set of deep-sleep brain waves predicted next-day glucose control, even after controlling for other factors such as age, gender and the duration and quality of sleep.
“This particular coupling of deep-sleep brain waves was more predictive of glucose than an individual’s sleep duration or sleep efficiency,” said Raphael Vallat, a UC Berkeley postdoctoral fellow and co-author of the study. “That indicates there is something uniquely special about the electrophysiological quality and coordinated ballet of these brain oscillations during deep sleep.”
Next, the team then set out to explore the descending pathway that might explain the connection between these deep-sleep brain waves sending a signal down into the body, ultimately predicting the regulation of blood glucose.
The findings from the team reveal an unfolding set of steps that could help explain how and why these deep-sleep brain waves are related to superior blood sugar control. First, they found that stronger and more frequent coupling of the deep-sleep brain waves predicted a switch in the body’s nervous system state into the more quiescent and calming branch, called the parasympathetic nervous system. They measured that change in the body and the shift to this low-stress state using heart rate variability as a proxy.
Next, the team turned its attention to the final step of blood sugar balance.
The researchers further discovered that this deep sleep switch to the calming branch of the nervous system further predicted an increased sensitivity of the body to the glucose-regulating hormone called insulin, which instructs cells to absorb glucose from the bloodstream, preventing a deleterious blood sugar spike.
That’s particularly important for people trying to back away from hyperglycemia and Type 2 diabetes.
“In the electrical static of sleep at night, there is a series of connected associations, such that deep-sleep brain waves telegraph a recalibration and calming of your nervous system the following day,” Walker said. “This rather marvelous associated soothing effect on your nervous system is then associated with a reboot of your body’s sensitivity to insulin, resulting in a more effective control of blood sugar the next day.”
The researchers subsequently replicated the same effects by examining a separate group of 1,900 participants.
“Once we replicated the findings in a different cohort, I think we actually started to feel more confident in the results ourselves,” Walker said. “But I’ll wait for others to replicate it before I truly start believing, such is my British skepticism.”
The scientists said the research is particularly exciting given the potential clinical significance years down the line. Diabetes treatments already on the market can sometimes be difficult for patients to adhere to. The same is true of the recommended lifestyle changes, including different eating habits and regular exercise.
Sleep, however, is a largely painless experience for most people.
And while sleep is not going to be the single magic bullet, the prospect of new technologies that can safely alter brain waves during deep sleep that this new research has uncovered may help people better manage their blood sugar. That, the research team said, is reason for hope.
END
New research finds deep-sleep brain waves predict blood sugar control
2023-07-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty linked to increased complication rates
2023-07-07
July 7, 2023 – Patients undergoing bilateral total knee arthroplasty (TKA) are at an increased risk of several types of complications, as compared with matched patients undergoing unilateral TKA, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
"Patients who underwent simultaneous bilateral TKA were at higher risk of experiencing postoperative complications such ...
New center merges math, AI to push frontiers of science
2023-07-07
ITHACA, N.Y. -- With artificial intelligence poised to assist in profound scientific discoveries that will change the world, Cornell is leading a new $11.3 million center focused on human-AI collaboration that uses mathematics as a common language.
The Scientific Artificial Intelligence Center, or SciAI Center, is being launched with a grant from the Office of Naval Research and is led by Christopher J. Earls, professor of civil and environmental engineering at Cornell Engineering. Co-investigators include Nikolaos Bouklas, assistant professor ...
Prostate cancer patients face financial toxicity: Who is affected and how do they cope?
2023-07-07
July 7, 2023 – Fifty percent of patients with metastatic prostate cancer experience some level of financial hardship due to their treatment, according to a study in the August issue of The Journal of Urology®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Our findings help in understanding the rates of and risk factors for financial toxicity among patients with advanced prostate cancer, along with the coping mechanisms, including the impact on personal spending, experienced by those reporting higher levels of financial toxicity," ...
Cancer’s origin story features predictable plot line, Stanford Medicine researchers find
2023-07-07
Cancer cells-to-be accumulate a series of specific genetic changes in a predictable and sequential way years before they are identifiable as pre-malignancies, researchers at Stanford Medicine have found. Many of these changes affect pathways that control cell division, structure and internal messaging — leaving the cells poised to go bad long before any visible signs or symptoms occur.
The study is the first to exhaustively observe the natural evolution of the earliest stages of human cancers, starting with ...
A novel chromosomal abnormality in AML patient: Case report and literature review
2023-07-07
“Here we report an unusual association of t (5; 17) with t (8; 21) in AML and we try to discuss the prognosis of this association and then the treatment.”
BUFFALO, NY- July 7, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Genes & Cancer on June 28, 2023, entitled, “A novel t (5; 17) (q35; q21) associated with t (8; 21) (q22; q22) in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia: case report and review of literature.”
The t (8; 21) (q22; q22) with the resulting RUNX1- RUNX1T1 rearrangement is one of the most common cytogenetic abnormalities in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). It is associated with a favorable prognosis. The t (5; 17) (q35; q21) is an ...
Art that integrates data visualizations can help bridge the US political divide over climate change
2023-07-07
MADISON – Communicating science to a general audience can be challenging. Successfully conveying research on polarizing topics such as climate change can be even more difficult.
But a new study from University of Wisconsin–Madison researcher Nan Li shows that intentionally integrating art with data visualizations can help non-expert audiences more meaningfully engage with climate change while also bridging political divides in ways that data alone cannot. In fact, data graphs on their own can exacerbate political division on climate change.
As an assistant professor in the Department of Life Sciences Communication, Li studies how innovative visual representations of science ...
Expanding Medicaid improved care without crowding out other patients
2023-07-07
People with low incomes who live in states that expanded Medicaid got more of the kind of health care that can keep them healthier in the long run, compared with similar people in non-expansion states, a new study finds.
They also received more health care overall, specifically clinic visits. But they didn’t crowd out patients covered by Medicare or private insurance such as from an employer, the study finds. Those groups continued to have clinic visits and receive preventive care at the same rate ...
nTIDE June 2023 Jobs Report: Employment hovers around all-time highs for people with disabilities
2023-07-07
East Hanover, NJ – July 7, 2023 – June’s job numbers remained around all-time highs for people with disabilities, according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE), issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD). nTIDE experts cautioned that employment of people with disabilities may be negatively affected by further anti-inflationary efforts by the Federal Reserve.
Month-to-Month nTIDE Numbers (comparing May 2023 to June 2023)
Based on data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) ...
Soft tissue restoration, blood vessel formation focus of $3M grant
2023-07-07
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The ability to regenerate and pattern blood vessels, the literal lifelines extending deep into soft tissues, remains an elusive milestone in regenerative medicine. Known as tissue revascularization, stimulating blood vessel growth and pattern formation in damaged or diseased tissues could accelerate the field of regenerative medicine, according to Penn State researchers.
With a four-year, $3 million grant awarded by the National Institutes of Health’s National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, Penn State chemical engineering and reconstructive surgery researchers plan to develop a new way to help restore soft tissue loss in patients ...
Learning the language of molecules to predict their properties
2023-07-07
Discovering new materials and drugs typically involves a manual, trial-and-error process that can take decades and cost millions of dollars. To streamline this process, scientists often use machine learning to predict molecular properties and narrow down the molecules they need to synthesize and test in the lab.
Researchers from MIT and the MIT-Watson AI Lab have developed a new, unified framework that can simultaneously predict molecular properties and generate new molecules much more efficiently ...