(Press-News.org) The material a bird selects for its nest depends on the dimensions of its beak, according to researchers.
Using data on nest materials for nearly 6,000 species of birds, a team based at the University of Bristol and the University of St Andrews utilised random forest models, a type of machine learning algorithm, to take data from bird beaks and try to predict what nest materials that species might use.
They found a surprisingly strong correlation. Using only information on beak shape and size, they were able to correctly predict broad nest material use in 60% of species, rising to 97% in some cases.
These findings, published today in Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, include a careful exploration of these models, investigating the ecological and evolutionary context behind these relationships. For example, not every species has the same access to all nest material types, which also affects these results.
The study’s lead author, Dr Catherine Sheard of Bristol’s School of Earth Sciences said: “We know a lot about primate hands, but not as much about how other animals use their limbs and mouths to manipulate objects. We’ve very excited about the potential applications of our findings, to further explore how beak shape may have co-evolved with other aspects of nest building or other functions.”
Dr Shoko Sugasawa, senior author of the study, based at the University of St Andrews, added: “Most animals, including birds, do not have hands like ours, but manipulating objects like nest material and food is such a crucial part of their lives. Our finding is the first step to reveal possible interactions between the evolution of beaks and manipulation like nest building, and helps us better understand how animals evolved to interact with the world with or without hands”.
The team are now working on a project documenting anthropogenic nest material in the world’s birds, trying to understand what type of birds put human-made material (like plastic, wire, or cigarette butts) in their nests. They are in particular looking to see whether this would be linked to urban-dwelling birds.
“I’m also interested in how beak shape relates to other properties of the nest, including overall nest structure,” added Dr Sheard, “such as whether birds build nests with walls, or a roof.”
Paper
‘Beak shape and nest material use in birds’ by Catherine Sheard, Sally E. Street, Caitlin Evans, Kevin N. Lala, Susan D. Healy, and Shoko Sugasawa in Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B.
END
Beak shape can predict nest material use in the world’s birds, study finds
2023-07-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bees get week early wakeup call from warming climate
2023-07-10
Warmer springs are causing British bees to wake up earlier, a new study has found, threatening the pollination of crops such as apples and pears.
The research – which is believed to be the largest of its kind in Great Britain – found that for every 1 degree Celsius rise in temperature caused by climate change, wild bees, such as bumblebees, emerge from their nests 6.5 days earlier on average.
As spring starts earlier and bees emerge closer to the start of the year, they may lose sync with the plants on which ...
Man-made materials in nests can bring both risks and benefit for birds
2023-07-10
We all discard a huge amount of plastic and other man-made materials into the environment, and these are often picked up by birds. New research has shown that 176 bird species around the world are now known to include a wide range of anthropogenic materials in their nests. All over the world, birds are using our left-over or discarded materials. Seabirds in Australia incorporate fishing nets into their nests, ospreys in North America include baler twine, birds living in cities in South America add ...
Li Yuan 's group from Northwest A&F University has made progress in the study of watermelon haploid induction
2023-07-08
Generating haploid plants for the purpose of obtaining pure doubled haploid (DH) lines is widely recognized as one of the most efficient breeding strategies in modern agriculture. Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus), an important fruit crop known for its nutritional value and flavor, has undergone long-term artificial selection resulting in genetic narrowing. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a haploid induction system to enhance traditional breeding methods and facilitate the development of valuable pure DH lines.
In March 2023, the Plant Biotechnology Journal published an online paper titled "Production of double haploid watermelon via ...
From bad to worse: h=How micro- and meso-plastics collect heavy metals
2023-07-08
Tokyo, Japan – A team led by researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University studied how microplastics in the environment accumulate heavy metals. As the microplastics spread, so do their toxic cargo. Focusing on polystyrene foam, they collected particles along a river running through Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. They found significant levels of heavy metals accumulated on the particles, reflecting local land use and industries, as well as surface features like holes and biofilms which help pollutants collect.
The spread of plastic debris into the natural environment is an ecological disaster. As plastic waste makes ...
Madagascar hippos were forest dwellers
2023-07-07
Extinct dwarf hippos that once roamed Madagascar lived in forests rather than open grasslands preferred by common hippos on mainland Africa, researchers at the University of Cincinnati discovered.
The findings suggest grasslands that now cover much of the enormous island off the eastern coast of southern Africa were a relatively recent change facilitated by people rather than a natural habitat sustained in part by these famously large vegetarians.
The study was published in the journal Plants, People, Planet.
When Madagascar broke away from Africa’s mainland 150 million years ago, its plants and animals evolved in geographic isolation in the ...
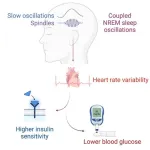
New research finds deep-sleep brain waves predict blood sugar control
2023-07-07
Researchers have known that a lack of quality sleep can increase a person’s risk of diabetes. What has remained a mystery, however, is why.
Now, new findings from a team of sleep scientists at the University of California, Berkeley, are closer to an answer. The researchers have uncovered a potential mechanism in humans that explains how and why deep-sleep brain waves at night are able to regulate the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which in turn improves blood sugar control the next day.
“These synchronized brain waves act like a finger that flicks the ...
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty linked to increased complication rates
2023-07-07
July 7, 2023 – Patients undergoing bilateral total knee arthroplasty (TKA) are at an increased risk of several types of complications, as compared with matched patients undergoing unilateral TKA, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
"Patients who underwent simultaneous bilateral TKA were at higher risk of experiencing postoperative complications such ...
New center merges math, AI to push frontiers of science
2023-07-07
ITHACA, N.Y. -- With artificial intelligence poised to assist in profound scientific discoveries that will change the world, Cornell is leading a new $11.3 million center focused on human-AI collaboration that uses mathematics as a common language.
The Scientific Artificial Intelligence Center, or SciAI Center, is being launched with a grant from the Office of Naval Research and is led by Christopher J. Earls, professor of civil and environmental engineering at Cornell Engineering. Co-investigators include Nikolaos Bouklas, assistant professor ...
Prostate cancer patients face financial toxicity: Who is affected and how do they cope?
2023-07-07
July 7, 2023 – Fifty percent of patients with metastatic prostate cancer experience some level of financial hardship due to their treatment, according to a study in the August issue of The Journal of Urology®, an Official Journal of the American Urological Association (AUA). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Our findings help in understanding the rates of and risk factors for financial toxicity among patients with advanced prostate cancer, along with the coping mechanisms, including the impact on personal spending, experienced by those reporting higher levels of financial toxicity," ...
Cancer’s origin story features predictable plot line, Stanford Medicine researchers find
2023-07-07
Cancer cells-to-be accumulate a series of specific genetic changes in a predictable and sequential way years before they are identifiable as pre-malignancies, researchers at Stanford Medicine have found. Many of these changes affect pathways that control cell division, structure and internal messaging — leaving the cells poised to go bad long before any visible signs or symptoms occur.
The study is the first to exhaustively observe the natural evolution of the earliest stages of human cancers, starting with ...