Microbial predators cause seasonal fluctuations in wastewater treatment
2023-07-10
(Press-News.org)
The community of microbial predators influences the composition of the bacterial community in wastewater. This explains seasonal variations in the microbial community that affect the efficiency of water treatment. This is the result of a study conducted by Nils Heck and PD Dr Kenneth Dumack from the University of Cologne’s Institute of Zoology. The study has been published under the title ‘Microeukaryotic predators shape the wastewater microbiome’ in the journal Water Research.
In wastewater treatment plants, a precisely coordinated interaction of different microorganisms takes place in order to effectively treat wastewater. However, a large part of the microorganisms involved in water treatment is still unknown. In addition to the beneficial bacteria that are responsible for purifying wastewater, many of their predators can also be found in the bioreactors. However, little is known so far about whether and to what extent these predators influence wastewater treatment.
Since the introduction of wastewater treatment plants, it has been known that the seasons influence the bacterial community in wastewater, and thus also the efficiency of water treatment. But why is this so? After all, bacteria do not possess an inbuilt sense of time. This question is by no means trivial, as seasonal changes are the result of a variety of factors. The best-known factors are certainly temperature and light conditions. However, the chemical composition of the wastewater, precipitation amounts and many other factors also vary with the changes throughout the year.
So which of these factors causes the bacterial community to change over the seasons? PD Dr Kenneth Dumack, the leader of the study, explained, “We found that seasonal variation in ambient temperature cannot explain the variation in the bacterial community. This surprised us, so we looked for another factor that could explain the variation in the bacterial community.” Nils Heck, first author of the study, added, “We found that the community of microbial predators, such as amoebae, ciliates and also rotifers, can explain the composition of the bacterial community to a certain extent. These predators are in turn dependent on the ambient temperature. Thus, the temperature factor represents an indirect influence on the bacteria through the community of predators.”
The new findings contribute to a better understanding of the so-called ‘black box’ of wastewater treatment in order to avoid, among other things, health risks that can arise from inadequately treated wastewater.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-10
University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have discovered how the cells that let us hear can repair themselves after being damaged. That important insight could benefit efforts to develop new and better ways to treat and prevent hearing loss.
“Hair cells” found in the inner ear, are important both for our ability to hear and our sense of balance. They are known as hair cells because the cells are covered in hair-like structures that serve as mechanical antennas for sound detection. When auditory hair cells are killed, as we learn in school, they are ...
2023-07-10
INDIANAPOLIS – Information on the nonmedical factors that influence health outcomes, known as social determinants of health, is often collected at medical appointments. But this information is frequently recorded as text within the clinical notes written by physicians, nurses, social workers, and therapists.
Researchers from Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University Fairbanks School of Public Health recently published one of the first studies in which natural language processing was applied to social determinants of health. The researchers developed three new natural language processing algorithms to successfully extract information from text data related to housing ...
2023-07-10
ROCKVILLE, Md. – July 10, 2023 – The Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP), the premier global molecular diagnostic professional society, today published consensus recommendations to aid in the design and validation of clinical CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 genotyping assays, promote standardization of testing across different laboratories, and improve patient care. The manuscript, “CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 Genotyping Recommendations: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the AMP, Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC), College of American Pathologists (CAP), Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) of the Royal Dutch Pharmacists ...
2023-07-10
NEW YORK, NEW YORK, July 10, 2023 – First Ladies from countries across Africa and experts from the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health will meet the week of July 10, 2023 to discuss current trends, critical research, and sustainable, evidence-based approaches to promote population health and well-being. From July 10th to the 13th, First Ladies and their senior advisors will participate in an executive leadership program to advance critical health and development issues in their countries and regions, including communicable and chronic disease ...
2023-07-10
Artificial intelligence has transformed how industries and organizations operate, putting data professionals in high demand. To meet this increasing need, Carnegie Mellon University recently launched an online Graduate Certificate in Computational Data Science Foundations program.
"Everything we teach will translate into skills that enable mobilization of data for significant impact in your organization," said Carolyn Rosé, the faculty program director and a professor in both the Human-Computer ...
2023-07-10
SEATTLE, Wash. – A boom in alcohol sales during the pandemic appears to have had dire consequences for some as hospital admissions for alcohol-related hepatitis, a life-threatening liver inflammation, increased dramatically, according to a study of national hospitalization data.
Researchers found increasing cases of the alcohol-related liver illness from 2016 through 2020, but the rise was particularly pronounced the year COVID-19 arrived in the U.S. in 2020, which saw a 12.4% increase over 2019 levels. It was worse in younger patients, ages 18 to 44, a group that had a nearly 20% ...
2023-07-10
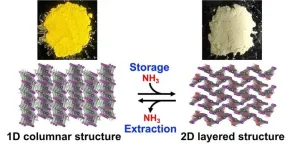
Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science (CEMS) in Japan have discovered a compound that uses a chemical reaction to store ammonia, potentially offering a safer and easier way to store this important chemical. This discovery, published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on July 10, makes it possible not only to safely and conveniently store ammonia, but also the important hydrogen is carries. This finding should help lead the way to a decarbonized society with a practical hydrogen economy.
For society to make the switch from carbon-based to hydrogen-based energy, we need a safe way to store and transport hydrogen, which by itself ...
2023-07-10
A lollipop might be a sweet reward for a kid who’s endured a trip to the doctor's office, but now, this candy could make diagnostic testing during a visit less invasive and more enjoyable. Researchers publishing in ACS’ Analytical Chemistry have shown, for the first time, that a lollipop-based saliva collection system can capture bacteria from adults and remain shelf-stable for up to a year. Study participants also preferred the candies over conventional collection systems.
Throat swabs are commonly used to collect samples for the diagnosis of a wide variety of illnesses, including strep throat. A less-gag-inducing method is saliva sampling, in which technicians ...
2023-07-10
Now that the emergency phase of the COVID-19 pandemic has ended, scientists are looking at ways to surveil indoor environments in real time for viruses. By combining recent advances in aerosol sampling technology and an ultrasensitive biosensing technique, researchers at Washington University in St. Louis have created a real-time monitor that can detect any of the SARS-CoV-2 virus variants in a room in about 5 minutes.
The inexpensive, proof-of-concept device could be used in hospitals and health care facilities, schools and ...
2023-07-10
Statement Highlights:
The American Heart Association supports a value-based care and payment (VBP) system that is person-centered, equitable, coordinated and seeks to improve equity, patient and provider experience, and individual and population health while controlling costs.
Defining and improving clinician understanding of value-based payment program design and best practices promotes informed decisions for participating and successfully engaging in these models.
Embargoed until 4:00 a.m. CT/5:00 a.m. ET, Monday, July 10, 2023
DALLAS, July 10, 2023 — The American Heart Association, a global force for longer, healthier lives for all, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Microbial predators cause seasonal fluctuations in wastewater treatment