(Press-News.org) Routine blood pressure readings recorded in the first half of pregnancy can be divided into 6 distinct patterns that can effectively stratify patients by their risk of developing preeclampsia and gestational hypertension later in pregnancy, Kaiser Permanente researchers found.
The study, published July 12 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, showed that 6 pregnancy blood pressure trajectories seen within the first 20 weeks of pregnancy along with clinical, social, and behavioral risk factors can accurately predict and stratify risk of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension in low- to moderate-risk patients. Three of the early pregnancy blood pressure trajectories identified 74% of the patients who went on to develop preeclampsia later in their pregnancy. The prediction model worked equally well in the white, Black, Hispanic, and Asian patients included in the study.
“The prediction models accurately classified the patients with an increased risk for developing preeclampsia and gestational hypertension based on early blood pressure patterns several months before the onset of disease,” said lead author Erica P. Gunderson, PhD, MPH, a senior research scientist at the Kaiser Permanente Division of Research and a professor at the Kaiser Permanente Bernard J. Tyson School of Medicine.
The study used routine clinical blood pressure measurements and clinical data from the electronic medical records of close to 250,000 healthy pregnant patients. A previous study, identified the 6 distinct blood pressure trajectories. The new study used data from approximately 75,000 women not included in the prior study. The patients studied were considered to be low- to moderate-risk by current U.S. Preventive Services Task Force risk criteria — a group for whom it has been challenging to identify individual risk of preeclampsia.
“Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy are leading causes of morbidity and mortality, particularly in people of color,” said Kari L. Carlson, MD, associate executive director for The Permanente Medical Group. “Identifying risk factors and then implementing a risk stratification program and treatment plan could have a huge impact for both the pregnant person and infant, dramatically reducing the chances of adverse outcomes.”
“The use of a simple measure — blood pressure — that is available as part of clinical care to fine tune clinical risk assessment and identify those at highest risk could allow modification of care and the use of preventive therapies to the most appropriate patients,” said co-author James M. Roberts, MD, a professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive science at the University of Pittsburgh.
The researchers plan to develop an automated tool within the electronic health record system to identify patients in real time based on blood pressure patterns seen before 16 to 20 weeks of pregnancy. Care providers can then advise these patients of their higher risk for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, offer available interventions, and provide additional monitoring.
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
END
Blood pressure patterns in the first half of pregnancy improve early prediction of preeclampsia and gestational hypertension
2023-07-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Gulf War illness caused by mitochondrial dysfunction, not inflammation
2023-07-12
Gulf War Illness (GWI) is a chronic multisymptom health condition affecting one-third of all veterans who served in the 1991 Gulf War, most of whom remain afflicted more than 30 years later. Common symptoms include fatigue, headaches, muscle aches, joint pain, diarrhea, insomnia and cognitive impairment.
The condition is believed to have been triggered by veterans’ exposure to environmental toxins. However, its exact mechanism in the body continues to be debated, making it difficult to diagnose and treat. The prevailing ...
Queen Mary-led research uncovers why people who have Down’s Syndrome age prematurely
2023-07-12
An overdosed gene on chromosome 21 causes people with Down’s Syndrome to age faster than the general population.
The molecular processes responsible for natural ageing of cells are poorly understood. Studying conditions in humans where ageing is accelerated due to genetic causes presents opportunities to learn about the mechanisms that control ageing and devise strategies to slow down the ageing process.
Adults who have Down’s Syndrome (DS) show earlier signs of ageing-related conditions: reduction in tissue regenerative capacity, alopecia, dry skin, ...
Scientists find evidence of world’s oldest glaciers
2023-07-12
Scientists have discovered the traces of the world’s oldest known glaciers, dating from 2.9 billion years ago, in rocks sitting under the world’s largest gold deposits in South Africa. This suggests the presence of continental ice caps at that time and that either the area was closer to the poles, or that parts of the Earth may have been frozen in a previously unknown “snowball Earth” period of extreme cold weather. This work is presented for the first time at the Goldschmidt geochemistry conference in Lyon, after recent peer-reviewed ...
Sea snakes may have evolved to see colors again
2023-07-12
A new paper in Genome Biology and Evolution, published by Oxford University Press, finds that the annulated sea snake, a species of venomous snake found in ocean waters around Australia and Asia, appears to have evolved to see an extended palette of colors after its ancestors lost that ability in response to changing environments.
Color vision in animals is primarily determined by genes called visual opsins. While there have been multiple losses of opsin genes during the evolution of tetrapods (the group including amphibians, reptiles, and mammals), the emergence of new opsin genes is extremely ...
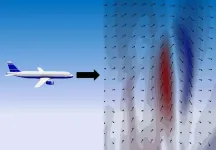
Supercomputer used to simulate winds that cause clear air turbulence
2023-07-12
A research group from Nagoya University has accurately simulated air turbulence occurring on clear days around Tokyo using Japan’s fastest supercomputer. They then compared their findings with flight data to create a more accurate predictive model. The research was reported in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
Although air turbulence is usually associated with bad weather, an airplane cabin can shake violently even on a sunny and cloudless day. Known as clear air turbulence (CAT), these turbulent ...
Sea snake vision evolved to regain color
2023-07-12
An international team of scientists examining the genetic history of sea snakes have found that the species has enhanced their colour vision in response to living in brighter and more colourful marine environments.
“Our research has found that the annulated sea snake possesses four intact copies of the opsin gene SWS1,” said PhD candidate Isaac Rossetto, from the University of Adelaide’s School of Biological Sciences who led the study.
“Two of these genes have the ancestral ultraviolet sensitivity, and two have evolved a new sensitivity to the longer wavelengths that dominate ocean habitats.
“The earliest ...
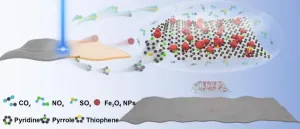
Scientists developed 180% relative bandwidth microwave absorber by ultrafast UV laser
2023-07-12
Scientists from Chinese Academy of Sciences Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, National Physical Laboratory (UK), The University of Manchester (UK) and National University of Singapore have developed a new approach, published in International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing (IF: 14.7), to fabricate a specifically designed wideband microwave absorption metamaterial with well-controlled electrical and magnetic characteristics on a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate using ultraviolet (UV) laser irradiation.
The process involves using a UV laser to precisely control the characteristics of 2-D pattern on a specially formulated donor ...
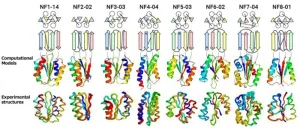
Beyond nature's imagination: Scientists discover extensive array of protein folds unexplored in nature
2023-07-12
A groundbreaking study has shed new light on the astonishing diversity of protein structures and their folds in nature. Researchers set out to reveal the extent to which nature has explored the vast landscape of possible protein topologies. The results have unveiled an astounding array of unexplored protein folds, expanding our understanding and uncovering the depth of the protein universe.
This research has been published in the journal Nature Structural and Molecular Biology on July 3, 2023.
Proteins, ...
Bound states in the continuum is possible in the acoustoelastic coupling
2023-07-12
Let’s imagine a hypothetical scenario where two individuals are gripping a rope, each holding one end. Person A proceeds to shake the rope in an up-and-down motion, thus generating a propagating wave that travels towards person B. Now, if person C, positioned between person A and B, engages in a comparable frequency of waving motion as that of the rope’s wave, could the wave be redirected back to person A rather than reaching person B? Initially, this situation appears implausible, as person C does not physically ...
Pre-operative exercise substantially helps with recovery – study
2023-07-12
Policy-makers are being urged to take notice of a University of Otago study that confirms that undertaking a short programme of high intensity interval training before surgery can substantially help with recovery.
The study, published in the journal Surgery, reviewed and analysed 12 studies including 832 patients who had undertaken preoperative high-intensity interval training. Such training involves repeated aerobic high-intensity intervals at about 80 per cent of the maximum heart rate followed by active recovery.
Lead investigator Dr Kari Clifford says the study included all types of major surgeries – those expected ...