(Press-News.org)
· Colorism – system of inequality that views lighter skin as more beautiful and advantageous – motivates skin lightening
· Users aren’t aware of adulterated ingredients in over-the-counter products such as mercury and steroids
· Products are purchased from chain grocery stores or online, used without medical advice
CHICAGO --- Skin lightening is prevalent in the U.S. among skin of color individuals – particularly women – but the people who use those products don’t know the risks, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study.
Colorism, the system of inequality that views lighter skin as more beautiful and advantageous, can be the motivation behind skin lightening, the study also found. The findings also reinforced the prevalence of skin lightening in the U.S.
“The most surprising finding was the lack of awareness of ingredients in products being purchased over the counter and their potential detrimental effects,” said lead investigator Dr. Roopal Kundu, founder and director of the Northwestern Medicine Center for Ethnic Skin and Hair. “These products are bought from chain grocery stores, community-based stores or even online and do not undergo the same type of regulation as large-chain store or prescription products.”
Kundu is also a professor of dermatology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine and a Northwestern Medicine board-certified dermatologist.
The study will be published July 13 in the International Journal of Women’s Dermatology.
Previous studies show these products are often adulterated with other things such as steroids and mercury that could be toxic to the skin.
One of Kundu’s patients used the lightening product hydroquinone, also called a bleacher, on his entire face for many years. The patient now has permanent hyperpigmentation.
Doctors prescribe skin lighteners for some skin conditions such as melasma, and the products can be safely used under physician guidance. But most people who use skin lighteners also do not consult a medical provider before use, Kundu said.
In 2020, the FDA received reports of serious side effects from the use of skin lightening products containing hydroquinone, including skin rashes, facial swelling and exogeneous ochronosis (discoloration of skin.) The FDA advised consumers not to use these products due to the potential harm they may cause.
Colorism is behind skin lightening
The participants – 80% women – who used skin lighteners perceived stronger colorism in their lives than those who did not use the products, according to the study.
“There is this perception that having lighter skin within a group – Southeast Asian or African populations, for example – is looked upon more favorably and manifests by making someone more attractive to a mate or more likely to get a job,” Kundu said. “The belief is that having lighter skin is tied to personal and professional success.”
Most of Kundu’s patients interested in skin lightening want to do so to even out skin tone due to a skin disease. But a fourth of study participants wanted to do general skin lightening. One of Kundu’s patients recently told her his goal was to completely lighten his skin. “I had to tell him that is not something we can do,” Kundu said. “We weren’t going to globally lighten his skin color.”
To conduct the study, researchers sent an anonymous 19-question survey to individuals with skin of color in the U.S. asking about their demographics, colorism attitudes, skin tone satisfaction and skin lightening habits. Of 455 individuals who completed the survey, 238 were Black, 83 were Asian, 84 were multiracial, 31 were Hispanic, 14 were American Indian or Alaskan Native and five identified as other.
The use of skin lightening agents was reported by 21.3% of respondents, with 75.3% of these respondents using them to treat a skin condition such as acne, melasma or hyperpigmentation. The others were using the agents for general skin lightening.
“As dermatologists, we hope to understand the cultural and societal influences that impact skin health and treatment of skin disease,” Kundu said. “Cultural mindfulness for clinicians as they get to know their patients battling pigmentary issues allows for the safe, effective, comprehensive and compassionate treatment of dermatological disease across all communities.”
Co-authors include Dr. Karishma Daftary, Sneha Poondru, Nina Patel, Maxwell Shramuk, and Lutifyya Muhammad.
The title of the article is “Colorism Attitudes and Use of Skin Lightening Agents in the United States.”
END
PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL 05:01 LONDON TIME (GMT) ON THURSDAY 13 JULY 2023
Images and paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/18XRYP9dHcC1Z8lc3B86j3k6BzgIesqUS?usp=sharing
Small-winged and lighter coloured butterflies likely to be at greatest threat from climate change
The family, wing length and wing colour of tropical butterflies all influence their ability to withstand rising temperatures, say a team led by ecologists at the University of Cambridge. The researchers believe this could help identify species whose survival is under threat from climate change.
Butterflies with smaller or lighter coloured wings are likely to ...
Defying conventional wisdom, researchers have uncovered a novel coupling mechanism involving leaky mode, previously has been considered unsuitable for high-density integration in photonic circuits. This unexpected finding opens new possibilities for dense photonic integration, revolutionizing the scalability and application of photonic chips in optical computing, quantum communication, light detection and ranging (LiDAR), optical metrology, and biochemical sensing.
In a recent Light Science & Application publication, Sangsik Kim, associate professor of electrical engineering ...
A study examining unemployment and underemployment figures and suicide rates in Australia has found both were significant drivers of suicide mortality between 2004-2016.
The researchers say the findings indicate that economic policies such as a Job Guarantee, which prioritise full employment, should be a core part of any comprehensive national suicide prevention strategy.
Predictive modelling also revealed an estimated 9.5 percent of suicides reported during that time resulted directly from unemployment ...
Overview
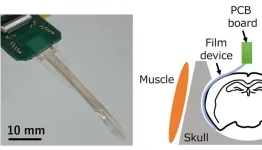
Associate Professor Hiroto Sekiguchi (Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology) and Assistant Professor Susumu Setogawa and Associate Professor Noriaki Ohkawa (Comprehensive Research Facilities for Advanced Medical Science, Dokkyo Medical University; Assistant Professor Setogawa is currently a Specially Appointed Assistant Professor at University Public Corporation Osaka) have developed a flexible electrocorticography (Note 1) film for simultaneous detection of multisensory information (Note 2) from multiple regions of the cerebral cortex by placing neural ...
Mycelium, an incredible network of fungal strands that can thrive on organic waste and in darkness, could be a basis for sustainable fireproofing. RMIT researchers are chemically manipulating its composition to harness its fire-retardant properties.
Associate Professor Tien Huynh, an expert in biotechnology and mycology, said they’ve shown that mycelium can be grown from renewable organic waste.
“Fungi are usually found in a composite form mixed with residual feed material, but we found a way to grow pure mycelium sheets that can be layered and engineered into different uses – from flat panels for the building industry to a leather-like material for ...
The structure of a molecular junction with noncovalent interaction plays a key role in electron transport, reveals a recent study conducted by researchers at Tokyo Tech. Through simultaneous surface-enhanced Raman scattering and current–voltage measurements, they found that a single dimer junction of naphthalenethiol molecule shows three different bondings, namely π–π intermolecular and through-π and through-space molecule–electrode interactions.
The π–π interaction is a type of noncovalent interaction that occurs when the electron clouds in the π orbitals ...
New research suggests that targeting autoimmune inflammation associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) using two drugs, one of them already approved for multiple sclerosis, could be a promising approach for treatment.
ALS, also known as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects the nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. It leads to the gradual loss of muscle control, eventually resulting in paralysis and difficulty with speech, swallowing, and breathing. The exact cause of ALS is not fully understood, and currently, there is no cure ...
Taylor & Francis has taken a significant step in reducing unnecessary plastic use with the introduction of paperwrap for journal print copies mailed in the UK.
Paperwrap, a relatively new packaging technology, has become more common in recent years, but is typically most suited to publications with very high print runs. Taylor & Francis’ Global Supplier Team spent several months investigating how it might be applied to journal print runs, which included rolling out live trial mailings to colleagues around the world to test how the journals could be packaged, and whether there was any impact on the speed ...
A new talking therapy for depression has shown encouraging early signs of being more effective and cheaper to deliver than the current best practice of Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT).
A pilot trial from the University of Exeter, funded by the National Institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR) and published in Lancet EClinical Medicine, has found Augmented Depression Therapy (ADepT) could be a significant advance in depression care.
A core feature of depression is anhedonia (reduced ...
A team of scientists led by CABI have conducted a new study which shows that three ways to fight the invasive Prosopis juliflora tree in Ethiopia, Kenya and Tanzania all proved very effective in almost all cases.
The three-year research, published in the journal CABI Agriculture and Bioscience, revealed that cut stump and basal bark herbicide application and manual uprooting were highly effective, killing the trees in between 85-100% of cases.
In addition, three incremental restoration interventions were tested ...