(Press-News.org) Use of low-dose atropine eyedrops (concentration 0.01%) was no better than placebo at slowing myopia (nearsightedness) progression and elongation of the eye among children treated for two years, according to a randomized controlled trial conducted by the Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group (PEDIG) and funded by the National Eye Institute (NEI). The trial aimed to identify an effective way to manage this leading and increasingly common cause of refractive error, which can cause serious uncorrectable vision loss later in life. Results from the trial were published in JAMA Ophthalmology.
Importantly, the findings contradict results from recent trials, primarily in East Asia, which showed a benefit from 0.01% atropine in slowing myopia.
“The overall mixed results on low-dose atropine show us we need more research. Would a different dose be more effective in a US population? Would combining atropine with other strategies have a synergistic effect? Could we develop other approaches to treatment or prevention based on a better understanding of what causes myopia progression?” said Michael F. Chiang, M.D., director of the NEI, which is part of the National Institutes of Health.
Identifying an optimal approach for preventing high (advanced) myopia is urgently needed given the escalating prevalence of myopia overall and the risk of it progressing to high myopia. By 2030, it’s predicted that 39 million people in the U.S. will have myopia. By 2050, that number is expected to grow to 44 million in the U.S. and to 50% of the global population.
Much stronger concentrations of atropine eyedrops (0.5-1.0%) have long been used by pediatric eye doctors to slow myopia progression. While effective, such doses cause light sensitivity and blurry near vision while on the nightly eyedrops. Thus, there is interest in clinical studies assessing lower concentrations that have been shown to have fewer side effects.
“The absence of a treatment benefit in our U.S.-based study, compared with East Asian studies, may reflect racial differences in atropine response. The study enrolled fewer Asian children, whose myopia progresses more quickly, and included Black children, whose myopia progresses less quickly compared with other races,” noted the study’s lead co-author, Michael X. Repka, M.D., professor of ophthalmology, Johns Hopkins University.
For the study, 187 children ages 5 to 12 years with low-to-moderate bilateral myopia were randomly assigned to use nightly atropine (0.01%) (125 children) or placebo (62 children) eyedrops for two years. Study participants, their parents, and the eye care providers were masked to the group assignments. Patient care was provided at 12 study center sites throughout the U.S.
After the treatment period, and 6 months after treatment stopped, there were no significant differences between the groups in terms of changes in degree of myopia compared with baseline. Nor were there significant differences in axial length within the two groups when compared with baseline measurements.
“It's possible that a different concentration of atropine is needed for U.S. children to experience a benefit,” noted the study’s other lead co-author, Katherine K. Weise, O.D., professor, University of Alabama at Birmingham. “Clinical researchers could evaluate new pharmaceuticals and special wavelengths of light in combination with optical strategies, like special glasses or contact lenses, to see what works in reducing the progression of myopia.”
Among children, myopia will stabilize in about half of children around age 16 years, and among an increasingly larger percentage as they get older. By their early twenties, about 10% of individuals with myopia will continue to grow more nearsighted, and by age 24 years that percentage is 4%.
“Vision scientists may help us figure out what’s different about the myopic eye, even among different races and ethnicities, to help create new treatment strategies,” she said. It will take a real convergence of eye research to solve the environmental, genetic, and structural mystery of myopia.”
PEDIG is a collaborative network of pediatric ophthalmologists and pediatric optometrists dedicated to conducting multi-center trials on eye disorders that affect children. The trial was funded by the NEI grants EY11751, EY18810 and EY23198. The ClinicalTrials.gov identifier is NCT03334253.
For more information about myopia, visit https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/nearsightedness-myopia
Reference:
Repka MX, Weise KK, Chandler DL, Wu R, Melia BM, Manny RE, Kehler LAF, Jordan CO, Raghuram A, Summers AI, Lee KA, Petersen DB, Erzurum SA, Pang Y, Lenhart PD, Ticho BH, Beck RW, Kraker RT, Holmes JM, Cotter SA, on behalf of the Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group. “Randomized trial of low-dose atropine eyedrops for myopia control”, published July 13, 2023 in JAMA Ophthalmology.doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2023.2855
##
NEI leads the federal government’s efforts to eliminate vision loss and improve quality of life through vision research…driving innovation, fostering collaboration, expanding the vision workforce, and educating the public and key stakeholders. NEI supports basic and clinical science programs to develop sight-saving treatments and to broaden opportunities for people with vision impairment. For more information, visit https://www.nei.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit https://www.nih.gov/.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
END
Low-dose atropine eyedrops no better than placebo for slowing myopia progression
NIH-funded trial underscores need for more research to head off high myopia
2023-07-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Low-dose atropine eye drops vs placebo for myopia control
2023-07-13
About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial of school-age children in the U.S. with low to moderate myopia (nearsightedness), atropine, 0.01%, eye drops administered nightly when compared with placebo did not slow myopia progression or axial elongation. These results do not support use of atropine, 0.01%, eye drops to slow myopia progression or axial elongation in U.S. children.
Authors: Michael X. Repka, M.D., M.B.A., of the Wilmer Eye Institute in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this ...
COVID-19 severity and waning immunity after up to 4 mRNA vaccine doses in patients with cancer
2023-07-13
About The Study: This study provides evidence of the clinical effectiveness of mRNA-based vaccines against COVID-19 in patients with cancer. Longevity of immunity in preventing severe COVID-19 outcomes in actively treated patients with cancer, cancer survivors, and matched controls was observed at least five months after the third or fourth dose.
Authors: Raghav Sundar, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., of the National University Health System in Singapore, and Kelvin Bryan Tan, Ph.D., of the Ministry of Health in Singapore, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
Objectively measured visual impairment and dementia prevalence in older adults
2023-07-13
About The Study: In this survey study, all types of objectively measured visual impairment were associated with a higher dementia prevalence. As most visual impairment is preventable, prioritizing vision health may be important for optimizing cognitive function.
Authors: Joshua R. Ehrlich, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2023.2854)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for ...
How COVID-19 crosses the placenta - study using placental tissue grown in the lab
2023-07-13
RESEARCH REVEALS HOW COVID-19 VIRUS INFECTS THE PLACENTA, AND HOW THIS CAN BE PREVENTED
In a landmark study published in Nature Cell Biology, Australian researchers, led by Professor Jose Polo from Monash University and the University of Adelaide and University of Melbourne’s Professor Kanta Subbarao from the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute), have revealed how COVID-19 can infect the human placenta.
Research has shown that COVID-19 infections during pregnancy ...
The timekeeper within: New discovery on how the brain judges time
2023-07-13
From Aristotle’s musings on the nature of time to Einstein’s theory of relativity, humanity has long pondered: how do we perceive and understand time? The theory of relativity posits that time can stretch and contract, a phenomenon known as time dilation. Just as the cosmos warps time, our neural circuits can stretch and compress our subjective experience of time. As Einstein famously quipped, “Put your hand on a hot stove for a minute, and it seems like an hour. Sit with a pretty girl for an hour, and it seems like a minute”.
In new work ...
Tau-based biomarker tracks Alzheimer’s progression
2023-07-13
Two pathologies drive the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Early on, amyloid beta plaques lead the way, but around the time cognitive symptoms arise, tau tangles take over as the driving force and cognition steadily declines. Tracking the course of the disease in individual patients has been challenging because there’s been no easy way to measure tau tangles in the brain.
But now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and Lund University in Lund, Sweden, have identified a form of tau that could serve as a marker to track Alzheimer’s progression. The marker also could be used by Alzheimer’s drug developers to assess ...
Engineering dual carriageways for signals
2023-07-13
Routing signals and isolating them against noise and back-reflections are essential in many practical situations in classical communication as well as in quantum processing. In a theory-experimental collaboration, a team led by Andreas Nunnenkamp from the University of Vienna and Ewold Verhagen based at the research institute AMOLF in Amsterdam has achieved unidirectional transport of signals in pairs of "one-way streets". This research published in Nature Physics opens up new possibilities for more flexible signaling devices.
Devices that allow ...
In historic procedure, donor liver protects heart transplant
2023-07-13
Doctors in Seattle are reporting a history-making case in which a patient received two donor organs, a liver and a heart, to prevent the extreme likelihood that her body would reject a donor heart transplanted alone. In this innovative case, the organ recipient’s own healthy liver was transplanted, domino-like, into a second patient who had advanced liver disease.
The dual-organ recipient, Adriana Rodriguez, 31, of Bellingham, Washington, has recovered well since the Jan. 14, 2023, procedures, said Dr. Shin Lin, a cardiologist ...
Red pill or blue pill? The critical decision to control the superbugs
2023-07-13
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) investigate a pharmacist-led intervention to optimize the oral antimicrobial prescriptions in dental setting
Tokyo, Japan - The battle to stop the increase of superbugs in hospitals has been an ongoing struggle for healthcare professionals. Dentists are currently facing a medical challenge that determines the faith of antimicrobial resistance in healthcare settings. To choose the “red pill” means to embrace the painful truth that bacteria are acquiring resistance to many antimicrobials. Meanwhile, the “blue pill” creates ...
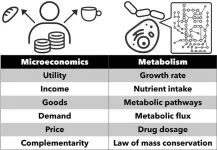
The economic life of cells
2023-07-13
A team from the University of Tokyo has combined economic theory with biology to understand how natural systems respond to change. The researchers noticed a similarity between consumers’ shopping behavior and the behavior of metabolic systems, which convert food into energy in our bodies. The team focused on predicting how different metabolic systems might respond to environmental change by using an economic tool called the Slutsky equation. Their calculations indicated that very different metabolic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Low-dose atropine eyedrops no better than placebo for slowing myopia progressionNIH-funded trial underscores need for more research to head off high myopia