(Press-News.org) Stars beam brightly out of the darkness of space thanks to fusion, atoms melding together and releasing energy. But what if there’s another way to power a star?
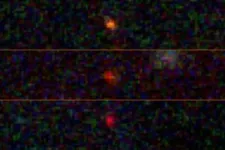
A team of three astrophysicists — Katherine Freese at The University of Texas at Austin, in collaboration with Cosmin Ilie and Jillian Paulin ’23 at Colgate University — analyzed images from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and found three bright objects that might be “dark stars,” theoretical objects much bigger and brighter than our sun, powered by particles of dark matter annihilating. If confirmed, dark stars could reveal the nature of dark matter, one of the deepest unsolved problems in all of physics.
“Discovering a new type of star is pretty interesting all by itself, but discovering it’s dark matter that’s powering this—that would be huge,” said Freese, director of the Weinberg Institute for Theoretical Physics and the Jeff and Gail Kodosky Endowed Chair in Physics at UT Austin.
Although dark matter makes up about 25% of the universe, its nature has eluded scientists. Scientists believe it consists of a new type of elementary particle, and the hunt to detect such particles is on. Among the leading candidates are Weakly Interacting Massive Particles. When they collide, these particles annihilate themselves, depositing heat into collapsing clouds of hydrogen and converting them into brightly shining dark stars. The identification of supermassive dark stars would open up the possibility of learning about the dark matter based on their observed properties.
The research is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Follow-up observations from JWST of the objects’ spectroscopic properties — including dips or excess of light intensity in certain frequency bands — could help confirm whether these candidate objects are indeed dark stars.
Confirming the existence of dark stars might also help solve a problem created by JWST: There seem to be too many large galaxies too early in the universe to fit the predictions of the standard model of cosmology.
“It’s more likely that something within the standard model needs tuning, because proposing something entirely new, as we did, is always less probable,” Freese said. “But if some of these objects that look like early galaxies are actually dark stars, the simulations of galaxy formation agree better with observations.”
The three candidate dark stars (JADES-GS-z13-0, JADES-GS-z12-0, and JADES-GS-z11-0) were originally identified as galaxies in December 2022 by the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES). Using spectroscopic analysis, the JADES team confirmed the objects were observed at times ranging from about 320 million to 400 million years after the Big Bang, making them some of the earliest objects ever seen.
“When we look at the James Webb data, there are two competing possibilities for these objects,” Freese said. “One is that they are galaxies containing millions of ordinary, population-III stars. The other is that they are dark stars. And believe it or not, one dark star has enough light to compete with an entire galaxy of stars.”
Dark stars could theoretically grow to be several million times the mass of our sun and up to 10 billion times as bright as the sun.
“We predicted back in 2012 that supermassive dark stars could be observed with JWST,” said Ilie, assistant professor of physics and astronomy at Colgate University. “As shown in our recently published PNAS article, we already found three supermassive dark star candidates when analyzing the JWST data for the four high redshift JADES objects spectroscopically confirmed by Curtis-Lake et al, and I am confident we will soon identify many more.”
The idea for dark stars originated in a series of conversations between Freese and Doug Spolyar, at the time a graduate student at the University of California, Santa Cruz. They wondered: What does dark matter do to the first stars to form in the universe? Then they reached out to Paolo Gondolo, an astrophysicist at the University of Utah, who joined the team. After several years of development, they published their first paper on this theory in the journal Physical Review Letters in 2008.
Together, Freese, Spolyar and Gondolo developed a model that goes something like this: At the centers of early protogalaxies, there would be very dense clumps of dark matter, along with clouds of hydrogen and helium gas. As the gas cooled, it would collapse and pull in dark matter along with it. As the density increased, the dark matter particles would increasingly annihilate, adding more and more heat, which would prevent the gas from collapsing all the way down to a dense enough core to support fusion as in an ordinary star. Instead, it would continue to gather more gas and dark matter, becoming big, puffy and much brighter than ordinary stars. Unlike ordinary stars, the power source would be evenly spread out, rather than concentrated in the core. With enough dark matter, dark stars could grow to be several million times the mass of our sun and up to 10 billion times as bright as the sun.
Funding for this research was provided by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of High Energy Physics program and the Vetenskapsradet (Swedish Research Council) at the Oskar Klein Centre for Cosmoparticle Physics at Stockholm University.
END
James Webb Telescope catches glimpse of possible first-ever ‘dark stars’
Stars powered with dark matter still need proving but could reveal clues about the nature of one of the universe’s great mysteries
2023-07-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Multidisciplinary team reduced hypothermia in NICU babies during and after surgery
2023-07-13
The percentage of infants from the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) experiencing hypothermia upon operating room (OR) arrival and at any point during the operation decreased from 48.7% to 6.4% and 67.5% to 37.4%, respectively, after implementation of a multidisciplinary quality improvement project at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago. The project and its success were featured in the journal Pediatric Quality and Safety.
About one-third of infants admitted to children’s hospitals’ NICUs require surgery and ...
Argonne engineers to drive innovation with three GAIN funding awards
2023-07-13
Argonne is shaping the future of clean and reliable energy solutions.
Research into nuclear energy is gaining attention as a critical piece of the solution to climate change. As part of this trend, nuclear engineers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have received three new funding awards from the Gateway for Accelerated Innovation in Nuclear (GAIN) initiative. These awards recognize the valuable contributions of Argonne’s world-class nuclear engineers and facilities in this field.
Among ...
C-Path and Vivpro formalize partnership to accelerate drug development
2023-07-13
TUCSON, Ariz., July 13, 2023 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path), a leading global nonprofit committed to expediting drug development through the acceleration of regulatory-endorsed solutions, today announced a newly formalized Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Vivpro, an industry-leading provider of a revolutionary biointelligence software platform and innovative services. The partnership will enhance C-Path’s core competencies in accelerating drug development, by utilizing advanced data analytics and deep machine learning insights offered by Vivpro to further revolutionize ...
Sanford health rare disease data registry partners with C-Path’s RDCA-DAP, cure Mito Foundation to aggregate rare disease data in platform
2023-07-13
TUCSON, Ariz., July 12, 2023 — Critical Path Institute (C-Path) announced today that the Coordination of Rare Diseases based at Sanford Research (CoRDS), in partnership with Cure MITO, will contribute its mitochondrial disorders data from its international patient registry to the C-Path-managed Rare Disease Cures Accelerator-Data and Analytics Platform (RDCA-DAP®).
RDCA-DAP provides a centralized and standardized infrastructure to support and accelerate rare disease characterization targeted to accelerate clinical drug development. Additionally, the platform advances best practices to support the rigorous conduct of natural history ...
Scripps Research receives momentous award from NIH to lead key programs in national All of Us Research Program
2023-07-13
LA JOLLA, CA—Scripps Research announced today that the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has renewed funding for its Translational Institute to continue its work enrolling and engaging participants in the All of Us Research Program. The initial funding of $54 million will support Scripps Research Translational Institute’s work with a nationwide consortium to help build one of the largest, most diverse health research resources of its kind. The project is expected to last five years, with anticipated total funding ...
Astronomers identify the coldest star yet that emits radio waves
2023-07-13
Astronomers at the University of Sydney have shown that a small, faint star is the coldest on record to produce emission at radio wavelength.
The ‘ultracool brown dwarf’ examined in the study is a ball of gas simmering at about 425 degrees centigrade – cooler than a typical campfire – without burning nuclear fuel.
By contrast, the surface temperature of the Sun, a nuclear inferno, is about 5600 degrees.
While not the coldest star ever found, it is the coolest so far analysed using radio astronomy. The findings are published today in The Astrophysical Journal.
Lead author and PhD student in the School of Physics, Kovi Rose, said: “It’s very rare ...
UT Health Science Center San Antonio develops tool that counts brain lesions in seconds
2023-07-13
SAN ANTONIO (July 13, 2023) — An artificial intelligence (AI) tool developed at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio accurately counts brain lesions on MRI scans within seconds. Once it is adapted to the clinic, the AI tool should help neuroradiologists to evaluate patients’ brain diseases at earlier stages.
“Certain kinds of brain lesions are tremendously difficult to quantify without AI,” said researcher Mohamad Habes, PhD, of the health science center’s Glenn Biggs Institute for Alzheimer’s and Neurodegenerative ...
New ways of getting to the heart of the matter
2023-07-13
Peter Keyel, an associate professor in Texas Tech University’s Department of Biological Sciences, has received an Innovative Project Award from the American Heart Association to study atherosclerosis, the condition that causes arteries to thicken and can trigger a variety of devastating health complications.
Statistics indicate diseases linked to atherosclerosis are the leading cause of death in the U.S. with as many as half of Americans between the ages of 45 and 84 having the condition but being unaware of its slow progression and ...
Researchers establish criterion for nonlocal quantum behavior in networks
2023-07-13
A new theoretical study provides a framework for understanding nonlocality, a feature that quantum networks must possess to perform operations inaccessible to standard communications technology. By clarifying the concept, researchers determined the conditions necessary to create systems with strong, quantum correlations.
The study, published in Physical Review Letters, adapts techniques from quantum computing theory to create a new classification scheme for quantum nonlocality. This not only allowed the researchers to unify ...
Youth of color turn to TikTok for diet, fitness information
2023-07-13
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Thursday, July 13, 2023
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Youth of Color Turn to TikTok for Diet, Fitness Information
A new study found that social media platforms, particularly TikTok and Instagram, are ideal spaces to educate and guide US youth of color on healthy weight management and ultimately reduce racial inequities in obesity.
Nearly 1 in 4 adolescents in the United States experienced obesity from 2017 to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
Researchers find that landowner trust, experience influence feral hog management
Breaking down the battery problem
[Press-News.org] James Webb Telescope catches glimpse of possible first-ever ‘dark stars’Stars powered with dark matter still need proving but could reveal clues about the nature of one of the universe’s great mysteries