m6A mRNA modification potentiates Th17 functions to inflame autoimmunity
2023-07-14
(Press-News.org)
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most extensive studied RNA modification across various species, and the important effect of m6A modification in immune system has been revealed in distinct contexts, including mRNA metabolism, cell differentiation, proliferation and response to stimulation. Previous studies from Hua-Bing Li group demonstrated that m6A methyltransferase METTL3 control T cells homeostasis and sustain the suppressive function of regulatory T cells (Tregs). However, the role of m6A methyltransferase in other subtype of T cells remains unknown.
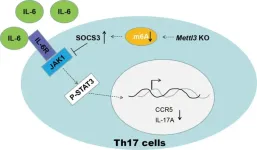
T helper cells 17 (Th17) play a pivotal role in host defense and autoimmunity. In this study, the scientists found that the loss of METTL3 in T cells caused serious defect of Th17 cell differentiation, and impeded the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). They generated Mettl3f/fIl17aCre mice and observed that METTL3 deficiency in Th17 cells significantly suppressed the development of EAE and displayed less Th17 cells infiltration into CNS.
m6A modification has been reported to participate in RNA metabolism, predominantly affecting RNA stability. SOCS gene mRNAs have been documented as m6A targets in CD4+ T cells, and deletion of METTL3 led to attenuation of SOCS mRNA decay. Here, they verified that depletion of METTL3 facilitated SOCS3 RNA stability, then further attenuated IL-17A and CCR5 expression, disrupted Th17 cells differentiation and infiltration, and eventually attenuated the process of EAE.
Collectively, the scientists highlight that m6A modification sustains Th17 cell function, which provides new insights into the regulatory network of Th17 cells, and also implies a potential therapeutic target for Th17 cell mediated autoimmune disease.
Wang, X., Chen, C., Sun, H., Mao, K., Yao, J., Zhang, W., Zhan, M., Li, H.B., Zhang, Z., Zhu, S., et al. (2023). m6A mRNA modification potentiates Th17 functions to inflame autoimmunity. Sci China Life Sci 66, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-022-2323-4
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-14
Patients who engage in light exercise while undergoing dialysis are physically fitter and are admitted to hospital less frequently than those who do not. These are the findings of a large-scale study conducted by a consortium led by the Technical University of Munich (TUM). The researchers believe that exercise programs should be offered to dialysis patients as standard.
Around 558,000 people in the United States have such severely impaired kidney function that they require dialysis several times per week. In Germany, about 80,000 people regularly undergo ...
2023-07-14
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a ubiquitous virus, and most people are infected at some point in their lives. HPV can infect epithelial cells of the skin and mucosa at various sites. There are more than 100 known HPV subtypes, most of which cause only benign lesions such as warts and condyloma. Thanks to a well-functioning immune response, most people who are infected don’t develop serious symptoms. However, some HPV subtypes are not so harmless. These subtypes, and especially subtype HPV16, can transform infected cells to become neoplastic, and these malignant transformed cells then develop into precancerous ...
2023-07-14
A team led by researchers at the Mechanisms of Inherited Kidney Disorders (MIKADO) group at the University of Zurich (Zurich, Switzerland) has used Insilico Medicine’s generative artificial intelligence (AI) target discovery engine, PandaOmics, to identify actionable drug targets for the lysosomal storage disease cystinosis and to validate them in preclinical models of the disease. These results, which open new therapeutic possibilities for this devastating disease, were published June 14 in the journal Nature Communications. Collaborators include scientists from Microsoft Research-University of Trento Centre for Computational ...
2023-07-14
University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have discovered a way to identify pregnant women at risk of preeclampsia, a serious disorder characterized by high blood pressure and kidney dysfunction which can result in premature delivery, seizures and even death. Complications from the condition are the second-leading cause of maternal death around the world.
The UVA scientists, led by Charles E. Chalfant, PhD, found that they could predict the risk of preeclampsia by examining lipids (fats) ...
2023-07-14
New observations using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) have distinguished the sites of star formation and a possible site of star death from the surrounding nebula in a galaxy 13.2 billion light-years away. This is the farthest that such structures have been observed.
A team led by Yoichi Tamura, an astronomer at Nagoya University, attempted high-resolution observations of MACS0416_Y1, located 13.2 billion light-years away in the constellation Eridanus. Previous observations of this galaxy by the same team had detected radio waves emitted by both oxygen and dust, two components of interstellar nebulae. Detailed observations of the ...
2023-07-14
A research group led by Dr. Jialei He of Nagoya University's Graduate School of Engineering has developed a method for processing cholesteric liquid crystals (CLCs) into micrometer-sized spherical particles. CLCs are a type of liquid crystal that possess a helical structure, giving them unique optical properties and the ability to selectively reflect light. By combining spherical CLC particles with commercially available pigments, the researchers developed a unique anti-counterfeiting QR code that can only be displayed under a specific circular polarizer. The results were published in the journal Advanced Optical Materials.
CLCs are an example of how nature can be ...
2023-07-14
Ishikawa, Japan -- Although grasping objects is a relatively straightforward task for us humans, there is a lot of mechanics involved in this simple task. Picking up an object requires fine control of the fingers, of their positioning, and of the pressure each finger applies, which in turn necessitates intricate sensing capabilities. It’s no wonder that robotic grasping and manipulation is a very active research area within the field of robotics.
Today, industrial robotic hands have replaced humans in various complex and hazardous ...
2023-07-14
Nursing homes were a key battleground during the COVID pandemic and prioritized for distribution of PPE, vaccines, and COVID testing kits. However, new research shows that monoclonal antibodies and oral antiviral drugs were not used in these facilities as much as would be expected given the high-risk of resident populations.
Brian McGarry, PhD, with the University of Rochester Medical Center, and collaborators at Harvard University, authored the new study, which appears today in JAMA. The authors examined data compiled ...
2023-07-14
The neurons in our bodies are dotted with tiny pores that let essential molecules pass in and out of our cells. Neurons need these channels to send the signals that allow us to move, think, and perceive the world around us. Now, structural biologists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) have captured never-before-seen images of one of the largest pores in human neurons. It’s called calcium homeostasis modulator protein 1, or CALHM1 for short.
Previous studies have shown that mutations in the Cahlm1 gene may be a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease. CSHL’s new ...
2023-07-14
Stony Coral Tissue Loss Disease (SCTLD) has wreaked havoc on coral reefs across the Caribbean, resulting in significant mortality of various coral species, including Pseudodiploria strigosa, which has been particularly affected in the Mexican Caribbean. In response to the decreased abundance and colony density caused by SCTLD, scientists have explored larval-based restoration methods, despite concerns about disease transmission. A new PeerJ Life & Environment study reveals that even colonies affected by SCTLD can play a vital role in the assisted sexual reproduction for the restoration of SCTLD-susceptible species.
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] m6A mRNA modification potentiates Th17 functions to inflame autoimmunity