(Press-News.org) About The Study: History of present illnesses generated by a chatbot or written by senior internal medicine residents were graded similarly by internal medicine attending physicians. These findings underscore the potential of chatbots to aid clinicians with medical documentation.
Authors: Ashwin Nayak, M.D., M.S., of Stanford University in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.2561)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/10.1001/jamainternmed.2023.2561?guestAccessKey=cf47b20f-a168-44da-9d77-0565e5e96a36&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=071723
END
Comparison of history of present illness summaries generated by a chatbot and senior internal medicine residents
JAMA Internal Medicine
2023-07-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Addressing adaptation inequalities in climate research
2023-07-17
A new study proposes ways to better incorporate adaptation in climate change research, addressing the uneven distribution of adaptation capacities and needs worldwide.
Research on adaptation to the risks posed by climate change has witnessed significant growth in the past decade, with increasing recognition of its urgency in policy agendas at the international, national, and local levels. Adaptation needs and capacities are not evenly distributed worldwide, with countries in the Global South generally experiencing the highest challenges. ...
Heading frequency and risk of cognitive impairment in retired male professional soccer players
2023-07-17
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that repetitive heading during a professional soccer career is associated with an increased risk of cognitive impairment in later life. Further study is needed to establish the upper threshold for heading frequency to mitigate this risk.
Authors: Weiya Zhang, Ph.D., of the University of Nottingham in Nottingham, United Kingdom, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.23822)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
COVID-19 vaccines saved dementia patients' lives in nursing homes
2023-07-17
Deaths among older adults with dementia fell starkly in nursing homes and long-term care centers after COVID-19 vaccinations became available, yet remained high for those living at home, according to a new study led by UC San Francisco.
The nationwide study published July 17, 2023 in JAMA Neurology, is the first to use data from 2019 to 2022 to quantify “excess” deaths – or those above what would have been anticipated had there been no pandemic – taking into account age, sex, racial and ethnic groups, as well as the settings where people died.
In the first year, there were 509,179 dementia-related ...
Reprogramming the shape of virus capsids could advance biomedicine
2023-07-17
Bioengineers have found a way to program the size and shape of virus particles by combining viral protein building blocks and templates made from DNA. The resulting nanostructures could have applications in vaccine development and transporting drugs inside the body.
Virus capsid proteins—the proteins that shield the genome of a virus—can be used to build precisely structured protein assemblies. Their shapes and geometry, however, depend largely on the virus strain. Reprogramming these assemblies, no matter the original ...
World-first clinical trial to help millions with penicillin allergies
2023-07-17
Penicillin allergy affects more than 25 million people in the United States (up to 1 in 10 Americans) and has been shown to lead to particularly poor health outcomes in pregnant women and surgical patients. It is also a public health threat, leading to antibiotic resistance and infections in hospitalized patients that can be life threatening.
Seventy-five% or more penicillin allergy labels come on by age 3 due to, for example, confusion with a viral rash. The majority of these rashes were never allergic, but the labels ‘stick’ into adulthood and carry many adverse consequences.”
Many low-risk patients with a penicillin allergy were able to have their ...
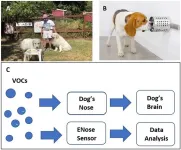
Scent dogs can detect COVID-19 more rapidly and accurately than current tests
2023-07-17
Scent dogs may represent a cheaper, faster and more effective way to detect COVID-19, and could be a key tool in future pandemics, a new review of recent research suggests. The review, published in De Gruyter’s Journal of Osteopathic Medicine, found that scent dogs are as effective, or even more effective, than conventional COVID-19 tests such as RT-PCR.
Dogs possess up to 300 million olfactory cells, compared to just 5 or 6 million in humans, and use one-third of their brains to process scent information, ...
Robotics: New skin-like sensors fit almost everywhere
2023-07-17
“Detecting and sensing our environment is essential for understanding how to interact with it effectively,” says Sonja Groß. An important factor for interactions with objects is their shape. “This determines how we can perform certain tasks,” says the researcher from the Munich Institute of Robotics and Machine Intelligence (MIRMI) at TUM. In addition, physical properties of objects, such as their hardness and flexibility, influence how we can grasp and manipulate them, for example.
Artificial hand: interaction with the robotic system
The ...
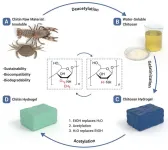
Team fabricates chitin hydrogel via chemical transformation of chitosan
2023-07-17
Chitin hydrogel is recognized as a promising material for a variety of biomedical applications. Its biocompatibility and biodegradability make it useful in tissue repair, artificial organs, and wound healing. Yet scientists continue to face challenges in fabricating chitin hydrogel. A team of researchers has developed a green, efficient and scalable preparation method for chitin hydrogels.
The team’s work provides a rational strategy to fabricate chitin hydrogels and paves the way for its practical applications as a superior biomedical material.
Their ...
Report highlights public health impact of serious harms from diagnostic error in US
2023-07-17
Improving diagnosis in health care is a moral, professional and public health imperative, according to the U.S. National Academy of Medicine. However, little is known about the full scope of harms related to medical misdiagnosis — current estimates range widely. Using novel methods, a team from the Johns Hopkins Armstrong Institute Center for Diagnostic Excellence and partners from the Risk Management Foundation of the Harvard Medical Institutions sought to derive what is believed to be the first rigorous national estimate of permanent disability and death from diagnostic error.
The original research article ...
NUTRITION 2023 press materials available now
2023-07-17
Press materials are now available for NUTRITION 2023, the annual flagship meeting of the American Society for Nutrition (ASN). Top nutrition scientists and practitioners from around the world will gather to share the latest research findings on food and nutrition during NUTRITION 2023, held July 22-25 at the Sheraton Boston.
Register for a press pass to attend NUTRITION 2023 in person or to access embargoed press materials before the meeting. Explore the meeting schedule, poster presentations, and oral presentations to see all the exciting research topics covered at this year’s meeting.
EMBARGOED MATERIALS
Researchers Identify Genes ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Breaking through water treatment limits with defect-free, high-efficiency next-generation ceramic filters!
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
[Press-News.org] Comparison of history of present illness summaries generated by a chatbot and senior internal medicine residentsJAMA Internal Medicine