From nature, a solution to save coral from climate change
Researchers at Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia – IIT and University of Milan-Bicocca have demonstrated the efficacy of a natural substance in protecting coral from the damage caused by climate change.
2023-07-19
(Press-News.org)
Genoa (Italy), 19 July 2023 – Researchers at Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Italian Institute of Technology - IIT) and Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca (University of Milan-Bicocca), in cooperation with Acquario di Genova (Genoa Aquarium) in Italy, have recently published a study in ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, which demonstrates the efficacy of curcumin, a natural antioxidant substance extracted from turmeric, in reducing coral bleaching, a phenomenon caused primarily by climate change. The research group developed a biodegradable biomaterial to deliver the molecule without causing damage to the surrounding marine environment. Tests conducted at the Genoa Aquarium have shown significant efficacy in preventing coral bleaching.
Coral bleaching is a phenomenon that, in extreme events, causes the death of these organisms with devastating consequences for coral reefs, which are crucial for the global economy, the protection of coastlines from natural disasters, and marine biodiversity. Most corals live in symbiosis with microscopic algae, which are indispensable for their survival and are responsible for their vibrant colours. Due to climate change, sea and ocean temperatures are rising, a condition that disrupts the relationship between these two organisms. When this happens, the coral, which turns white due to the loss of algae, literally risks starvation.
In recent years, as a result of climate change, this condition has affected most of the world’s major coral barrier reefs, including Australia’s Great Barrier Reef. However, to date there are no effective methods of countering this phenomenon and preventing coral bleaching without seriously endangering the survival of these habitats and the exceptional biodiversity associated with them.
Researchers at Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia and the University of Milan-Bicocca, in collaboration with the Genoa Aquarium, have demonstrated the efficacy of a natural molecule, curcumin, in blocking coral bleaching caused by climate change. Curcumin is administered to the coral in a controlled manner by applying a biomaterial based on zein, a protein derived from maize, a system developed by the partners themselves in order to ensure safety for the environment.
During the tests, performed at the Genoa Aquarium, overheating conditions in tropical seas were simulated by raising the water temperature up to 33°C. Under these conditions, all untreated corals were affected by the bleaching phenomenon as would occur in nature, while, on the contrary, all specimens treated with curcumin showed no signs of this tendency, a result that makes this technique effective in reducing the susceptibility of corals to thermal stress. A coral species (Stylophora pistillata) typical of the tropical Indian Ocean, included in the IUCN (International Union for the Conservation of Nature) Red List of endangered species, was used for this study.
“This technology is the subject of a patent application that has been filed, and in fact the next steps of this research will focus on its application in nature and on a large scale,” said Marco Contardi, first author of the study, research affiliate of the Smart Materials group at Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia and researcher in DISAT (Department of Environmental and Earth Sciences) at the University of Milan-Bicocca. “At the same time, we will examine the use of other antioxidant substances of natural origin to block the bleaching process and thus prevent the destruction of coral reefs.”
“The use of new biodegradable and biocompatible materials capable of releasing natural substances that can reduce coral bleaching is something entirely new,” said Simone Montano, researcher at DISAT and deputy director of the MaRHE centre (Marine Research and High Education Centre) at the University of Milan-Bicocca. “I strongly believe that this innovative approach will represent a significant breakthrough in the development of strategies for the recovery of marine ecosystems.”
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-07-19
About The Study: The results of this study of 1.6 million patients suggest that residence within more disadvantaged neighborhoods was associated with higher risk of dementia among older veterans integrated in a national health care system.
Authors: Christina S. Dintica, Ph.D., of the University of California, San Francisco, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.2120)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...
2023-07-19
A study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society found that immediately after retirement, white adults tended to experience a significant decline in cognitive function, whereas Black adults experienced minimal cognitive decline. White men showed the steepest post-retirement cognitive decline across sex/race combinations, whereas Black women showed the least decline.
White women performed better cognitively at retirement than other race/sex subgroups, and after retirement, their cognitive functioning declined at a rate that was slightly ...
2023-07-19
New research published in Contemporary Economic Policy indicates that Disability Insurance (DI) may improve economic opportunities for children whose parents have health conditions that limit work.
The study included 52,575 parent-child pairs in the United States. When investigators examined economic mobility patterns for children whose parents reported work-limiting disability, they found that children had less upward economic mobility and more downward mobility relative to children of non-limited parents. Children of parents ...
2023-07-19
A randomized controlled trial conducted in Canada and published in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry found that Nurse-Family Partnership (NFP), a nurse-home visiting program, improved child language and mental health at age 2 years when compared with existing services. Rates of child injuries and maternal subsequent pregnancies were similar in the two groups.
This real-world effectiveness trial involved sustained research-policy-practice collaborations from 2011–2022. Investigators successfully reached/enrolled and sustained engagement with 739 participants (368 NFP, 371 comparison) and their 737 children for ...
2023-07-19
Functional Family Therapy is a family-based intervention for youth with behavior problems, and although it’s been implemented in 45 states in the U.S and in nine other high-income countries, a recent analysis of published and unpublished studies found that the therapy is not consistently more or less effective than other treatments, including various forms of individual, family, and group interventions.
The authors of the analysis, which is published in Campbell Systematic Reviews and included 20 studies, also noted that there is insufficient evidence ...
2023-07-19
In the late 1950s and 1960s, more than 12,000 malformed babies with short arms and legs were born as a side effect of thalidomide, a drug sold to pregnant women to prevent morning sickness. The tragedy was caused by the drug's side effect, which exists in a racemic mixture of two mirror-image forms. Research to determine the molecular structure of various compounds is essential for understanding biological phenomena and developing drugs to treat diseases and is mainly based on the interpretation ...
2023-07-19
Overview
A research team from the Department of Applied Chemistry and Life Science at the Toyohashi University of Technology (Professor Ryugo Tero et al.) discovered a phenomenon in which specific lipids were concentrated on graphene oxide in a multicomponent lipid bilayer membrane serving as a cell membrane model. This research team also clarified the mechanism by which the components of “lipid rafts" (where important cell membrane reactions such as neurotransmission and metabolism occur) gather owing to the surface characteristics of graphene oxide. This discovery is ...
2023-07-19
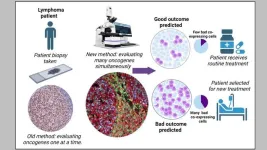
A team of researchers from the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore (NUS), led by Assistant Professor Anand Jeyasekharan, has discovered a unique combination of oncogenes that could predict treatment resistance, and hence unfavourable outcomes, of patients with Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common type of blood cancer in Singapore and globally.
This unique oncogenic combination, serving as an indicator of treatment resistance, can be detected through state-of-the-art technology. The researchers, however, went a step ...
2023-07-19
SINGAPORE, XX July 2023 – Long-running research by Duke-NUS Medical School into the omega-3 transporter protein Mfsd2a has shown that it plays a key role in a specific mechanism that prevents the liver from storing too much fat from food. Published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, this latest study by Duke-NUS and collaborators from Singapore General Hospital (SGH) signals the possibility that a dietary supplement could be developed to help prevent non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Eating too much fatty food increases the risk of many health problems, including cardiovascular disease, obesity, diabetes and NAFLD. The excess fat that accumulates in the ...
2023-07-19
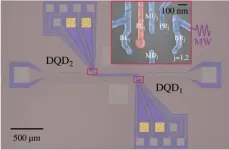
A team led by Prof. GUO Guoping and Prof. CAO Gang from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborating with Sigmund Kohler from Materials Science Institute of Madrid, developed a response theory applicable to strongly coupled and multiqubit systems. Their study was published in Physical Review Letters.
Semiconductor quantum dot (QD) strongly coupled to microwave photons is the key to investigate light-matter interactions. In previous studies, the team used high-impedance super-conducting resonant cavity to implement the strong coupling of the QD-cavity hybrid system. Based on this strong ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] From nature, a solution to save coral from climate change
Researchers at Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia – IIT and University of Milan-Bicocca have demonstrated the efficacy of a natural substance in protecting coral from the damage caused by climate change.