(Press-News.org) Functional Family Therapy is a family-based intervention for youth with behavior problems, and although it’s been implemented in 45 states in the U.S and in nine other high-income countries, a recent analysis of published and unpublished studies found that the therapy is not consistently more or less effective than other treatments, including various forms of individual, family, and group interventions.
The authors of the analysis, which is published in Campbell Systematic Reviews and included 20 studies, also noted that there is insufficient evidence to draw conclusions about the effects of Family Functional Therapy compared with no treatment.
“Functional Family Therapy is actively marketed as a 'scientifically proven' or 'evidence-based' program, but there are serious concerns about the quality of the evidence for FFT and available evidence does not support claims that FFT is consistently more effective than other treatments,” said corresponding author Julia H. Littell, PhD, Professor Emerita of Bryn Mawr College.
Dr. Littell and her colleagues looked at the best available studies and found that they all had some serious risks of bias. “At least three-quarters of these studies did not fully report their results. Some FFT studies have not made any of their results public. Available data show that results are inconsistent within and across FFT studies,” she said. “Also, information on the cost effectiveness of FFT appears to be based on inflated estimates of treatment effects; therefore, claims about FFT's cost effectiveness are not convincing.”
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cl2.1324
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
Campbell Systematic Reviews is an open access journal prepared under the editorial control of the Campbell Collaboration. The journal publishes systematic reviews, evidence and gap maps, and methods research papers.
About Wiley
Wiley is a knowledge company and a global leader in research, publishing, and knowledge solutions. Dedicated to the creation and application of knowledge, Wiley serves the world’s researchers, learners, innovators, and leaders, helping them achieve their goals and solve the world's most important challenges. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
How effective is Functional Family Therapy for addressing youth behavior problems?
2023-07-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Developing NMR method for drug structure elucidation
2023-07-19
In the late 1950s and 1960s, more than 12,000 malformed babies with short arms and legs were born as a side effect of thalidomide, a drug sold to pregnant women to prevent morning sickness. The tragedy was caused by the drug's side effect, which exists in a racemic mixture of two mirror-image forms. Research to determine the molecular structure of various compounds is essential for understanding biological phenomena and developing drugs to treat diseases and is mainly based on the interpretation ...
Concentration of cell membrane components with nanocarbon materials
2023-07-19
Overview
A research team from the Department of Applied Chemistry and Life Science at the Toyohashi University of Technology (Professor Ryugo Tero et al.) discovered a phenomenon in which specific lipids were concentrated on graphene oxide in a multicomponent lipid bilayer membrane serving as a cell membrane model. This research team also clarified the mechanism by which the components of “lipid rafts" (where important cell membrane reactions such as neurotransmission and metabolism occur) gather owing to the surface characteristics of graphene oxide. This discovery is ...
NUS researchers develop novel approach for predicting resistance against cancer therapy
2023-07-19
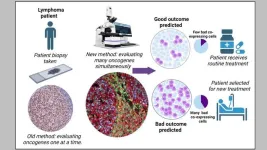
A team of researchers from the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore (CSI Singapore) at the National University of Singapore (NUS), led by Assistant Professor Anand Jeyasekharan, has discovered a unique combination of oncogenes that could predict treatment resistance, and hence unfavourable outcomes, of patients with Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the most common type of blood cancer in Singapore and globally.
This unique oncogenic combination, serving as an indicator of treatment resistance, can be detected through state-of-the-art technology. The researchers, however, went a step ...
Singapore scientists find that a special omega-3 lipid might prevent fatty liver disease
2023-07-19
SINGAPORE, XX July 2023 – Long-running research by Duke-NUS Medical School into the omega-3 transporter protein Mfsd2a has shown that it plays a key role in a specific mechanism that prevents the liver from storing too much fat from food. Published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, this latest study by Duke-NUS and collaborators from Singapore General Hospital (SGH) signals the possibility that a dietary supplement could be developed to help prevent non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Eating too much fatty food increases the risk of many health problems, including cardiovascular disease, obesity, diabetes and NAFLD. The excess fat that accumulates in the ...
New theory developed for periodically driven quantum dots-cavity system
2023-07-19
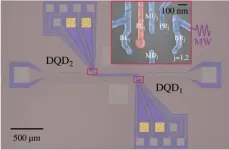
A team led by Prof. GUO Guoping and Prof. CAO Gang from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborating with Sigmund Kohler from Materials Science Institute of Madrid, developed a response theory applicable to strongly coupled and multiqubit systems. Their study was published in Physical Review Letters.
Semiconductor quantum dot (QD) strongly coupled to microwave photons is the key to investigate light-matter interactions. In previous studies, the team used high-impedance super-conducting resonant cavity to implement the strong coupling of the QD-cavity hybrid system. Based on this strong ...
3D digital technologies tackling mental injury prevention in healthcare
2023-07-19
The Safety Sensescaping project, funded by WorkSafe's WorkWell Mental Health Improvement Fund, is part of Peninsula Health’s Thriving in Health program, which aims to create safe and mentally healthy environments for healthcare workers to thrive in.
Project lead and RMIT Senior Lecturer Dr Olivier Cotsaftis worked with doctors, nurses and non-clinicians at Peninsula Health for three years to understand the psychosocial hazards in their workplace and find design-led solutions to prevent mental injury.
Cotsaftis said hospital scrubs were an unconscious source of stress for many healthcare workers.
Designed according to the standard male ...
VERA unveils surroundings of rapidly growing black holes
2023-07-19
An international team of astronomers used the state-of-the-art capability of VERA, a Japanese network of radio telescopes operated by NAOJ, to uncover valuable clues about how rapidly growing “young” supermassive black holes form, grow, and possibly evolve into more powerful quasars.
It is now widely accepted that nearly every active galaxy harbors a supermassive black hole at its core, with masses ranging from millions to billions of times that of the Sun. The growth history by which these black holes have gained such huge masses, however, remains an open question.
Led by Mieko Takamura, ...
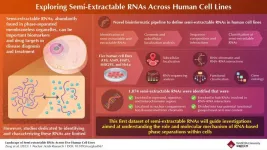
Unraveling the mystery of semi-extractable RNAs from human cell lines
2023-07-19
Membraneless organelles (MLOs), also known as “biomolecular condensates,” are formed by the biological process of liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS). MLOs are highly dynamic bodies containing proteins and nucleic acids. While the role of proteins in LLPS has been extensively investigated, there is a growing interest in the scientific community to understand the role of RNAs—the nucleic acid responsible for innumerable biological functions including coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes, and ultimately proteins—in phase separation.
Recent studies have revealed that MLOs are rich in RNAs ...
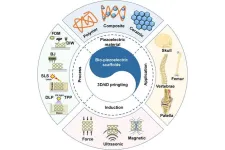
3D/4D printed bio-piezoelectric smart scaffolds for next-generation bone tissue engineering
2023-07-19
Piezoelectricity in native bones has been well recognized as the key factor in bone regeneration. However, the current additive-manufactured scaffolds mainly focus on the reconstruction of bionic topological structure and mechanical microenvironment, while the crucial electrical microenvironment (EM) in bone regeneration is neglected. Piezoelectricity in native bones has been well recognized as the key factor in bone regeneration. However, the current additive-manufactured scaffolds mainly focus on the ...
Study identifies how diabetes slows healing in the eye
2023-07-19
Investigators from Cedars-Sinai have provided new understanding of how diabetes delays wound healing in the eye, identifying for the first time two related disease-associated changes to the cornea.
The findings, published today in the peer-reviewed journal Diabetologia, also identified three therapeutic pathways that reversed these changes and partially restored wound-healing function to the cornea—a discovery that could ultimately inform new treatments for diabetes.
“We have found that diabetes induces more cellular changes than we were aware of previously,” ...