(Press-News.org) An international team of astronomers used the state-of-the-art capability of VERA, a Japanese network of radio telescopes operated by NAOJ, to uncover valuable clues about how rapidly growing “young” supermassive black holes form, grow, and possibly evolve into more powerful quasars.
It is now widely accepted that nearly every active galaxy harbors a supermassive black hole at its core, with masses ranging from millions to billions of times that of the Sun. The growth history by which these black holes have gained such huge masses, however, remains an open question.
Led by Mieko Takamura, a graduate student at the University of Tokyo, an international team focused on a distinct category of active galaxies known as Narrow-line Seyfert 1 (NLS1) galaxies. These galaxies are suspected to contain relatively small yet rapidly growing massive black holes, thus offering a potential opportunity to study an early evolutionary stage of these cosmic monsters. To gain a deeper understanding of the immediate surroundings of these peculiar black holes, the team observed the cores of six nearby active NLS1 galaxies using VERA – a radio telescope network with an eyesight over 100,000 times more powerful than the human eye. In particular, the team leveraged the newly enhanced ultra-wideband recording capability of VERA, enabling them to detect faint “polarized” radio waves emanating from the core of these galaxies with unprecedented precision.
A portion of radio waves emitted near supermassive black holes is known to exhibit polarization. As this polarized emission propagates through the magnetized gas surrounding the black hole, the plane of polarization gradually rotates, causing an effect known as Faraday rotation. The extent of this rotation (at a given wavelength) is proportional to the gas density and the strength of the magnetic field within the propagating medium. Therefore, polarization and Faraday rotation provide valuable insights into the immediate environment surrounding a central black hole.
Together with the sharpest-ever view towards the cores of these galaxies, the new data have unveiled significantly greater Faraday rotation compared to measurements obtained towards older, more-massive, well-developed black holes. This indicates the presence of abundant gas in the nuclear regions of these galaxies, facilitating the rapid growth of the central black holes. “Supermassive black holes undergo a growth process similar to that of humans,” says Takamura. “The black holes we observed have characteristics comparable to a food enthusiast, akin to young boys and girls who have a strong craving for rice.”
These results appeared as Takamura et al. “Probing the heart of active narrow-line Seyfert 1 galaxies with VERA wideband polarimetry” in the Astrophysical Journal.
END
VERA unveils surroundings of rapidly growing black holes
2023-07-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
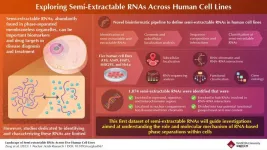
Unraveling the mystery of semi-extractable RNAs from human cell lines
2023-07-19
Membraneless organelles (MLOs), also known as “biomolecular condensates,” are formed by the biological process of liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS). MLOs are highly dynamic bodies containing proteins and nucleic acids. While the role of proteins in LLPS has been extensively investigated, there is a growing interest in the scientific community to understand the role of RNAs—the nucleic acid responsible for innumerable biological functions including coding, decoding, regulation, and expression of genes, and ultimately proteins—in phase separation.
Recent studies have revealed that MLOs are rich in RNAs ...
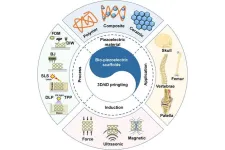
3D/4D printed bio-piezoelectric smart scaffolds for next-generation bone tissue engineering
2023-07-19
Piezoelectricity in native bones has been well recognized as the key factor in bone regeneration. However, the current additive-manufactured scaffolds mainly focus on the reconstruction of bionic topological structure and mechanical microenvironment, while the crucial electrical microenvironment (EM) in bone regeneration is neglected. Piezoelectricity in native bones has been well recognized as the key factor in bone regeneration. However, the current additive-manufactured scaffolds mainly focus on the ...
Study identifies how diabetes slows healing in the eye
2023-07-19
Investigators from Cedars-Sinai have provided new understanding of how diabetes delays wound healing in the eye, identifying for the first time two related disease-associated changes to the cornea.
The findings, published today in the peer-reviewed journal Diabetologia, also identified three therapeutic pathways that reversed these changes and partially restored wound-healing function to the cornea—a discovery that could ultimately inform new treatments for diabetes.
“We have found that diabetes induces more cellular changes than we were aware of previously,” ...
Plenary closeup: Biomolecular condensates the foundation for innovations to come
2023-07-19
Biomolecular condensates, the tiny combinations of proteins and mRNA forming membrane-less compartments within cells, have big potential implications for the future of not just plants but humans. On Sunday, August 6, at 9:00 am, the #PlantBio2023 plenary “Highlights of New and Emerging Research on Biomolecular Condensates in Plants” will dive into this new field and its recent discoveries.
“It’s going to be a great way to get your feet wet and understand what biomolecular condensates are,” ...
New Black baby equity clinic helps infants and moms flourish
2023-07-19
Not being heard, not being taken seriously and being misunderstood by health care providers often describes a routine medical visit for many Black parents. For Black parents of young children, that lack of cultural understanding can lead to grim consequences for the health of the baby and mother.
According to the California Department of Public Health, Black babies in the Bay Area are two to three times more likely to be born too soon or too small or to die before their first birthday, compared to white babies. Scientific evidence points to structural racism and a systemic lack ...
Dual wavelengths of light effective against antibiotic-resistant bacterium
2023-07-19
Scientists have combined two light wavelengths to deactivate a bacterium that is invulnerable to some of the world’s most widely used antibiotics, giving hope that the regime could be adapted as a potential disinfectant treatment.
Under the guidance of project leader Dr Gale Brightwell, scientists at New Zealand’s AgResearch demonstrated the novel antimicrobial efficiency of a combination of two light wavelengths against a ‘superbug’ known as antibiotic-resistant extended-spectrum beta-lactamase E. coli.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a major global threat of ...
Learning from superheroes and AI: UW researchers study how a chatbot can teach kids supportive self-talk
2023-07-19
At first, some parents were wary: An audio chatbot was supposed to teach their kids to speak positively to themselves through lessons about a superhero named Zip. In a world of Siri and Alexa, many people are skeptical that the makers of such technologies are putting children’s welfare first.
Researchers at the University of Washington created a new web app aimed to help children develop skills like self-awareness and emotional management. In Self-Talk with Superhero Zip, a chatbot guided pairs of siblings ...
Consortium explores energy-efficient electronics and photonics
2023-07-19
The University of Texas at Arlington is part of a new consortium funded by the Department of Energy that involves the development of new technologies and college courses covering everything from radiation detection to nuclear engineering.
The grant also will help UTA develop 2D materials that can be integrated into new hand-held photonic technologies with multiple uses.
Electrical Engineering Professor Weidong Zhou and Associate Professor Alice Sun will use the five-year, $1.8 million grant to work with collaborators at UT Arlington, University of North Texas, University of Arkansas Pine Bluff, ...
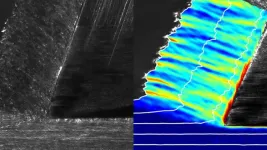
Staying sharp: Researchers turn to an everyday shop tool to study how materials behave
2023-07-19
Researchers at Texas A&M University are taking a traditional manufacturing tool — metal cutting — and developing a more accessible method for understanding the behavior of metals under extreme conditions.
Metal cutting – scraping a thin layer of material from a metal’s surface using a sharp knife (not unlike how we scrape butter) – might not be the first thing that comes to mind for studying material properties. However, Drs. Dinakar Sagapuram and Hrayer Aprahamian, assistant professors ...
Bipolar disorder linked to 6-fold heightened risk of early death from external causes
2023-07-19
People with bipolar disorder—characterised by extreme mood swings—are 6 times more likely to die before their time from external causes, such as accidents, violence, and suicide, than those without the condition, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health.
And they are twice as likely to die from somatic (physical) causes, with alcohol a major contributing factor, the findings show.
A heightened risk of an early death from any cause has been consistently reported in those with ...