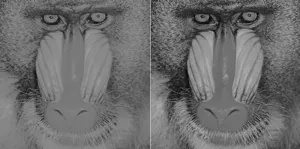
(Press-News.org) Prof Sei-ichi Tsujimura of the Nagoya City University and Prof Su-Ling Yeh of National Taiwan University and Kagoshima University, have discovered that our visual acuity (contrast sensitivity) can be improved by using a light with a special spectrum that can selectively stimulate melanopsin cells in the retina.
Background
The retina of our eye contains cone photoreceptor cells, which identify colors in bright environment, and rod photoreceptor cells, which work in the dark. It has long been thought that humans see and identify objects by these two types of photoreceptor cells alone. On the other hand, around 2000, the third photoreceptor cells called melanopsin ganglion cells (ipRGCs) were discovered in the retina. The melanopsin cells have been reported to influence circadian rhythm regulation, pupillary light reflex, brightness perception, mood and so on. For this reason, the study of melanopsin cell function is of great importance and has challenged many researchers.
Research findings
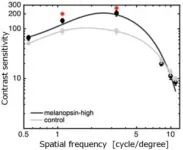
Professor Tsujimura's laboratory had developed the experimental device that can stimulate only melanopsin cells for the first time in the world by adjusting the colour of light (spectrum), and has conducted experiments on the contribution of melanopsin cells to contrast sensitivity. Contrast sensitivity is the ability to distinguish between different shades of brightness in text and images and is one of the most important characteristics in our vision. For example, a high contrast sensitivity enables people to distinguish between an object and the background behind it. In general, contrast sensitivity is lower in dark environments and increases as the light becomes brighter. On the other hand, further brightening does not improve sensitivity any further. In this research, Professor Tsujimura and his collaborators discovered that contrast sensitivity in humans is enhanced when the amount of stimulation to melanopsin cells is increased without changing the luminance or chromaticity of the illumination light.
In this study, contrast sensitivity was enhanced by using a lighting system with a special spectrum that selectively stimulates melanopsin cells without changing the brightness or colour of the light. This could lead to the development of new innovative lighting devices and displays, rather than simply changing the colour or light intensity. We will continue our research into human vision and propose optimal light environments by clarifying the mechanisms in the brain.
END
Light quality enhances contrast vision
Contrast sensitivity (text and shading) can be improved by stimulating melanopsin cells in the retina
2023-07-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Monitoring often excludes crucial river ecosystems; Can citizen science fill the gap?
2023-07-19
Intermittent rivers and ephemeral streams are the world's dominant river ecosystem, yet monitoring and management typically focus on rivers that flow year round. Writing in BioScience, Amélie Truchy of the French National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food, and the Environment (INRAE) and colleagues describe the problem, as well as a potential solution: citizen science.
The authors discuss the results from a new app, DRYRivERS, which allows scientist and nonscientist users alike to record data on ephemeral streams and intermittent ...
Cardiac rehabilitation reduces risk of death years after heart surgery, still underutilized
2023-07-19
For millions of Americans who have heart surgery or experience cardiovascular complications, like heart attack or heart failure, they may be encouraged to participate in cardiac rehabilitation. The medically supervised program combines lifestyle changes, education and physical activity to help patients recover and reduce their risk of future problems.
A Michigan Medicine study now finds that people who participate in cardiac rehabilitation have a decreased risk of death years after surgery, with a trend towards better outcomes in patients who attend more sessions.
“Time and time again, cardiac rehabilitation has been shown to ...
A quick and inexpensive test for osteoporosis risk
2023-07-19
As life expectancy increases worldwide, age-associated diseases such as osteoporosis are having an increasing impact. Although early detection could help physicians intervene as soon as possible — when treatment might offer the greatest benefit — this type of detection is not yet possible with current osteoporosis diagnostic tests. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have developed a biosensor that could someday help identify those most at risk for osteoporosis using less than a drop of blood.
Early intervention is critical to reducing the morbidity and mortality associated with osteoporosis, a condition characterized by an elevated ...
Espresso can prevent Alzheimer’s protein clumping in lab tests
2023-07-19
Whether enjoyed on its own or mixed into a latte, Americano or even a martini, espresso provides an ultra-concentrated jolt of caffeine to coffee lovers. But it might do more than just wake you up. Research now published in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry shows that, in preliminary in vitro laboratory tests, espresso compounds can inhibit tau protein aggregation — a process that is believed to be involved in the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
Roughly half of all Americans drink coffee every day, and espresso is a popular way to consume ...
A vegan way to stop damage from excessive ice build-up and freezer burn
2023-07-19
Almost everyone has a bag of veggies shoved into the dark recesses of their freezer that’s now essentially an unrecognizable block of ice crystals. And when thawed, foods damaged by excessive ice lose their texture and become mushy. Now, researchers reporting in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry have shown that broken-down soy proteins can prevent ice crystal growth and could be especially useful for preserving frozen vegan foods or biological samples.
Some animals that ...
Towards new antibiotics with the first artificial synthesis of tanzawaic acid b
2023-07-19
The discovery of antibiotics in 1928 was a major turning point in the history of medicine. For the first time since the dawn of human civilization, doctors had gained access to an extremely powerful and effective tool to fight against a wide variety of bacterial infections. Today, bacterial diseases that were previously a death sentence can be cured, and infections following surgery or chemotherapy can be prevented or treated more effectively.
Unfortunately, the worldwide use (and abuse) of antibiotics led to the emergence of drug-resistant bacterial strains. Over time, bacteria that could normally be killed by ...
Early signs of Alzheimer’s: Most older adults see the value of screening but haven’t been tested
2023-07-19
Eighty percent of older adults see the benefit of tests that can give an early warning that a person’s memory and thinking abilities have started to decline, a new poll of people age 65 to 80 finds. And 60% think that health care providers should offer cognitive screening, in the form of brief memory tests, to all older adults every year.
If they had a cognitive screening test and it showed signs of trouble, the vast majority of those polled said it would spur them to take action to protect their brain health (96%) and adjust their financial and health ...
Does this exoplanet have a sibling sharing the same orbit?
2023-07-19
Using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), astronomers have found the possible ‘sibling’ of a planet orbiting a distant star. The team has detected a cloud of debris that might be sharing this planet’s orbit and which, they believe, could be the building blocks of a new planet or the remnants of one already formed. If confirmed, this discovery would be the strongest evidence yet that two exoplanets can share one orbit.
“Two decades ago it was predicted in theory that pairs of planets of similar mass may share the same orbit around their star, the so-called Trojan or co-orbital planets. For the first time, we have found evidence ...
Michael Wong named fellow of the Royal Society of Chemistry
2023-07-19
HOUSTON – (July 19, 2023) – Rice University’s Michael Wong was named a fellow to the Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC), the oldest chemical society in the world, whose mission is to “advance excellence in the chemical sciences.” More than 180 years old, the United Kingdom-based chemical society has over 54,000 members worldwide.
“It’s a confirmation that the work we do in our group is something that people appreciate and is making a meaningful contribution ...
From nature, a solution to save coral from climate change
2023-07-19
Genoa (Italy), 19 July 2023 – Researchers at Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Italian Institute of Technology - IIT) and Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca (University of Milan-Bicocca), in cooperation with Acquario di Genova (Genoa Aquarium) in Italy, have recently published a study in ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, which demonstrates the efficacy of curcumin, a natural antioxidant substance extracted from turmeric, in reducing coral bleaching, a phenomenon caused primarily by climate change. The research group developed a biodegradable biomaterial to deliver the molecule without ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] Light quality enhances contrast visionContrast sensitivity (text and shading) can be improved by stimulating melanopsin cells in the retina