(Press-News.org) What determines whether we become overweight? Aside from lifestyle, predisposition plays a role, but genes cannot fully explain the inherited propensity to accumulate excess weight. A new study by Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin in Science Translational Medicine* shows that a kind of formatting of the DNA code in one gene that is associated with satiety is implicated in a slightly elevated risk of excess body weight – at least in women. This “epigenetic marking” is established early on during the embryonic stage.
People who are overweight, especially those who are severely overweight, are at increased risk of a number of serious diseases such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. It is a growing health issue. All over the world, the number of overweight people is increasing. In the European Region, two out of three adults (59 percent) are overweight or obese, according to the World Health Organization.
But what determines whether people will become overweight? Genetic predisposition plays a major role, alongside lifestyle. The similarity of the body mass index (BMI) in identical twins ranges from 40 to 70 percent. Even identical twins raised in different families still show the same significant similarity. Scientists have identified several genetic variants that influence a person’s body weight – and with it, the risk of developing obesity. But even taken all together, they cannot explain the heritability that has been observed. Researchers began to suspect there must be additional non-genetic factors that affect a person’s propensity to gain excess weight.
Satiety gene is not altered, but formatted
Researchers led by Prof. Peter Kühnen, Director of the Department of Pediatric Endocrinology at Charité, have now identified one such factor in their recent study. According to their findings, women’s risk of being overweight increases by about 44 percent if there are an especially large number of methyl groups adhering to the POMC (pro-opiomelanocortin) gene, which is responsible for the feeling of satiety. Methyl groups are tiny chemical units the body uses to mark the letters in the DNA code to activate or deactivate genes without modifying the sequence of letters in the DNA. In other words, the effect is much like highlighting a section of a text without rewriting the text itself. This type of “DNA formatting” is known as epigenetic marking.
For their study, the team of researchers analyzed the “formatting” of the POMC gene in more than 1,100 people. They found more methyl groups attached to the satiety gene in obese women with a BMI of over 35 than in women with normal body weight. “A 44 percent increase in the risk of obesity is about the same as the effect that has been observed for individual gene variants as well,” says Kühnen. “By comparison, socioeconomic factors have a much stronger effect. They can increase the risk by a factor of two to three. As for why the methylation effect only shows up in women, we don’t know yet.”
The POMC gene is “formatted” very early on during embryonic development, as the researchers showed by comparing methylation patterns in more than 15 sets each of identical and fraternal twins. While the “formatting” of the satiety gene was the same in most of the identical twins, there was hardly any correlation in the fraternal twins. “This indicates that the epigenetic marking of the POMC gene is established shortly after the egg and sperm cells merge, before the fertilized egg divides into two twin embryos,” explains Lara Lechner, the study’s first author, who works at the Department of Pediatric Endocrinology. This means the very early stage of pregnancy is crucial.
What influences formatting?
But what influences how much methylation the satiety gene undergoes – and thus, the risk that a person will become overweight? Past studies indicated that the presence or absence of certain nutrients that supply methyl groups could have an effect on epigenetic processes. These nutrients include betaine, methionine, and folic acid, all of which are typically absorbed through a person’s diet. A newly developed method involving individual human stem cells allowed the Charité researchers to simulate in the lab how the methylation pattern is determined during embryonic development and how nutrients affect it.
“On the one hand, our studies and others as well show that folic acid, betaine, and other nutrients have a limited effect on the extent of methylation,” Kühnen notes. “We’ve observed that the ‘DNA formatting system’ is very stable on the whole, with cells compensating for minor fluctuations in the nutrient supply. On the other hand, there are indications that the variability of this ‘formatting’ develops at random. That means that it is not possible – not yet, at any rate – to externally influence whether a person has more or less methylation in the POMC region.”
Medications may help
At least in theory, women who are at elevated risk of developing obesity due to methylation of the POMC gene could receive medications to help them lose weight, as initial studies of four severely obese women and one man with this exact type of “formatting” of the satiety gene suggest. The subjects were given a specific drug that curbs the feeling of hunger and has already been approved to treat obese patients with a mutation of the POMC gene. Within three months after starting treatment, all five patients experienced less hunger. They lost an average of seven kilograms, or about five percent of their body weight. Some of them continued the treatment and continued to lose weight.
“These findings show, for a start, that a POMC gene that has undergone epigenetic changes can in fact potentially be addressed through medication,” Kühnen says. “Further large controlled studies will be needed to show whether treatment with this drug would also be effective over a longer period, and if so, how effective and how safe this type of treatment is. Overall, though, a medication like this would still need to be just one piece of a holistic treatment strategy.”
About the study
Prof. Peter Kühnen, who led the study, is the Director of the Department of Pediatric Endocrinology at Charité. He holds a Heisenberg Professorship and received the Paul Martini Prize, which comes with 50,000 euros in award money, in 2020 for his work on normalizing body weight. The current study arose under the auspices of a Consolidator Grant from the European Research Council (ERC), which Kühnen obtained to study the role of epigenetic variability in the emergence of metabolic and endocrine disorders (E-VarEndo). Other sources of funding for the team’s work included the German Research Foundation (DFG), the SPARK-BIH program at the Berlin Institute of Health at Charité (BIH), and a BIH doctoral stipend.
*Lechner L et al. Early-set POMC methylation variability is accompanied by increased risk for obesity and is addressable by MC4R agonist treatment. Sci Transl Med 2023 Jul 19. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adg1659
END
More than just lifestyle and genes: New factor influencing excess body weight discovered
2023-07-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Fighting brain cancer
2023-07-19
“Don’t eat me!” That’s how one might translate the signal that the cancer cells in a glioblastoma send to the macrophages (white blood cells specialized in removing dead and dying cellular matter) in the brain. Immunotherapy attempts to enable these cells to eradicate the abnormal cells, but so far, it has met with little success when it comes to glioblastomas.
Researchers led by Professor Gregor Hutter from the Department of Biomedicine at the University and University Hospital Basel have recently used patient data, experiments with mice, and samples from human tumors to study one of these “don’t eat me!” signals and its inhibitory ...
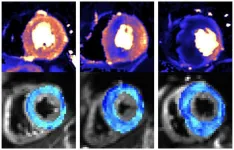
New scanning methods can detect deadly heart condition before symptoms appear
2023-07-19
The research, funded by the British Heart Foundation and published in the journal Circulation, opens the prospect of treating the condition at the earliest stages.
Being able to detect HCM earlier than ever before will also assist trials investigating gene therapies and drug treatments aimed at stopping the disease developing in those at risk.
HCM is an inherited condition that affects around 1 in 500 people in the UK. It causes the muscular walls of the heart to become thicker than normal, affecting how well the heart can pump blood around the body. It is ...
Why ongoing worker safety training is critical to effective disaster response
2023-07-19
When it comes to disaster response and recovery operations, it is crucial that workers are prepared before there is an emergency, according to Rutgers researchers.
Their study, published in New Solutions: A Journal of Environmental and Occupational Health Policy, outlines the importance of the Worker Training Program to United States emergency and disaster-response infrastructure.
"It is essential to identify and deliver core disaster training to responders and workers on a routine basis prior to an [emergency] event," said Mitchel Rosen, an associate professor at the Rutgers School of Public Health. “The failure ...
MD Anderson research highlights for July 19, 2023
2023-07-19
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments include promising results from combining immunotherapy with radiation for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), a novel combination therapy for secondary and treatment-resistant ...
Aluminum materials show promising performance for safer, cheaper, more powerful batteries
2023-07-19
A good battery needs two things: high energy density to power devices, and stability, so it can be safely and reliably recharged thousands of times. For the past three decades, lithium-ion batteries have reigned supreme — proving their performance in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
But battery researchers have begun to approach the limits of lithium-ion. As next-generation long-range vehicles and electric aircraft start to arrive on the market, the search for safer, cheaper, and more powerful ...
Noninvasive method for vagus nerve stimulation shows promise for enhancing motor rehabilitation after stroke
2023-07-19
The longest nerve in the human body starts in the brain and meanders its way down the neck and into the chest, where it splits into separate branches, winding its twisting tendrils to touch each internal organ. Known as the “information superhighway” and aptly named from the Latin word meaning “wanders,” the vagus nerve is a bundle of fibers responsible for the parasympathetic nervous system: digestion, heart rate, breathing.
Sending electrical impulses down this tenth cranial nerve has proven effective in treating conditions like depression and epilepsy, ...
Dedicated older people’s emergency department reduces wait times
2023-07-19
The formation of the country’s first emergency department for the over 80s led to a significant decrease in time spent in A&E – according to research from the Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital (NNUH) and University of East Anglia (UEA).
The first Older People’s Emergency Department in England was opened at NNUH in December 2017 to bring specialists in older people’s medicine to the front doors of the hospital and provide earlier assessment and treatment for patients.
A new study evaluates the outcomes for patients who received treatment in the main emergency department at NNUH and a similar ...
Genetics explains why some individuals never have COVID-19 symptoms
2023-07-19
Have you ever wondered why some people never became sick from COVID-19? A study published today in Nature shows that common genetic variation among people is responsible for mediating SARS-CoV-2 asymptomatic infection. The results indicate that individuals having this variant never feel sick once infected. This exciting discovery was a result of a U.S.-Australia collaborative work led by Danillo Augusto, Ph.D., assistant professor at the University of North Carolina at Charlotte; Jill Hollenbach, Ph.D., professor ...
Unveiling the quantum dance: Experiments reveal nexus of vibrational and electronic dynamics
2023-07-19
Nearly a century ago, physicists Max Born and J. Robert Oppenheimer developed an assumption regarding how quantum mechanics plays out in molecules, which are comprised of intricate systems of nuclei and electrons. The Born-Oppenheimer approximation assumes that the motion of nuclei and electrons in a molecule are independent of each other and can be treated separately.
This model works the vast majority of the time, but scientists are testing its limits. Recently, a team of scientists demonstrated the breakdown ...
Gender disparities in Lyme disease: Women face higher risk of severe and prolonged illness
2023-07-19
Women with Lyme disease take longer to get diagnosed, have more severe symptoms and experience higher rates of disability when compared to men. They may also be more likely to develop persistent Lyme disease. Those are among the findings of a recent study that analyzed information from the MyLymeData patient registry. The results have been published in the International Journal of General Medicine.
The present study, which was conducted by LymeDisease.org, a research and advocacy organization, assessed sex-based differences in Lyme disease patients who remained ill for six months or more after antibiotic treatment. In ...