(Press-News.org) Key Takeaways:
Volunteering later in life may protect the brain against cognitive decline and dementia.
New study of older adults found better memory and executive function among those who volunteered.
Watch the video.
(Sacramento) Volunteering in late life is associated with better cognitive function — specifically, better executive function and episodic memory. Those are the findings of a new study from UC Davis Health presented today (July 20) at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference 2023 in Amsterdam.
“We hope these new data encourage individuals of all ages and backgrounds to engage in local volunteering — not only to benefit their communities, but potentially their own cognitive and brain health,” said Donna McCullough, Alzheimer’s Association chief mission and field operations officer.
Volunteer activities — such as supporting educational, religious, health-related or other charitable organizations — allow older adults to be more physically active, increase social interaction and provide cognitive stimulation that may protect the brain. However, there has been a lack of information on the relationship between volunteering and cognitive function, especially in large, diverse populations.
Yi Lor, an epidemiology doctoral student at UC Davis, and Rachel Whitmer, the study's principal investigator, examined volunteering habits among an ethnic and racially diverse population of 2,476 older adults. The participants are in the Kaiser Healthy Aging and Diverse Life Experiences Study (KHANDLE) and the Study of Healthy Aging in African Americans (STAR).
The study group had an average age of 74 and contained 48% Black, 20% white, 17% Asian and 14% Latino participants. A total of 1,167 (43%) of the participants reported volunteering in the past year.
The researchers found that volunteering was associated with better baseline scores on tests of executive function and verbal episodic memory. This was true even after adjusting for age, sex, education, income, practice effects and interview mode (phone versus in-person).
Those who volunteered several times per week had the highest levels of executive function.
“Volunteering may be important for better cognition in late life and could serve as a simple intervention in all older adults to protect against risk for Alzheimer’s disease and associated dementias,” Lor said. “Our next steps are to examine whether volunteering is protective against cognitive impairment, and how physical and mental health may impact this relationship.”
Volunteering was also associated with a trend toward less cognitive decline over the follow-up time of 1.2 years, but this association did not reach statistical significance.
“You’re not in control of your family history or age — you can’t turn back the clock. But you are in control of how you spend your day and life,” Whitmer said. “Volunteering is about keeping your brain active. It’s also about socializing, which keeps you engaged and happy, and potentially lowers stress.”
Resources
Video: Volunteering in Late Life May Protect the Brain from Dementia
Media kit (b-roll and interview soundbites)
Whitmer Lab END
Volunteering in late life may protect the brain against cognitive decline and dementia
2023-07-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
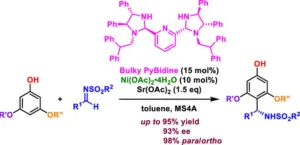
New study expands the scope of aza-friedel−crafts reactions
2023-07-20
From life-saving drugs and synthetic polymers to diverse advanced materials, the products containing organic compounds seem endless, thanks in part to regioselectivity, a feature in chemical reactions where a substituent is selectively added to a specific position of an organic compound. This favors the formation of desired products with specific functionalities. One notable regioselective reaction used for the precise design of organic compounds is the Friedel−Crafts reaction, which enables the addition of substituents to specific positions on aromatic compounds ...
Omega-3 fatty acids appear promising for maintaining lung health
2023-07-20
Omega-3 fatty acids appear promising for maintaining lung health
NIH-funded study supports new role for nutrient found in fish, dietary supplements
Omega-3 fatty acids, which are abundant in fish and fish oil supplements, appear promising for maintaining lung health, according to new evidence from a large, multi-faceted study in healthy adults supported by the National Institutes of Health. The study provides the strongest evidence to date of this association and underscores the importance of including omega-3 fatty acids in the diet, especially given that many Americans do not meet current guidelines. Funded largely by the National Heart, ...
Engineering plants for a changing climate
2023-07-20
Climate change is affecting the types of plant varieties we can cultivate, as well as how and where we can do so. A new collection of articles in the open access journal PLOS Biology explores the twin challenges of engineering plants for resilience to climate change and enhancing their carbon-capture potential. PLOS Biology Editors Pamela Ronald & Joanna Clarke provide a summary editorial, and details regarding the other papers may be found below.
To meet the agricultural challenges caused by climate change and a growing population, we need to improve crop production. This Perspective from industry leaders including Catherine Feuillet calls for more and better ...
Precision measurement of polarization
2023-07-20
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – A doctoral dissertation examining the most precise measurement of electron beam polarization ever made was just awarded the prestigious 2022 Jefferson Science Associates (JSA) Thesis Prize. Since 2017, award-winner Allison Zec has been part of a collaboration that ran experiments at the U.S. Department of Energy's Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility.
The goal of both the CREX and PREX-II experiments was to run an experiment and its mirror opposite simultaneously to determine ...
New study shows Black cancer survivors face increased mortality from heart disease; neighborhood socioeconomic status and insurance contributing factors
2023-07-20
ATLANTA, July 20, 2023 – A new study from researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS) found that Black cancer survivors in the United States experience a higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease (CVD) compared with White cancer survivors. The research showed Black cancer survivors carry from 30% up to a three-fold higher mortality risk from CVD, depending on the type of cancer that was diagnosed. Differences in neighborhood socioeconomic status and health insurance between Black and White cancer survivors explained the disparities in cardiovascular death rates between populations, according to the study authors. ...
High body temperature increases resistance to pathogenic viral infections, new study finds
2023-07-20
Researchers from The University of Tokyo unravel the connection between high body temperature and increased viral resistance.
Clinical evidence suggests that elderly individuals are at a higher risk of contracting viral infections. Quite notably, the older people also have lower mean body temperatures. However, the effects of increased body temperature on fighting viral infections remain largely unexplored. A team of Japanese researchers has now been able to bridge the gap by linking higher body temperature with an increased infection-fighting capability of the gut microorganisms or "microbiota." Their study was published in Volume 14 ...
New research sheds light on factors influencing trust and bias in societies
2023-07-20
People with more positive perceptions of their nation’s institutions are more likely to show favoritism toward fellow citizens, according to new research in Social Psychological and Personality Science. This research suggests that support for national institutions could pose a challenge for establishing trust across borders.
Researchers also found that people who identify strongly with their own nation are likely to favor their fellow citizens, which aligns with previous studies. The possible role of trust in national institutions, however, was an unexpected development for researchers.
“We observed greater favoritism in trust toward fellow citizens ...
Mark Hauber to lead the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center
2023-07-20
New York, NY – The City University of New York Graduate Center is pleased to announce the appointment of Mark Hauber as the executive director of its Advanced Science Research Center (CUNY ASRC).
Established in 2014, the CUNY ASRC is a world-class STEM research and education institution dedicated to interdisciplinary science that addresses global challenges and develops innovative technologies that will advance the economies of New York State and the nation. Its five research initiatives center on nanoscience, photonics, structural ...
New advances in integrating mechanisms of multiple stress response in conifers
2023-07-20
The proper response to various abiotic stresses is essential for plants’ survival to overcome their sessile nature, especially for perennial trees with very long-life cycles. However, in conifers, the molecular mechanisms that coordinate multiple abiotic stress responses remain elusive.
This article has been published on Horticulture Research with title: An ethylene-induced NAC transcription factor acts as a multiple abiotic stress responsor in conifer.
Here, the transcriptome response to various abiotic stresses like salt, cold, drought, heat shock and osmotic were systematically detected in Pinus tabuliformis (P. ...
Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers
2023-07-20
The fastest way to heat food and drink might also rank as the fastest route to ingesting massive quantities of minuscule plastic particles, says new research from the University of Nebraska–Lincoln.
Experiments have shown that microwaving plastic baby food containers available on the shelves of U.S. stores can release huge numbers of plastic particles — in some cases, more than 2 billion nanoplastics and 4 million microplastics for every square centimeter of container.
Though the health effects of consuming micro- and nanoplastics remain unclear, the Nebraska team further found that three-quarters of cultured embryonic ...