(Press-News.org) Some people’s brain function still affected by Long COVID years after infection
UK researchers have found that people with longer-term COVID-19 symptoms including brain fog showed reduced performance in tasks testing different mental processes up to two years after infection with the virus.
Researchers from King’s College London looked at whether infection with COVID-19 affected performance in two rounds of online cognitive testing that took place in 2021 and 2022. Data was collected for over 3,000 participants of the COVID Symptom Study Biobank study, across 12 tasks that tested memory, attention, reasoning, processing speed and motor control.
The participants whose test scores were most affected by COVID-19 were those who had experienced symptoms related to the virus for 12 weeks or more. In these people, the effect of COVID-19 on test accuracy was comparable in size to the effect of a 10-year increase in age.
There was no significant improvement in these test scores between the two rounds of testing, which took place nine months apart. By the second round of testing, the average time since participants’ initial COVID-19 infection was almost two years.
Digging deeper into the analysis, the researchers separated participants by whether they felt fully recovered following COVID-19 infection. People who felt fully recovered after COVID-19 infection performed similarly to those who had not had the virus at all. In contrast, participants who did not feel fully recovered after infection had lower task accuracy scores on average.
Lead author Dr Nathan Cheetham, a Senior Postdoctoral Data Scientist at King’s College London said:
“Our findings suggest that, for people who were living with long-term symptoms after having COVID-19, the effects of the coronavirus on mental processes such as the ability to recall words and shapes are still detectable at an average of almost two years since their initial infection.
“However, the result that COVID had no effect on performance in our tests for people who felt fully recovered, even if they’d had symptoms for several months and could be considered as experiencing ‘long COVID’, was good news. This study shows the need to monitor those people whose brain function is most affected by COVID-19, to see how their cognitive symptoms continue to develop and provide support towards recovery.”
Professor Claire Steves, a Professor of Ageing and Health at King’s College London, added:
“We used sensitive tests to measure speed and accuracy across a range of brain challenges. This study shows that some individuals have measurable changes in these tests after COVID-19 going on for nearly two years. The fact remains that two years on from their first infection, some people don’t feel fully recovered and their lives continue to be impacted by the long-term effects of the coronavirus. We need more work to understand why this is the case and what can be done to help.”
The paper, ‘The effects of COVID-19 on cognitive performance in a community-based cohort: A COVID Symptom Study Biobank prospective cohort study,’ is published today in eClinicalMedicine.
END
Some people’s brain function still affected by Long COVID years after infection
2023-07-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MASER technology scientist awarded funding for new research
2023-07-21
A scientist from Northumbria University has been awarded almost half a million pounds to develop a new technology which could transform deep-space communication, radio astronomy, medical imaging and airport security scanning.
Dr Juna Sathian has received a grant from the government’s Engineering & Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) to develop a new type of MASER (Microwave Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) device.
The forerunner to LASERs, MASERs were first discovered in the 1950s. But there has been ...
Researchers decipher the secrets of Benjamin Franklin’s paper money
2023-07-21
Benjamin Franklin may be best known as the creator of bifocals and the lightning rod, but a group of University of Notre Dame researchers suggest he should also be known for his innovative ways of making (literal) money.
During his career, Franklin printed nearly 2,500,000 money notes for the American Colonies using what the researchers have identified as highly original techniques, as reported in a study published this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The research team, led by Khachatur Manukyan, an associate research professor ...
KIPA potentially predicts chemotherapy response in triple negative breast cancer
2023-07-21
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions are developing a strategy to predict the response of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) to chemotherapy, which would be a valuable tool for physicians deciding on the treatment with better probability of success on an individual basis. The study appears in Cancer Research Communications, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
“Multiple research innovations in cancer diagnostics are on display in this work,” said co-corresponding author Dr. Matthew Ellis, member of the Lester and Sue Smith Breast Center and the Dan ...
On the hunt for strangeness
2023-07-21
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – Peter Hurck has been searching for strange particles, named such because they contain strange quarks, since beginning work on his Ph.D. As the 2023 Jefferson Science Associates (JSA) Postdoctoral Prize winner, he’ll continue conducting data analyses to identify strange particles and learn about their properties.
Many of these experiments that contribute to the data Hurck is analyzing are conducted at the U.S. Department of Energy's Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility, which is managed and operated by JSA.
“Strangeness hasn't been studied as much because it's quite ...
ASBMB expresses concerns on proposed NIH budget cuts
2023-07-21
On July 19, the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology released a statement expressing concerns on the National Institutes of Health budget proposed in the House Labor, Health and Human Services, Education and Related Agencies funding bill. The bill allocates only $44.7 billion for NIH, which represents a 6.4% decrease from fiscal year 2023 levels and would have detrimental repercussions for the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Stroke, the National Cancer Institute and the National Institute ...
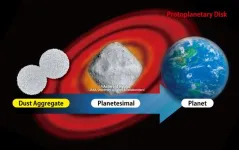
To stick or to bounce: Size determines the stickiness of cosmic dust aggregates
2023-07-21
Microparticle dust aggregates, which are thought to play a role in the formation of new planets, are less likely to stick together after a collision when the aggregates are larger.
Current evidence suggests that microparticles of cosmic dust collide and stick together to form larger dust aggregates that may eventually combine and develop into planets. Numerical models that accurately characterize the conditions required for colliding microparticle aggregates to stick together, rather than bounce apart, are therefore ...
Long-term changes in waves and storm surges have not impacted global coastlines
2023-07-21
Changes in ocean wave and storm conditions have not caused long-term impacts on sandy coastlines in the past 30 years, a new study has found.
Published today in Scientific Reports, the study draws on data from 30 years of global satellite and model studies to investigate whether changes in ocean wave conditions will have an impact on the stability of coastal environments.
The compounding effect of climate change driven variations in waves, storm surge and sea level rise is projected to lead to shoreline position change along most of the world’s sandy coasts.
A team ...
Subseasonal transition of sea-ice anomalies in the Barents–Kara Sea in winter modulated by the “warm Arctic–cold Eurasia” pattern
2023-07-21
The “warm Arctic–cold Eurasia” is one of the most significant patterns of winter climate system changes in the mid-high latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere. In winter 2020/21, this large-scale pattern underwent a significant and intense subseasonal reversal between the early and late winter. At the same time, the sea-ice anomalies in the Barents–Kara Sea changed from being significantly negative in early winter to positive in late winter. For the slow-varying process of winter sea ice, the rapid freezing ...
Miocene period fossil forest of Wataria found in Japan
2023-07-21
An exquisitely preserved fossil forest from Japan provides missing links and helps reconstruct a whole Eurasia plant from the late Miocene epoch.
Complete plant fossils are seldom found as a single piece, as wood, leaves, flowers, fruits, seeds, or pollen detach easily from plants. This results in leaves and trunks having separate scientific names. Putting together the different parts to reveal the complete plant is like putting together a jigsaw puzzle. Connecting these dots and reconstructing plants is important to establish their taxonomic identity—their ...
Going the distance for better wireless charging
2023-07-21
A better way to wirelessly charge over long distances has been developed at Aalto University. Engineers have optimized the way antennas transmitting and receiving power interact with each other, making use of the phenomenon of “radiation suppression”. The result is a better theoretical understanding of wireless power transfer compared to the conventional inductive approach, a significant advancement in the field.
Charging over short distances, such as through induction pads, uses magnetic near fields to transfer power with high efficiency, but at longer distances the efficiency dramatically drops. New research shows that this high efficiency ...