(Press-News.org) Babies are more likely to be born prematurely when either their father or mother has had a psychiatric diagnosis, according to a study conducted by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the Karolinska Institutet and published July 20 in the open access journal PLOS Medicine.
The research shows, for the first time, that the risk of preterm birth is higher in infants whose father or mother has a psychiatric diagnosis than in those whose parents do not, and higher still when both parents have such diagnoses.
Preterm birth is associated with negative health consequences for infants. Women with psychiatric diagnoses have long been known to be at increased risk for preterm birth, but less is known about the risk in offspring of fathers with psychiatric diagnoses and couples where both parents had psychiatric diagnoses.
For this study, the research team analyzed data on all live births to Nordic parents (parents who were born in Sweden, Finland, Norway, Denmark and Iceland) in Sweden between 1997 and 2016. They obtained psychiatric diagnoses from the National Patient Register and data on gestational age from the Medical Birth Register.
There were 1.5 million births in the cohort, and 15 percent of those babies were born to parents with a psychiatric diagnosis. The team observed a trend towards earlier gestational age in offspring of parents with psychiatric disorders. For parents without a diagnosis, 5.8 percent of babies were born preterm. A paternal diagnosis increased that number to 6.3 percent of births and a maternal diagnosis increased it to 7.3 percent of births. Where both parents had a diagnosis, 8.3 percent of births were preterm.
The researchers also found that the risk was further increased for offspring of parents—mothers as well as fathers—who had several co-existing psychiatric disorders.
“Although the study was conducted in Sweden, if we speculate that inherited genetic risk a well as biological or psychological stress can carry over to other populations, the results are generalizable beyond Sweden. Given that roughly one in five children in the United States has at least one parent with a mental health disorder, the results of this study hold potential significance for public health,” said Sven Sandin, PhD, Associate Professor of Psychiatry and an epidemiologist at the Seaver Autism Center for Research and Treatment at Icahn Mount Sinai and senior author on the paper.
“Preterm birth can result in significant lifelong complications for the infant, and in my clinical experience, the mother has traditionally been held responsible for the events,” said Michael Silverman, PhD, Associate Professor of Psychiatry at Icahn Mount Sinai and an author on the paper. “While the gestational parent’s (the mother’s) behaviors have been historically implicated in a wide range of disorders like depression, autism, schizophrenia, and even food allergy, the non-gestational parent’s contributions have been a neglected but vital topic in the child developmental literature. This new work demonstrates that the non-gestational biologic parent’s (the father’s) psychiatric history is also associated with the increased likelihood of obstetric outcomes traditionally attributed solely to the mother.”
“Children of parents with mental illness are at increased risk of being born too early and our study shows that both the mothers and fathers are important,” says Weiyao Yin, PhD, postdoctoral researcher at the Karolinska Institutet and lead author of the paper.
Future studies should examine whether additional social support and prenatal care for families with a positive psychiatric history could have an impact on gestational age, the researchers said.
This press release was adapted from a release written by the PLOS Biology staff.
About the Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System is one of the largest academic medical systems in the New York metro area, with more than 43,000 employees working across eight hospitals, over 400 outpatient practices, nearly 300 labs, a school of nursing, and a leading school of medicine and graduate education. Mount Sinai advanced health for all people, everywhere, by taking on the most complex health care challenges of our time — discovering and applying new scientific learning and knowledge; developing safer, more effective treatments; educating the next generation of medical leaders and innovators; and supporting local communities by delivering high-quality care to all who need it.
Through the integration of its hospitals, labs, and schools, Mount Sinai offers comprehensive health care solutions from birth through geriatrics, leveraging innovative approaches such as artificial intelligence and informatics while keeping patients’ medical and emotional needs at the center of all treatment. The Health System includes approximately 7,300 primary and specialty care physicians; 13 joint-venture outpatient surgery centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida; and more than 30 affiliated community health centers. We are consistently ranked by U.S. News & World Report's Best Hospitals, receiving high "Honor Roll" status, and are highly ranked: No. 1 in Geriatrics and top 20 in Cardiology/Heart Surgery, Diabetes/Endocrinology, Gastroenterology/GI Surgery, Neurology/Neurosurgery, Orthopedics, Pulmonology/Lung Surgery, Rehabilitation, and Urology. New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai is ranked No. 12 in Ophthalmology. U.S. News & World Report’s “Best Children’s Hospitals” ranks Mount Sinai Kravis Children's Hospital among the country’s best in several pediatric specialties.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Twitter and YouTube.
###
END
ROCKVILLE, MD—JULY 19, 2023 – As organizations representing a wide range of scientific, engineering, and mathematical disciplines, we will not be deterred by the U.S. Supreme Court ruling on race considerations in college and university admissions.
America’s inherent strength and economic competitiveness among nations is its domestic and international talent across every race, ethnicity, gender, and geography. To meet current and emerging job demands and retain our research and development leadership globally, we must broaden who participates in science, technology, engineering, mathematics, and medicine. Doing so will improve lives, advance our nation’s living standards, ...
“[Machine learning] has the potential to transform early cancer detection in primary care [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- July 21, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncoscience (Volume 10) on June 9, 2023, entitled, “Transforming early cancer detection in primary care: harnessing the power of machine learning.”
Cancer remains a significant global health burden, and early detection plays a crucial role in improving patient outcomes. Primary care settings serve as frontline gatekeepers, providing an opportunity for early detection through symptom assessment and ...
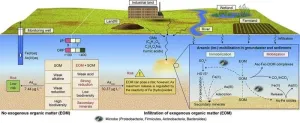
Researchers from the Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences have conducted a study to assess the impact of environmental factors and microbial communities on the mobilization of arsenic (As). The findings, published in Volume 15 of the journal Environmental Science and Ecotechnology, reveal important insights into the biogeochemical processes involved in As release. The study focused on processes such as desorption, reduction, complexation, and co-precipitation that affect the As behaviour in the environment. The interaction ...
DALLAS, July 21, 2023 — More than 100 scientists from across the U.S. are receiving special grants to support their research work in finding innovative solutions to fight heart disease and stroke. The grants, totaling $20 million, are part of the Second Century of Science Initiative of the American Heart Association, the world’s leading voluntary organization dedicated to a world of longer, healthier lives. The financial awards are announced as the Association, the largest non-government supporter of heart and brain health research in the U.S., prepares to celebrate ...
Green hydrogen can be produced directly in a photoelectrochemical cell, splitting water with solar energy. However, this requires the development of super-efficient photoelectrodes that need to combine many talents at the same time: They must be excellent at converting sunlight into electricity, remain stable in acidic or basic water, act as catalysts to promote the splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen, and be cheap, abundant and non-toxic. The large material class of metal oxides comes into question. However, it is difficult to find out what really happens at the interfaces ...
URBANA, Ill. — New mothers can expect sleep deprivation in the first few years of baby’s life. But too little sleep can take a toll on the health of both mother and child. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign looks at maternal and infant sleep patterns, identifying predictors and providing recommendations for instilling healthy habits.
“The first two years is a really critical period where a lot of development is going on, and sleep is important for health. We wanted to look at the association of mother and infant sleep and whether it changes over time,” said Tianying ...
During our history, ancient civilisations have considerably shaped the global ecosystems through a coevolution of landscape and local populations. In some cases, the legacy of the disappeared civilizations is still visible in the form of buildings and other monuments such as the Stonehenge, the buildings of the Roman and Hellenic Empires, and ancient burial places and fortresses built by several cultures. These monuments are invaluable parts of our history and cultural heritage. Although it is often not in the spotlight, they can also hold a considerable biodiversity conservation potential.
In the vast steppes of Eurasia (and probably ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Developing technology to quickly and efficiently bioprint human tissues at scale is the goal of a new project led by Penn State researchers. When fully developed, the technology will be the first to enable the fabrication of scalable, native tissues such as bones, tracheas and organs.
The National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Engineering at the National Institute of Health has awarded over $2 million in support of the project, led by Ibrahim T. Ozbolat, professor of engineering science and mechanics, biomedical engineering, and neurosurgery at Penn State.
“This will be a platform technology, which can be used for multiple purposes,” ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Worldwide, high rates of obesity and other inflammatory conditions are associated with increased risk for cancer, cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Investigating how environmental chemical exposure impacts the gut microbiome to exacerbate these conditions is the goal of a new $7 million grant awarded to Andrew Patterson, professor of molecular toxicology and the John T. and Paige S. Smith Professor in the College of Agricultural Sciences.
The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, part of the National ...
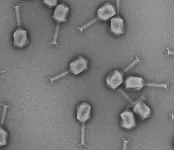
About one in two women are affected by cystitis during her lifetime, and many suffer from recurrent urinary tract infections. Bladder infections are not only painful and potentially dangerous, but they also pose a significant dilemma for physicians. With antibiotic resistance becoming widespread in urinary tract infections and continually increasing, physicians are often forced to blindly prescribe antibiotics without knowing their effectiveness against the pathogen causing the infection. This is because it takes several days to identify a specific ...