(Press-News.org) As artificial intelligence expands across more professions, robot preachers and AI programs offer new means of sharing religious beliefs, but they may undermine credibility and reduce donations for religious groups that rely on them, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“It seems like robots take over more occupations every year, but I wouldn’t be so sure that religious leaders will ever be fully automated because religious leaders need credibility, and robots aren’t credible,” said lead researcher Joshua Conrad Jackson, PhD, an assistant professor at the University of Chicago in the Booth School of Business.
The research was published in the Journal of Experimental Psychology: General.
Jackson and his colleagues conducted an experiment with the Mindar humanoid robot at the Kodai-Ji Buddhist temple in Kyoto, Japan. The robot has a humanlike silicon face with moving lips and blinking eyes on a metal body. It delivers 25-minute Heart Sutra sermons on Buddhist principles with surround sound and multi-media projections.
Mindar, which was created in 2019 by a Japanese robotics team in partnership with the temple, cost almost $1 million to develop, but it might be reducing donations to the temple, according to the study.
The researchers surveyed 398 participants who were leaving the temple after hearing a sermon delivered either by Mindar or a human Buddhist priest. Participants viewed Mindar as less credible and gave smaller donations than those who heard a sermon from the human priest.
In another experiment in a Taoist temple in Singapore, half of the 239 participants heard a sermon by a human priest while the other half heard the same sermon from a humanoid robot called Pepper. That experiment had similar findings -- the robot was viewed as less credible and inspired smaller donations. Participants who heard the robot sermon also said they were less likely to share its message or distribute flyers to support the temple.
While participants said they believed human preachers were more credible, it was still a close contest with the robots. On a scale from 1 to 5, with 5 being most credible, the robot preachers received an average credibility rating of 3.12, compared with 3.51 for human preachers.
“This suggests that there are a lot of people out there who think robots could be effective preachers, but there are more people who aren’t convinced,” Jackson said.
While the robot preacher studies focused on Eastern religions, Jackson believes the findings could apply to other religions.
A third experiment included 274 Christian participants from the United States who read a sermon online. Half of the participants were told it was written by a human preacher while the other half were told the sermon was generated by a highly advanced AI program. Participants in the AI sermon group reported the sermon was less credible because they felt an AI program had less capacity to think or feel like a human.
“Robots and AI programs can’t truly hold any religious beliefs so religious organizations may see declining commitment from their congregations if they rely more on technology than on human leaders who can demonstrate their faith,” Jackson said.
Article: “Exposure to Robot Preachers Undermines Religious Commitment,” Joshua Jackson, PhD, University of Chicago; Kai Chi Yam, PhD, and Ting Liu, PhD, National University of Singapore; Pok Man Tang, PhD, University of Georgia Terry College of Business; and Azim Shariff, PhD, The University of British Columbia, Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, published online July 24, 2023.
Contact: Joshua Conrad Jackson, PhD, may be contacted at Joshua.Jackson@chicagobooth.edu.
END
Robot preachers get less respect, fewer donations
Robots, AI programs may undermine credibility of religious groups, study finds
2023-07-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Plastic surgery goes to the movies: Journal of Craniofacial Surgery looks at facial disfigurement
2023-07-24
July 24, 2023 – Characters with facial disfigurement have long been a recurring theme in films. Their characteristics and outcomes lend insights into perceptions of facial deformities and the effects of plastic surgery, reports a study in The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery under the guidance of Editor-in-Chief Mutaz B. Habal, MD, FRCS, FACS of Tampa, Florida. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
Movie characters who undergo successful plastic surgery to improve their facial appearance are more likely to have happy endings, according to the new research by Young Suk Kim, BA, and Kun Hwang, MD, PhD, of Armed Forces ...
Opting for olive oil could boost brain health
2023-07-24
A new study suggests that incorporating olive oil into your diet could help reduce the risk of dying from dementia. As many countries face rising rates of Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia, the study offers hope that healthy lifestyle factors such as diet can help to prevent or slow the progression of these devastating conditions.
“Our study reinforces dietary guidelines recommending vegetable oils such as olive oil and suggests that these recommendations not only support heart health but potentially brain health, as well,” said Anne-Julie Tessier, RD, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the Harvard T.H. ...
Upping your intake of omega-3s may help protect your hearing
2023-07-24
Researchers report that blood levels of the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) were inversely correlated with hearing difficulty in a new population-based cross-sectional study. Middle-aged and older adults with higher DHA levels were 8-20% less likely to report age-related hearing issues than those with lower DHA levels.
“Higher DHA levels have previously been found to be associated with a lower risk of heart disease, cognitive impairment, and death. Our study extends these findings to suggest a role for DHA in maintaining ...
What is the best dieting strategy for people with type 2 diabetes?
2023-07-24
Losing weight is often a goal for people with type 2 diabetes, which is strongly associated with being overweight or obese. However, it hasn’t been clear what dieting strategy works best for people with this metabolic disorder.
A new randomized controlled study of people with type 2 diabetes showed that study participants who restricted eating to between noon and 8 p.m. daily lost more weight than those who reduced their overall calorie intake by counting calories. Both dieting strategies produced similar improvements in blood sugar levels.
“Many people find counting calories very hard to stick to in the long term, ...
Wormlike animals are first amphibians shown to pass microbes to their offspring
2023-07-24
Caecilians are an elusive type of amphibian that primarily live underground and look like a cross between a worm and a snake. One of the few things that is known about caecilians is their unique method for feeding their young. Mothers produce a special layer of fatty skin tissue, which juvenile caecilians tear off with baby teeth that evolved specifically for that purpose.
A new study shows that skin-feeding does more than provide nutrients for young caecilians. It also helps the mother pass microbes from her skin and gut down to her young, inoculating them to jump-start a healthy ...
Image-guided adaptive radiation treatments reduce short-term side effects for patients with prostate cancer
2023-07-24
A technique that uses imaging technology as a guide can make radiation therapy safer for patients with prostate cancer by helping clinicians accurately aim radiation beams at the prostate while avoiding nearby tissue in the bladder, urethra, and rectum. That is the finding of a thorough analysis of all published clinical trials of the technique, called magnetic resonance–guided daily adaptive stereotactic body radiotherapy (MRg-A-SBRT). The analysis is published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
By providing detailed images, MRg-A-SBRT can be used to adjust a patient’s radiation plan every ...
Children and adolescents in food-insecure homes had more mental health visits
2023-07-24
Children and adolescents living in food-insecure households had a 55% higher frequency of physician visits for mental health reasons than those with adequate food supplies, according to new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.230332.
In 2021, almost 6 million people Canada, including 1.4 million children and adolescents younger than 18 years faced food insecurity; that is, inadequate food intake because of financial problems.
The study looked at population health survey data from the Canadian Community Health Survey on ...
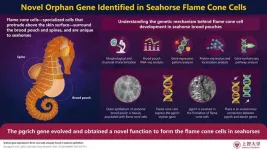
Gene conferring novel function to seahorse brood pouch identified
2023-07-24
Teleost fish encompass a diverse group, among which seahorses display a unique morphology. The characteristic spines and brood pouch seen in seahorses feature distinctive epithelial cells—called flame cone cells—covered by a mucous cap. However, these cells are not found in the barbed pipefish Urocampus nanus or the seaweed pipefish Syngnathus schlegeli, close relatives of the seahorse, belonging to the Syngnathidae lineage. While research has hypothesized the function of the flame cone cells, their evolutionary origins have remained a mystery.
Now, a team of scientists led by Assoc. Prof. Mari Kawaguchi and Prof. Shigeki Yasumasu from the Department of Materials ...
Two in three cosmetic surgery injections in the UK are not administered by doctors
2023-07-24
According to an analysis of the UK’s cosmetic injectables industry by UCL researchers, 68% of cosmetic practitioners who are administering injections such as Botox are not qualified medical doctors.
The study, published in the Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery, is the first survey of who is providing cosmetic injectable services, such as Botulinum Toxin (Botox) and Dermal Fillers, in the UK. Currently, little is known about the background qualifications, training and experience levels of those who are administering treatments.
To fill this ...
A whole new dimension for 3D printing
2023-07-24
3D printing of complex objects typically takes a long time due to the printing process necessarily laying down a large number of 2D layers to build up the object. The process usually wastes a lot of material required to support the unfinished object. Some novel ways to make flat materials self-fold into 3D shapes exist, but have shortcomings. For the first time, researchers combined 2D printing, origami, and chemistry to create a method of rapid 3D object fabrication without creating any waste material. These shapes self-fold in seconds.
For some time, 3D printing has been used to prototype ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Novel structural insights into Phytophthora effectors challenge long-held assumptions in plant pathology
Q&A: Researchers discuss potential solutions for the feedback loop affecting scientific publishing
A new ecological model highlights how fluctuating environments push microbes to work together
Chapman University researcher warns of structural risks at Grand Renaissance Dam putting property and lives in danger
Courtship is complicated, even in fruit flies
Columbia announces ARPA-H contract to advance science of healthy aging
New NYUAD study reveals hidden stress facing coral reef fish in the Arabian Gulf
36 months later: Distance learning in the wake of COVID-19
Blaming beavers for flood damage is bad policy and bad science, Concordia research shows
The new ‘forever’ contaminant? SFU study raises alarm on marine fiberglass pollution
Shorter early-life telomere length as a predictor of survival
Why do female caribou have antlers?
How studying yeast in the gut could lead to new, better drugs
Chemists thought phosphorus had shown all its cards. It surprised them with a new move
A feedback loop of rising submissions and overburdened peer reviewers threatens the peer review system of the scientific literature
Rediscovered music may never sound the same twice, according to new Surrey study
Ochsner Baton Rouge expands specialty physicians and providers at area clinics and O’Neal hospital
New strategies aim at HIV’s last strongholds
Ambitious climate policy ensures reduction of CO2 emissions
Frontiers in Science Deep Dive webinar series: How bacteria can reclaim lost energy, nutrients, and clean water from wastewater
UMaine researcher develops model to protect freshwater fish worldwide from extinction
Illinois and UChicago physicists develop a new method to measure the expansion rate of the universe
Pathway to residency program helps kids and the pediatrician shortage
How the color of a theater affects sound perception
Ensuring smartphones have not been tampered with
Overdiagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer
Association of dual eligibility and medicare type with quality of postacute care after stroke
Shine a light, build a crystal
AI-powered platform accelerates discovery of new mRNA delivery materials
Quantum effect could power the next generation of battery-free devices
[Press-News.org] Robot preachers get less respect, fewer donationsRobots, AI programs may undermine credibility of religious groups, study finds