(Press-News.org) Glenview, Illinois – Published monthly, the journal CHEST® features peer-reviewed, cutting-edge original research in chest medicine: Pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine and related disciplines. Journal topics include asthma, chest infections, COPD, critical care, diffuse lung disease, education and clinical practice, pulmonary vascular disease, sleep, thoracic oncology and the humanities.
The July issue of the CHEST journal contains 49 articles, including clinically relevant research, reviews, case series, commentary and more. Each month, the journal also offers complementary web and multimedia resources, including visual abstracts, to expand the reach of its most interesting, timely and relevant research.
“With July serving as Disability Pride Month, I recommend reading ‘Disability Rights and Life-Sustaining Treatment: Building Bridges Between Clinicians and Advocates,’” says Editor in Chief of the journal CHEST, Peter Mazzone, MD, MPH, FCCP. “Included in our Humanities section, the article discusses the rights of individuals with disabilities when planning for Crisis Standards of Care.”
Also included in the current issue of the journal CHEST:
Chest Infections
Original research, “Patient-Reported Symptom and Health-Related Quality-of-Life Validation and Responsiveness During the First 6 Months of Treatment for Mycobacterium avium Complex Pulmonary Disease,” finds the Quality of Life-Bronchiectasis questionnaire exhibited good psychometric properties in patients with Mycobacterium avium complex.
Critical Care
A multicenter prospective cohort study, “HealthExpectations and Quality of Life After Acute Respiratory Failure,” suggests implementing a mechanism underpinning successful ICU recovery programs that incorporate normalization and expectation management. View the visual abstract for this research.
Sleep
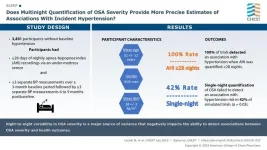
Original research, “Single-Night Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea Contributes to Inconsistent Cardiovascular Outcome Findings,” shows that multinight monitoring of OSA allows for better estimates of hypertension risk and potentially other adverse health outcomes associated with OSA. View the visual abstract for this research.
Thoracic Oncology
“Outcomes From More Than 1 Million People Screened for Lung Cancer With Low-Dose CT Imaging” finds that adherence to lung cancer screening was poor among underserved communities and likely contributes to the lower-than-expected cancer detection rate. View the visual abstract for this research.
To view the entire July issue of the CHEST journal, visit journal.chestnet.org, and follow @journal_CHEST on Twitter for the latest journal news.
About the American College of Chest Physicians
The American College of Chest Physicians® (CHEST) is the global leader in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of chest diseases. Its mission is to champion advanced clinical practice, education, communication and research in chest medicine. It serves as an essential connection to clinical knowledge and resources for its 19,000+ members from around the world who provide patient care in pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine. For information about the American College of Chest Physicians, and its flagship journal CHEST®, visit chestnet.org.
END
Highlights from the journal CHEST®, July 2023
2023-07-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New study reveals self-replicating RNA and novel vaccine delivery technology demonstrate enhanced safety and efficacy
2023-07-24
As the world continues to combat various infectious diseases, the development of novel vaccine technologies remains at the forefront of scientific research. mRNA-based vaccines and utilization of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) for their delivery, have recently shown encouraging results in diseases such as COVID-19.
However, a critical concern revolves around the wide biodistribution of LNPs in the body, which, in some cases, may result in unintended side effects. A recent publication in the peer-reviewed ...
Often, consumers inadvertently give too much credit to products’ ‘scientifically studied’ claims
2023-07-24
Key takeaways
A new study finds that consumers often misremember if a product is labeled “scientifically studied” or “scientifically proven” — despite the significant difference in meaning between the two phrases.
UCLA psychologists conducted an experiment with one group of college students and another group of older adults to determine whether they would accurately recall which claim was made in an advertisement for a dietary supplement.
Only 26% of subjects correctly remembered which phrase was used, and the percentage who recalled the information ...
ACP says the US needs immediate action to prepare for future pandemics
2023-07-24
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 24 July 2023
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
Community health workers improved homebound care during pandemic
2023-07-24
SAN ANTONIO (July 24, 2023) — Staying healthy and connected was difficult for everyone during the COVID-19 pandemic, but especially so for homebound older patients and their caregivers. Fortunately, a program developed by the geriatrics and supportive care team of The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio effectively integrated community health workers (promotores de salud in Spanish) into patient outreach to improve health. Thanks to the program, annual visits to older adults with type 2 diabetes, dementia and other health issues in underserved ...
Stretchy integrated electronics may be possible with sandwiched semiconductor
2023-07-24
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — There’s a barrier preventing the advent of truly elastic electronic systems, the kind needed for advanced human-machine interfaces, artificial skins, smart health care and more, but a Penn State-led research team may have found a way to stretch around it.
According to principal investigator Cunjiang Yu, who holds is the Dorothy Quiggle Career Development Associate Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics and of Biomedical Engineering at Penn State, fully elastic electronic systems require flexibility and stretchability in every ...
Water-scarce cultures value long-term thinking more than their water-rich neighbors do
2023-07-24
Water is the world’s most valuable natural resource. Although a human can survive weeks or even months without food, going as little as three days without water could spell the end. The effects of water scarcity aren’t limited to immediate survival situations, however. Recently published research in Psychological Science suggests that cultures from water-scarce environments tend to be more likely than cultures from water-rich areas to value long-term thinking and to scorn short-term indulgence.
“Individuals from historically water-scarce climates tend to be ...
New method for noninvasive detection of circulating tumor cells in blood
2023-07-24
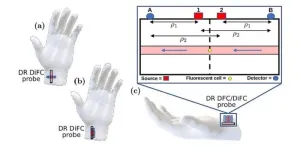
Metastasis occurs when cancer cells acquire the ability to spread and form new tumors in different places in the body, usually by traveling within blood or lymph vessels. Since metastasis is a hallmark of advanced cancer and severely complicates treatment, its early diagnosis is essential. One way to do this is by looking for circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in blood samples.
However, CTCs can be very rare, and they might be completely absent in small blood samples despite being present in a patient’s bloodstream. To address this problem, researchers have developed a technique called diffuse in-vivo flow cytometry (DiFC). It involves labeling CTCs with ...
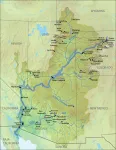
Colorado River Basin has lost water equal to Lake Mead due to climate change
2023-07-24
American Geophysical Union
Release No. 23-28
24 July 2023
For Immediate Release
This press release and accompanying multimedia are available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/colorado-river-basin-has-lost-water-equal-to-lake-mead-due-to-climate-change/
Colorado River Basin has lost water equal to Lake Mead due to climate change
A rapid rate of reductions in runoff associated with the Colorado Basin’s snowpack region, quantified here for the first time, is largely responsible for the water loss.
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, news@agu.org +1 (202) 777-7492 (UTC-4 hours)
Contact ...
Beyond protected areas: Novel method shows promise for monitoring biodiversity on working lands
2023-07-24
New research led by Adam Dixon, a conservation scientist with the World Wildlife Fund, describes the successful pilot of a novel method to study how well grassland birds are faring on croplands. The study, published in Ecological Applications, looked at 44 pockets of non-crop vegetation in the gaps between crop rows and at the edges of fields on lands under intensive agricultural cultivation in Iowa. The study may serve as a model for monitoring wildlife on working lands more generally, which can include crop fields, cattle ranches, and logged forests.
The researchers analyzed satellite imagery data to determine each pocket's area and “texture,” ...
Is snacking bad for your health? It depends on what and when you eat
2023-07-24
Snacking is becoming increasingly popular, with more than 70% of people reporting they snack at least twice a day. In a new study involving more than 1,000 people, researchers examined whether snacking affects health and if the quality of snack foods matters.
“Our study showed that the quality of snacking is more important than the quantity or frequency of snacking, thus choosing high quality snacks over highly processed snacks is likely beneficial,” said Kate Bermingham, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at King's College London. “Timing is also important, with late night snacking being unfavorable for health.”
Bermingham ...