(Press-News.org) University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers have discovered a key driver of chronic inflammation that accelerates aging. That finding could let us slow the clock to live longer, healthier lives, and may allow us to prevent age-related conditions such as deadly heart disease and devastating brain disorders that rob us of our faculties.
So what drives this harmful inflammation? The answer is improper calcium signaling in the mitochondria of certain immune cells. Mitochondria are the power generators in all cells, and they rely heavily on calcium signaling.
The UVA Health researchers, led by Bimal N. Desai, PhD, found that mitochondria in immune cells called macrophages lose their ability to take up and use calcium with age. This, the researchers show, leads to chronic inflammation responsible for many of the ailments that afflict our later years.
The researchers believe that increasing calcium uptake by the mitochondrial macrophages could prevent the harmful inflammation and its terrible effects. Because macrophages reside in all organs of our bodies, including the brain, targeting such “tissue-resident macrophages” with appropriate drugs may allow us to slow age-associated neurodegenerative diseases.
“I think we have made a key conceptual breakthrough in understanding the molecular underpinnings of age-associated inflammation,” said Desai, of UVA’s Department of Pharmacology and UVA’s Carter Immunology Center. “This discovery illuminates new therapeutic strategies to interdict the inflammatory cascades that lie at the heart of many cardiometabolic and neurodegenerative diseases.”
The Inflammation of Aging – ‘Inflammaging’
Macrophages are white blood cells that play critical roles in our immune systems and, in turn, our good health. They swallow up dead or dying cells, allowing our bodies to remove cellular debris, and patrol for pathogens and other foreign invaders. In this latter role, they act as important sentries for our immune systems, calling for help from other immune cells as needed.
Scientists have known that macrophages become less effective with age, but it has been unclear why. Desai’s new discovery suggests answers.
Desai and his team say their research has identified a “keystone” mechanism responsible for age-related changes in the macrophages. These changes, the scientists believe, make the macrophages prone to chronic, low-grade inflammation at the best of times. And when the immune cells are confronted by an invader or tissue damage, they can become hyperactive. This drives what is known as “inflammaging” – chronic inflammation that drives aging.
Further, the UVA Health scientists suspect that the mechanism they have discovered will hold true not just for macrophages but for many other related immune cells generated in the bone marrow. That means we may be able to stimulate the proper functioning of those cells as well, potentially giving our immune systems a big boost in old age, when we become more susceptible to disease.
Next Steps
Fixing “inflammaging” won’t be as simple as taking a calcium supplement. The problem isn’t a shortage of calcium so much as the macrophages’ inability to use it properly. But Desai’s new discovery has pinpointed the precise molecular machinery involved in this process, so we should be able to discover ways to stimulate this machinery in aging cells.
“This highly interdisciplinary research effort, at the interface of computational biology, immunology, cell biology and biophysics, wouldn’t have been possible without the determination of Phil Seegren, the graduate student who spearheaded this ambitious project,” Desai said. “Now, moving forward, we need an equally ambitious effort to figure out the wiring that controls this mitochondrial process in different types of macrophages and then manipulate that wiring in creative ways for biomedical impact.”
Aging Findings Published
The researchers have published their findings in the scientific journal Nature Aging. The article is open access, meaning it is free to read.
The research team consisted of Seegren, Logan R. Harper, Taylor K. Downs, Xiao-Yu Zhao, Shivapriya B. Viswanathan, Marta E. Stremska, Rachel J. Olson, Joel Kennedy, Sarah E. Ewald, Pankaj Kumar and Desai. The scientists reported that they have no financial interests in the work.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, grants AI155808, GM108989, GM138381, P30 CA044579 and T32 GM007055-46, and by the Owens Family Foundation.
To keep up with the latest medical research news from UVA, subscribe to the Making of Medicine blog.
END
Inflammation discovery could slow aging, prevent age-related diseases
2023-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UK and Europe join forces for construction of largest ever European Solar Telescope
2023-07-25
**Images available**
Nine European countries, including the UK, have today (25 July 2023) joined forces to commit to the construction of the European Solar Telescope (EST)
The EST will be the biggest solar telescope ever constructed in Europe and aims to provide unparalleled new insights into the phenomena of space weather
The University of Sheffield will lead a consortium of UK universities that will help to develop designs for the construction of the large-aperture solar telescope
The first light of the EST is ...
PSMA PET imaging improves accuracy of predicting prostate cancer recurrence
2023-07-25
A molecular imaging tool developed by researchers at the University of California’s two nationally ranked medical centers, UCLA and UCSF, helps improve the accuracy of predicting the risk of cancer recurrence in patients with intermediate to high-risk prostate cancer who undergo surgery.
The tool, known as prostate-specific membrane antigen PET imaging, or PSMA PET, provides prognostic information before treatment begins that can predict if the patient will have a high risk for the cancer returning after surgery.
“In patients ...
All US racial and ethnic minority groups are underrepresented in Alzheimer’s neuroimaging research, study shows
2023-07-25
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), which affects an estimated 6.5 million adults in the United States, hits some groups harder than others. Compared to non-Hispanic whites, Hispanic Americans are 1.5 times as likely to develop AD, and African Americans are twice as likely.
But scientists know little about the reasons behind these disparities, because the vast majority of AD research has been done with non-Hispanic white people.
A new study that reviewed 11,871 research articles on AD brain imaging, led by researchers at the Keck School of Medicine of USC, has now revealed the extent of ...
84% cut in Covid deaths for UK cancer patients following vaccine rollout
2023-07-25
Cancer patients saw a significant fall in Covid-related hospitalisations and mortality following the rollout of vaccines in the first panoramic study of its kind.
The research published in Scientific Reports today (Tuesday 25 July) looked at the impact of the global pandemic on case-outcome rates for cancer patients across a 21-month period from November 2020 to August 2022. The team of researchers led by the University of Birmingham found that hospitalisations in the period fell from nearly one in three patients (30.58%) to one in 13 patients (7.45%); and, case-mortality rates fell from more than one in five patients (20.53%) to less than one in 30 patients (3.25%).
Among ...
A chance to design better vaccines?
2023-07-25
A new paper in Biology Methods & Protocols, published by Oxford University Press, shows it may be possible to design vaccines that will induce a stronger immune response to infecting pathogens, such as the virus causing COVID-19. In this study, the authors proposed and tested a new bioinformatic approach and tool that allows researchers to select parts of proteins that will elicit a strong immune response. Vaccines developed based on this approach would provide better protection from diseases.
The immune system of humans (and other vertebrates) discriminates between self and non-self structures to attack and destroy the latter. T cells are the part of the immune system ...
A high-pressure flux method to synthesize high-purity oxyhydrides
2023-07-25
Adding a flux during the synthesis of oxyhydrides is a promising strategy to obtain a pure, homogenous product, reveal scientists from Tokyo Tech. An SrCl2 flux promoted the melting of a part of reactants and facilitated their diffusion of reactants, which proved to be the key to producing highly pure SrVO2.4H0.6 or Sr3V2O6.2H0.8 perovskite oxyhydrides in high-pressure and high-temperature reactions. These compounds have potential as catalysts and as electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries.
Perovskite oxyhydrides ...
Multi-levitation bioprinting of heart models for space exploration and medicine
2023-07-25
As a bold venture at the forefront of biomedical research, the PULSE project is poised to develop paradigm-changing bioprinting technology for applications in space and on Earth. Awarded nearly 4 million euros by the European Innovation Council’s Pathfinder Open, PULSE emerges from interdisciplinary scientific collaborations and, over five years, will foster technological innovations to improve human health and pave the way for safer and more sustainable space exploration.
By combining magnetic and acoustic levitation into an innovative bioprinting platform, PULSE’s device should be capable of achieving unparalleled spatiotemporal control of cell deposition. ...
CHOP researchers validate pediatric “allergic march” in largest national study of its kind
2023-07-25
Philadelphia, July 25, 2023—In the largest study of its kind, researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) used electronic health record (EHR) data from more than 200,000 pediatric patients to describe patterns of pediatric allergies across the United States, validating a population-level pattern of allergy development known as the “allergic march,” in which allergies first present as eczema, followed by food allergies, asthma, and environmental allergies. The ...
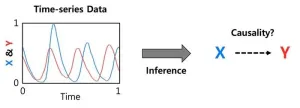
Introducing GOBI: A breakthrough computational package for inferring causal interactions in complex systems
2023-07-25
In the quest to unravel the underlying mechanisms of natural systems, accurately identifying causal interactions is of paramount importance. Leveraging the advancements in time-series data collection through cutting-edge technologies, computational methods have emerged as powerful tools for inferring causality. However, existing model-free methods have struggled to differentiate between generalized synchrony* and causality, leading to false predictions. On the other hand, model-based methods, while accurate, have been limited by their dependence on specific models, hindering their widespread applicability.
*Synchrony ...
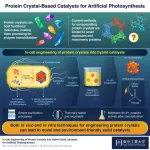
Towards artificial photosynthesis with engineering of protein crystals in bacteria
2023-07-25
In-cell engineering can be a powerful tool for synthesizing functional protein crystals with promising catalytic properties, show researchers at Tokyo Tech. Using genetically modified bacteria as an environmentally friendly synthesis platform, the researchers produced hybrid solid catalysts for artificial photosynthesis. These catalysts exhibit high activity, stability, and durability, highlighting the potential of the proposed innovative approach.
Protein crystals, like regular crystals, are well-ordered molecular structures with diverse properties and a huge potential for customization. They can assemble naturally from materials found within cells, which not only greatly reduces the synthesis ...