(Press-News.org) A multi-institutional team of scientists led by Dr. Mario Gaudino, the Stephen and Suzanne Weiss Professor in Cardiothoracic Surgery and assistant dean for clinical trials at Weill Cornell Medicine, has been approved for a nearly $30 million funding award from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI). The award will fund the first study among women and Black and Hispanic patients comparing the effectiveness of two revascularization options used to treat coronary artery disease.
Coronary artery disease, a narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries due to plaque buildup, is the leading cause of death in the United States. More than one million Americans undergo a procedure to restore normal blood flow to the heart annually. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is a minimally invasive procedure that passes stents into the coronary artery using catheters inserted into a small incision in the groin or wrist. It requires minimal anesthesia and patients typically go home the same day.
By contrast, coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) is more invasive, requiring opening the chest with or without using a heart-lung bypass machine while under general anesthesia. The surgeon creates grafts using arteries or veins taken from the chest, arms or legs to bypass blocked coronary arteries. CABG involves a longer hospital stay and recovery time and has higher rates of complications during surgery than PCI. Still, it has longer-lasting benefits, including less risk of heart attack and the need for repeat intervention.
Over half of patients facing a decision on PCI or CABG are women or racial groups that have been underrepresented in past clinical trials. “Clinical practice guidelines recommend choosing between PCI or CABG based on evidence,” said Dr. Gaudino, who is also a cardiothoracic surgeon at NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center. “However, prior studies have enrolled mostly non-Hispanic white men, leaving other patients with little guidance for making an informed decision.”
The RECHARGE (REvascularization CHoices Among UnderRepresented Groups Evaluation) research program will provide a robust analysis of PCI versus CABG in women and Black and Hispanic patients in two parallel clinical studies called RECHARGE: Women and RECHARGE: Minorities. Each study will aim to recruit 600 participants at up to 60 study sites, primarily in the United States. Patients for whom PCI or CABG are equally appropriate options as determined by their local Heart Team will be randomized to receive either procedure. The trials will take place over five years following an 18-month feasibility phase.
Previous randomized controlled trials of surgical options for coronary artery disease evaluated major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events, such as heart attack, stroke and the need for repeat procedures. However, in focus groups, Dr. Gaudino and colleagues discovered that survival and quality of life were the outcomes that matter most to patients faced with a choice between PCI or CABG. “Patients care most about living longer and better,” he said.
Dr. Gaudino, who is also the director of the Joint Clinical Trials Office and the director of translational and clinical research in the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery at Weill Cornell Medicine, will oversee the RECHARGE program overall, including study startup and patient recruitment strategies. The co-principal investigator is Dr. Gregg Stone, director of academic affairs for the Mount Sinai Health System and professor of medicine and population health science and policy at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, who will lead data collection and analysis.
“Women and Black and Hispanic populations have different physical and clinical characteristics; experience different social biases affecting diagnosis and access to healthcare; and have higher rates of complications and long-term adverse outcomes after both procedures compared with white men,” Dr. Gaudino said. “We hope our study provides strong evidence for more informed decision-making.”
The award has been approved pending completion of a business and programmatic review by PCORI staff and issuance of a formal award contract. PCORI is an independent, nonprofit organization authorized by Congress in 2010. Its mission is to fund research that will provide patients, their caregivers, and clinicians with the evidence-based information needed to make better-informed healthcare decisions.
END
Large PCORI award funds study of surgical options for coronary artery disease in underrepresented patient populations
2023-07-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Offsetting or reducing CO2: This is what consumers want
2023-07-25
Whether it’s recycled aluminum at Apple’s MacBook Air or compensation payments from Microsoft for emissions over the life of an Xbox, climate-friendly products are becoming more and more popular. But do consumers also pay attention to how a neutral climate balance is created? Companies use two ways to accomplish this goal: reducing emissions directly or compensating them afterward. “Both approaches can make a product climate-neutral and have a positive impact on the environment, while compensatory measures are being discussed more and more critically in the public. To this end, the consumers in our study were ...
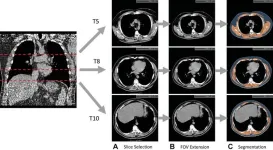
AI uses lung CT data to predict mortality risk
2023-07-25
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Artificial intelligence (AI) can use data from low-dose CT scans of the lungs to improve risk prediction for death from lung cancer, cardiovascular disease and other causes, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
The U.S Preventive Services Task Force recommends annual lung screening with low-dose CT (LDCT) of the chest for individuals ages 50 to 80 years with a high risk of lung cancer, such as longtime ...
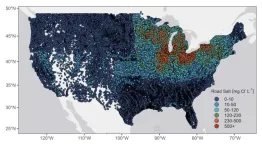
Road salt pollution in many US lakes could stabilize at or below thresholds set by the EPA
2023-07-25
Since de-icing with road salt began in the 1930s, the salinity of lakes across much of the US has been steadily increasing, posing a potential threat to aquatic life and drinking water supplies. However, a cautiously optimistic new study in Limnology and Oceanography Letters concludes that if we can hold steady or decrease road salt use, levels in many lakes could stabilize below thresholds set by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
“For the majority of US lakes, road salt pollution could be a solvable problem, if ...
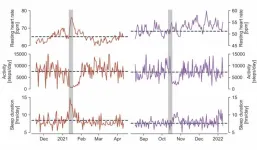
Data from wearable devices shows power of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2
2023-07-25
Data harvested from wearable devices and health apps could be valuable in public health research, according to a study. Vaccines can prevent SARS-CoV-2 infections and, in cases where the virus is able to break through, vaccination lowers the risks of severe disease, hospitalization, ICU admission, and death. Marc Wiedermann and colleagues used data from smartwatches and fitness trackers collected by the Corona Data Donation Project to investigate whether vaccination produces measurable changes in personal health and wellbeing. The Corona-Datenspende-App was launched ...
Spraying just 12% of the room kills 85% of the mosquitoes
2023-07-25
A study in a semi-natural setting finds that targeting just the very bottom of a room’s walls with insecticide will kill most of the mosquitoes, suggesting a cheaper and easier way to treat houses during disease outbreaks. The mosquito Aedes aegypti is a vector for serious diseases, including dengue, chikungunya and Zika. In Asia and Latin America, one approach taken to control mosquitoes that rest inside homes is indoor residual spraying, in which interior walls are coated with a persistent insecticide. However, the large surface area that must be coated makes the approach expensive to implement. Luca Facchinelli and colleagues sought to identify ...
Deep Longevity and House of Gaia announce strategic partnership to advance longevity research and wellness solutions
2023-07-25
Deep Longevity is at the forefront of AI-based longevity science, using deep learning techniques to analyse multiple data types and develop accurate aging clocks. These clocks provide valuable insights into an individual's biological age, offering a holistic understanding of their health and longevity potential. By partnering with House of Gaia, Deep Longevity seeks to bring their cutting- edge technologies and expertise to a wider audience, empowering individuals to take control of their well-being.
House of Gaia is a respected name in the wellness industry, known for its comprehensive range of holistic health services and programs. By ...
SwRI developing advanced electronic warfare system for U.S. Air Force
2023-07-25
SAN ANTONIO — July 25, 2023 —The U.S. Air Force awarded Southwest Research Institute a $4.8 million contract to further develop an adaptable, “continuously staring,” next-generation electronic warfare system capable of detecting advanced enemy radar signals. Using cutting-edge algorithms in a congested signal test environment, the system demonstrated more than 99% probability of intercepting signals with no false detections in a USAF verified simulated environment, a software model loaded with enemy radar.
“Eliminating ...
Food allergy in infancy linked to childhood asthma and reduced lung function
2023-07-25
Having a food allergy as a baby is linked to asthma and reduced lung function later in childhood, according to a world first study.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute and published in the Lancet Child & Adolescent Health, found that early life food allergy was associated with an increased risk of both asthma and reduced lung growth at six years of age.
Murdoch Children’s Associate Professor Rachel Peters said this was the first study to examine the relationship between challenge-confirmed food allergy in infancy and asthma and poorer lung health ...
New study sheds light on awareness and preferences for bioplastics in Japan
2023-07-25
Non-biodegradable plastics are major contributors to land and marine pollution, destroying habitats and causing harm to both flora and fauna. Hence, the switch to bioplastics is imperative to ensure sustainability. The success of environmental initiatives aimed at increasing bioplastic adoption critically hinges on understanding consumer behavior. However, consumer preferences and perceptions around bioplastics, particularly in Japan and other Asian countries, are not well understood.
A recent study published online on July 10, 2023 in the Journal of Cleaner Production attempted to find answers to questions surrounding Japanese consumers’ preferences ...
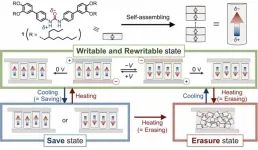
A nano switchable polar column system that allows high-density data storage
2023-07-25
In today’s world of digital information, an enormous amount of data is exchanged and stored on a daily basis. In the 1980s, IBM unveiled the first hard drive—which was the size of a refrigerator—that could store 1 GB of data, but now we have memory devices that have a thousand-fold greater data-storage capacity and can easily fit in the palm of our hand. If the current pace of increase in digital information is any indication, we require yet newer data recording systems that are lighter, have low environmental impact, and, most importantly, have higher data storage density.
Recently, a new class of materials called axially ...