(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. – Artificial intelligence (AI) can use data from low-dose CT scans of the lungs to improve risk prediction for death from lung cancer, cardiovascular disease and other causes, according to a study published in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
The U.S Preventive Services Task Force recommends annual lung screening with low-dose CT (LDCT) of the chest for individuals ages 50 to 80 years with a high risk of lung cancer, such as longtime smokers. Along with images of the lungs, the scans also provide information about other structures in the chest.
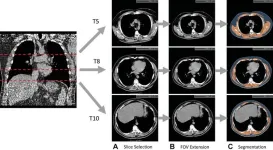
“When we’re looking at the CT images, the primary focus is on identifying nodules suspicious for lung cancer, but there is much more anatomical information coded in the space, including information on body composition,” said study lead author Kaiwen Xu, a Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Computer Science at Vanderbilt University in Nashville, Tenn.
Xu and colleagues previously developed, tested and publicly released an AI algorithm that automatically derives body composition measurements from lung screening LDCT. Body composition is a measure of the percentage of fat, muscle and bone in the body. Abnormal body composition, such as obesity and loss of muscle mass, is linked with chronic health conditions like metabolic disorders. Studies have also shown that body composition is useful in risk stratification and prognosis for cardiovascular disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In lung cancer therapy, body composition has been shown to affect survival and quality of life.
For the new study, the researcher assessed the added value of the AI-derived body composition measurements. They used the CT scans of more than 20,000 individuals drawn from the National Lung Screening Trial.
Results showed that including these measurements improved risk prediction for death from lung cancer, cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality.
“Automatic AI body composition potentially extends the value of lung screening with low-dose CT beyond the early detection of lung cancer,” Xu said. “It can help us identify high-risk individuals for interventions like physical conditioning or lifestyle modifications, even at a very early stage before the onset of disease.”
Measurements associated with fat found within a muscle were particularly strong predictors of mortality—a finding consistent with existing research. Infiltration of skeletal muscle with fat, a condition known as myosteatosis, is now thought to be more predictive for health outcomes than reduced muscle bulk.
The body composition measurements from lung screening LDCT are an example of opportunistic screening when imaging for one purpose provides information about other conditions. The practice is thought to have great potential for routine clinical use.
“The images in a CT ordered for quite a different purpose—in our case, early detection of lung cancer—contain much more information,” Xu said. “In the space of the chest CT used for lung cancer screening, you can also check other information like body composition or coronary artery calcification that is directly associated with cardiovascular disease risk.”
The study looked at individuals at a baseline screening only. For future research, the researchers want to perform a study longitudinally; that is, follow the individuals over time to see how changes in the body composition relate to health outcomes.
###
“AI Body Composition in Lung Cancer Screening: Added Value Beyond Lung Cancer Detection.” Collaborating with Kaiwen Xu were Mirza S. Khan, M.D., M.S., Thomas Z. Li, B.S., Riqiang Gao, Ph.D., James G. Terry, M.S., Yuankai Huo, Ph.D., Thomas A. Lasko, M.D., Ph.D., John Jeffrey Carr, M.D., M.Sc., Fabien Maldonado, M.D., M.Sc., Bennett A. Landman, Ph.D., and Kim L. Sandler, M.D.
In 2023, Radiology is celebrating its 100th anniversary with 12 centennial issues, highlighting Radiology’s legacy of publishing exceptional and practical science to improve patient care.
Radiology is edited by Linda Moy, M.D., New York University, New York, N.Y., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/journal/radiology)
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on CT and lung cancer screening, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
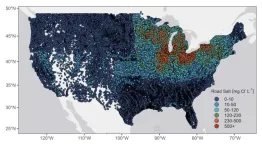
Since de-icing with road salt began in the 1930s, the salinity of lakes across much of the US has been steadily increasing, posing a potential threat to aquatic life and drinking water supplies. However, a cautiously optimistic new study in Limnology and Oceanography Letters concludes that if we can hold steady or decrease road salt use, levels in many lakes could stabilize below thresholds set by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
“For the majority of US lakes, road salt pollution could be a solvable problem, if ...
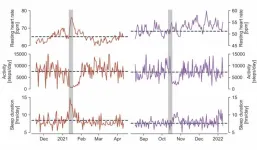
Data harvested from wearable devices and health apps could be valuable in public health research, according to a study. Vaccines can prevent SARS-CoV-2 infections and, in cases where the virus is able to break through, vaccination lowers the risks of severe disease, hospitalization, ICU admission, and death. Marc Wiedermann and colleagues used data from smartwatches and fitness trackers collected by the Corona Data Donation Project to investigate whether vaccination produces measurable changes in personal health and wellbeing. The Corona-Datenspende-App was launched ...
A study in a semi-natural setting finds that targeting just the very bottom of a room’s walls with insecticide will kill most of the mosquitoes, suggesting a cheaper and easier way to treat houses during disease outbreaks. The mosquito Aedes aegypti is a vector for serious diseases, including dengue, chikungunya and Zika. In Asia and Latin America, one approach taken to control mosquitoes that rest inside homes is indoor residual spraying, in which interior walls are coated with a persistent insecticide. However, the large surface area that must be coated makes the approach expensive to implement. Luca Facchinelli and colleagues sought to identify ...
Deep Longevity is at the forefront of AI-based longevity science, using deep learning techniques to analyse multiple data types and develop accurate aging clocks. These clocks provide valuable insights into an individual's biological age, offering a holistic understanding of their health and longevity potential. By partnering with House of Gaia, Deep Longevity seeks to bring their cutting- edge technologies and expertise to a wider audience, empowering individuals to take control of their well-being.
House of Gaia is a respected name in the wellness industry, known for its comprehensive range of holistic health services and programs. By ...
SAN ANTONIO — July 25, 2023 —The U.S. Air Force awarded Southwest Research Institute a $4.8 million contract to further develop an adaptable, “continuously staring,” next-generation electronic warfare system capable of detecting advanced enemy radar signals. Using cutting-edge algorithms in a congested signal test environment, the system demonstrated more than 99% probability of intercepting signals with no false detections in a USAF verified simulated environment, a software model loaded with enemy radar.
“Eliminating ...
Having a food allergy as a baby is linked to asthma and reduced lung function later in childhood, according to a world first study.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute and published in the Lancet Child & Adolescent Health, found that early life food allergy was associated with an increased risk of both asthma and reduced lung growth at six years of age.
Murdoch Children’s Associate Professor Rachel Peters said this was the first study to examine the relationship between challenge-confirmed food allergy in infancy and asthma and poorer lung health ...
Non-biodegradable plastics are major contributors to land and marine pollution, destroying habitats and causing harm to both flora and fauna. Hence, the switch to bioplastics is imperative to ensure sustainability. The success of environmental initiatives aimed at increasing bioplastic adoption critically hinges on understanding consumer behavior. However, consumer preferences and perceptions around bioplastics, particularly in Japan and other Asian countries, are not well understood.
A recent study published online on July 10, 2023 in the Journal of Cleaner Production attempted to find answers to questions surrounding Japanese consumers’ preferences ...
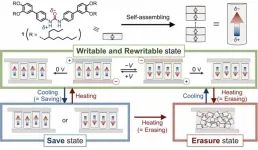
In today’s world of digital information, an enormous amount of data is exchanged and stored on a daily basis. In the 1980s, IBM unveiled the first hard drive—which was the size of a refrigerator—that could store 1 GB of data, but now we have memory devices that have a thousand-fold greater data-storage capacity and can easily fit in the palm of our hand. If the current pace of increase in digital information is any indication, we require yet newer data recording systems that are lighter, have low environmental impact, and, most importantly, have higher data storage density.
Recently, a new class of materials called axially ...
A spectacular new image released today by the European Southern Observatory gives us clues about how planets as massive as Jupiter could form. Using ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT) and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), researchers have detected large dusty clumps, close to a young star, that could collapse to create giant planets.
“This discovery is truly captivating as it marks the very first detection of clumps around a young star that have the potential to give rise to giant planets,” says Alice Zurlo, a researcher at the Universidad Diego Portales, Chile, involved ...
If you were ever to see sewage sludge up close, you might be hard-pressed to find any redeemable value; however, researchers at UBC’s Bioreactor Technology Group see it another way.
Using a combination of heat, water and phase separation, UBC researchers have developed a cost-effective method to concentrate phosphorous—which can be efficiently recovered by extraction—from wastewater sludge.
“Phosphorous is a non-renewable, but essential, element for life and has many industrial uses,” explains Huan Liu, a doctoral student with UBCO’s School of Engineering and lead author of a new study investigating ...